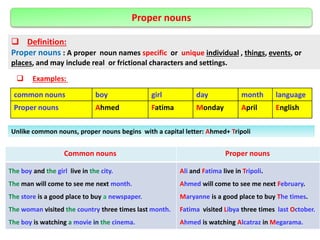
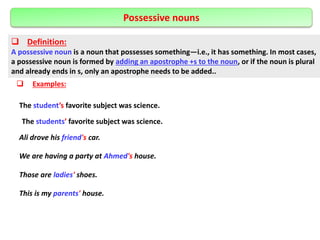
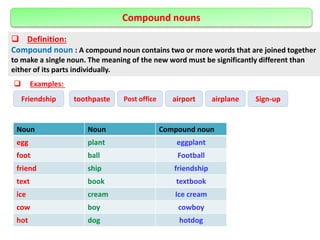
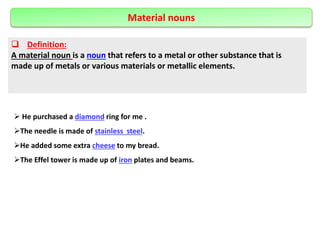
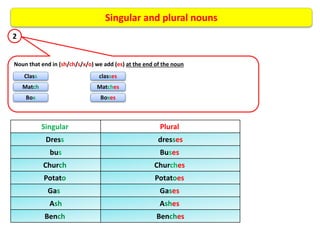
The document defines and provides examples of different types of nouns in English including common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, countable/uncountable nouns, possessive nouns, compound nouns, verbal nouns, and material nouns. It also discusses singular and plural forms of nouns and includes examples. Finally, it briefly covers different types of pronouns such as personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, reflexive pronouns, relative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, reciprocal pronouns, and distributive pronouns. The document also defines verbs and provides examples of different types including