The document discusses different types of nouns:
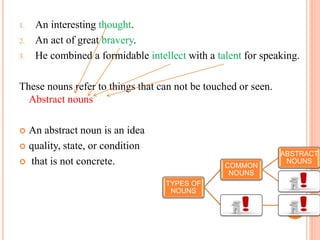
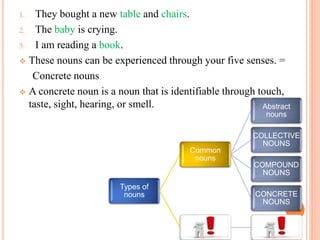
1. Common nouns refer to general people, places, or things and are not capitalized. Abstract nouns refer to ideas, qualities or conditions that cannot be seen or touched.
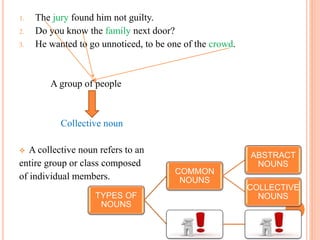
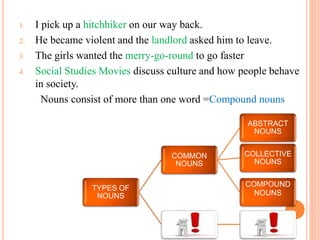
2. Collective nouns refer to a group of individuals and compound nouns are made of more than one word. Concrete nouns can be experienced by the senses while proper nouns name specific people or places and are always capitalized.
3. The subject of a sentence performs the action of the verb. The direct object receives the action. The complement renames or provides more information about the subject. Objects of prepositions are connected to the sentence by a preposition