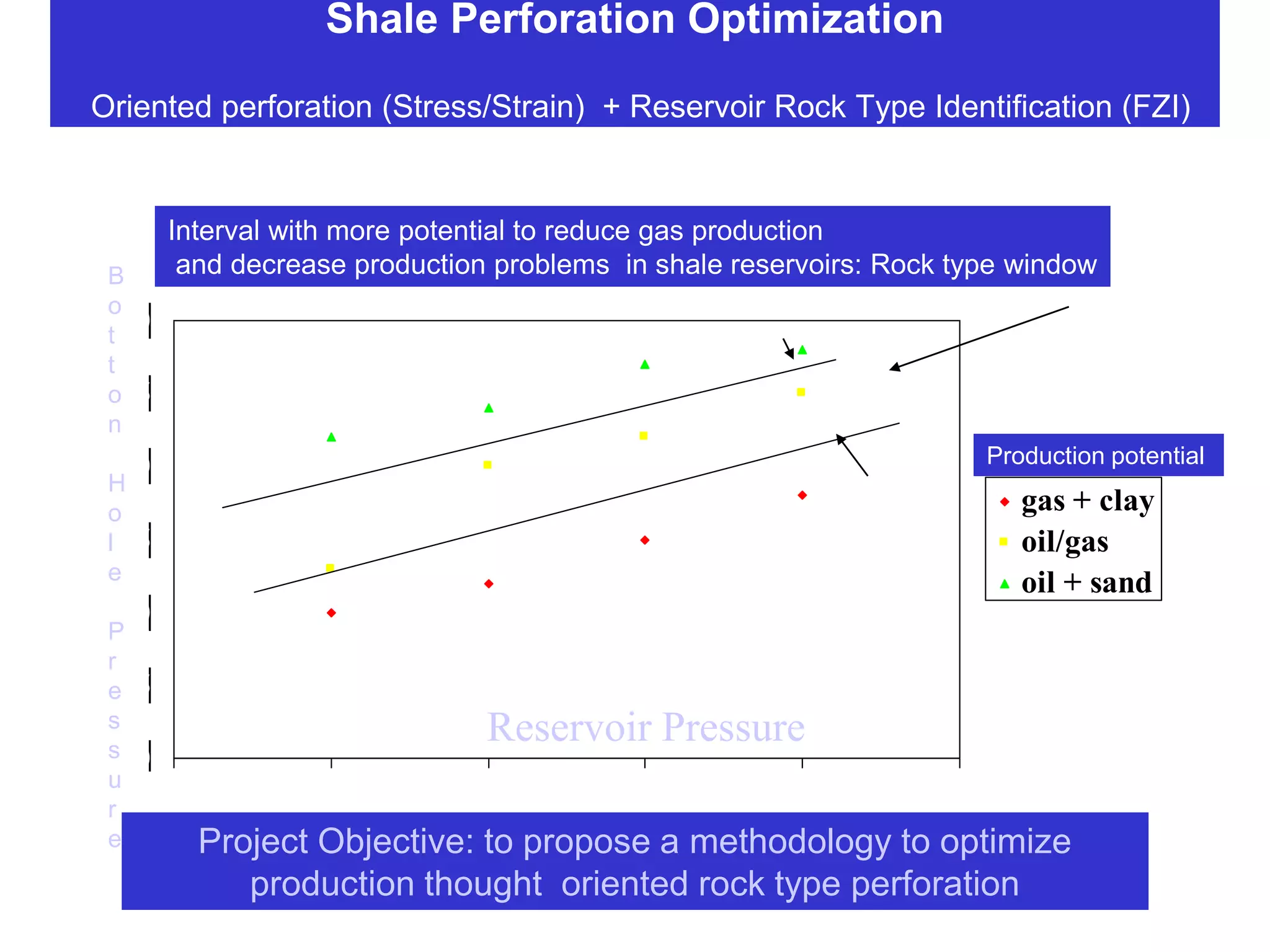
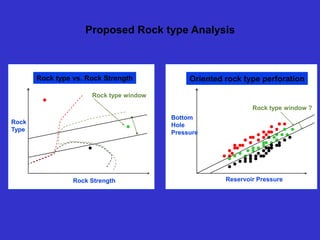
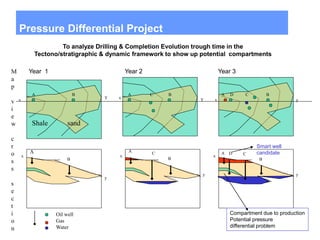
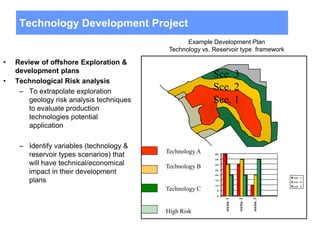
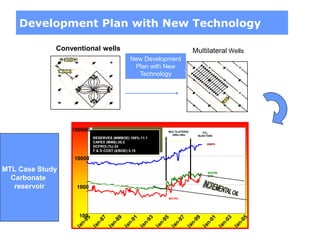
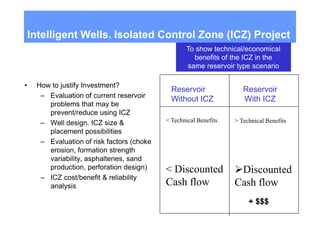
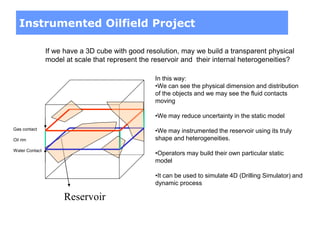
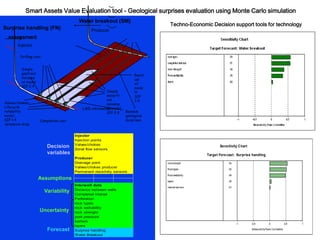
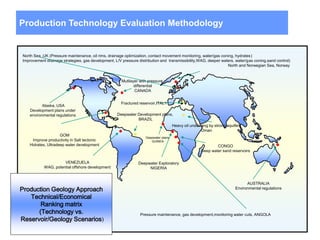
This document discusses several projects related to optimizing shale production through oriented perforation based on rock type identification. It proposes analyzing drilling and completion data over time to identify pressure differential issues and potential production compartments. Other projects discussed include evaluating new technologies for offshore developments by analyzing how they may impact development plans and reservoir types, justifying investments in isolated control zones to address reservoir issues, and building physical models of reservoirs to aid in instrumentation and dynamic simulation. The document also discusses regional environmental authorities' visions and a proposed methodology for evaluating production technologies under different environmental regulations.