1) Nouns in Spanish are classified as either masculine or feminine. Masculine nouns typically end in o, í, ú or consonants while feminine nouns typically end in a, ad, ción, or sión.
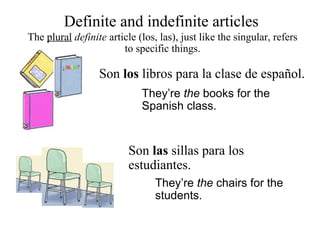
2) Definite articles (el, la, los, las) refer to specific nouns while indefinite articles (un, una, unos, unas) refer to non-specific nouns.
3) Spanish pluralizes nouns differently than English. Most nouns are made plural by adding -s, but some are made plural by adding -es if they end in a consonant, z, or stressed vowel. Adjectives follow the same plural