Notes.pptx
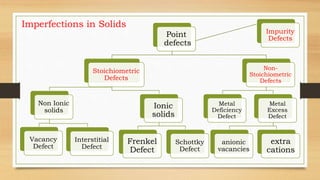
- 2. Imperfections in Solids Point defects are the irregularities or deviations from ideal arrangement around a point or an atom in a crystalline substance (a) Stoichiometric Defects These are the point defects that do not disturb the stoichiometry of the solid. They are also called intrinsic or thermodynamic defects. Stoichiometric Defects in Non-Ionic solids
- 3. Vacancy Defect can also develop when a substance is heated
- 4. Stoichiometric Defects in Ionic solids Seen in Solids having high Co-ordination number Seen in Solids having low Co- ordination number
- 5. Non – stoichiometric defects: These are the point defects that disturb the stoichiometry of the solid. Non-stoichiometric defects are of two types (i) Metal Excess Defect Metal excess defect due to anionic vacancies A compound may have an extra metal ion if the negative ion is absent from its lattice site. This empty lattice site is called a Anionic vacancy. To maintain electrical neutrality this site is occupied by an electron. The Anionic vacancy occupied by an electron is called F-centre or Farbenzenter. F- centre is responsible for the colour of the compound. Alkali halides like NaCl and KCl show this type of defect
- 6. Method: Crystals of NaCl are heated in an atmosphere of sodium vapour, the sodium atoms are deposited on the surface of the crystal. The Cl– ions diffuse to the surface of the crystal and combine with Na atoms to give NaCl. This happens by loss of electron by sodium atoms to form Na+ ions. The released electrons diffuse into the crystal and occupy anionic sites. As a result the crystal now has an excess of sodium. Example NaCl : yellow LiCl : pink KCl : violet (or lilac).
- 7. Metal excess defect due to Presence of extra cations: A compound is said to have extra cations, if a cation is present in the interstitial site. An electron is present in the interstitial site to maintain the electrical neutrality. Eg : Zinc oxide is white in colour at room temperature. On heating it loses oxygen and turns yellow Now there is excess of zinc in the crystal and its formula becomes Zn1+xO. The excess Zn2+ ions move to interstitial sites and the electrons to neighbouring interstitial sites
- 8. Non-stoichiometric defects Metal deficiency: This defect arises because of absence of metal ions from its lattice sites. This defect arises when a cation exists in more than one oxidation state and the cation of higher oxidation state replaces the cation of lower oxidation state. The electrical neutrality is maintained by an adjacent ion having a higher positive charge. Solids contain less amount of the metal as compared to the stoichiometric proportion Eg : FeO which is mostly found with a composition of Fe0.95O. (Fe0.93O to Fe0.96O) In crystals of FeO some Fe2+ cations are missing and the loss of positive charge is made up by the presence of required number of Fe3+ ions.
- 9. (b) Impurity Defects These are the defects in ionic solids due to the presence of impurities in them. Eg : (1) NaCl with SrCl2 as impurity If molten NaCl containing a little amount of SrCl2 is crystallized, some of the sites of Na+ ions are occupied by Sr2+. Each Sr2+replaces two Na+ ions. The cationic vacancies thus produced are equal in number to that of Sr2+ ions (2) AgCl with CdCl2 as impurity.
- 10. Close Packed structures In solids, the constituent particles are close-packed, leaving the minimum vacant space these are called as Close packed structures Three dimensional structure is studied in three steps or levels Assumption: 1. Constituent particles are hard spheres 2. Spherical particles are of equal size. 3. In Metallic crystals the constituents particle are nearly of the above said type Step1 : Close packing in one dimension Step 2 : Close packing in two dimension Square close packing in 2D Hexagonal close packing in 2D
- 11. Step 3 : Close packing in three dimension From Square close packed 2D layer Simple cubic unit cell (with primitive unit cell) From Hexagonal close packed 2D layer Hexagonal Close packed structure (hcp) (by Covering tetrahedral voids) Cubic close packed structure (ccp) or Face –centered cubic (fcc) structure (by covering Octahedral voids) The number of nearest neighbours of a particle (in direct contact) is called its coordination number.(C.N)
- 12. Close packing in one dimension In 1D there is only one way of arranging spheres . In this arrangement spheres are arranged in a row and touching each other Coordination number is two Close packing in two dimensions It is generated by stacking the rows of close packed spheres in two ways: i). Square close packing: When the spheres of the second row are placed exactly above those of the first row. This way the spheres are aligned horizontally as well as vertically. The arrangement is AAA type. Coordination number is 4.
- 13. ii. Hexagonal close packing: When the spheres of the second row are placed above the first one in a staggered manner such that its spheres fit in the depression of the first row. The arrangement is ABAB type. Coordination number is 6. Voids or interstitial site: The vacant space between the close packed touching spheres Triangular Voids : Voids are triangular in shape and centers lie at the corners of an equilateral triangle.
- 14. Close packing in three dimensions: They can be obtained by stacking the two dimensional layers one above the other. It can be obtained in two ways: From two dimensional square close packed layers: The spheres of the upper layer (two dimensional square close packed layers) are placed exactly over the first layer such the spheres of the layers are perfectly aligned horizontally and vertically. It has a AAAA..type pattern. The lattice is simple cubic lattice. CN = 6
- 15. From two dimensional hexagonal close packed layers: If a two dimensional layer (hexagonal close packed) is considered as A, the second layer which is placed above the first layer in such a way that the spheres of the second layer (considered as B) are placed in the depressions of the first layer(by covering the triangular voids). This gives rise to two types of voids: tetrahedral voids and octahedral voids.
- 16. If the number of close packed particles = N Number of particles present in octahedral voids = N Number of particles present in tetrahedral voids = 2N Tetrahedral voids : The Void formed between four touching spheres, a tetrahedron is formed when the centres of these four spheres are joined Octahedral voids : The interstitial void formed by combination of two triangular voids (6 spheres) a octahedron is formed when the centres of these six spheres are joined
- 17. 1. Covering the tetrahedral voids: Here, tetrahedral voids of the second layer may be covered by the spheres of the third layer. It gives rise to ABABAB… type pattern. The three dimensional structure is called hexagonal close packed structure. Coordination number is 12. Example: Mg, Zn Placing the third layer over the third layer: There are two possibilities:
- 18. 2. Covering the octahedral voids: Here, octahedral voids of the second layer may be covered by the spheres of the third layer. It gives rise to ABCABCABC… type pattern. The three dimensional structure is called cubic close packed structure or face centred cubic structure. Coordination number is 12. Example: Cu, Ag