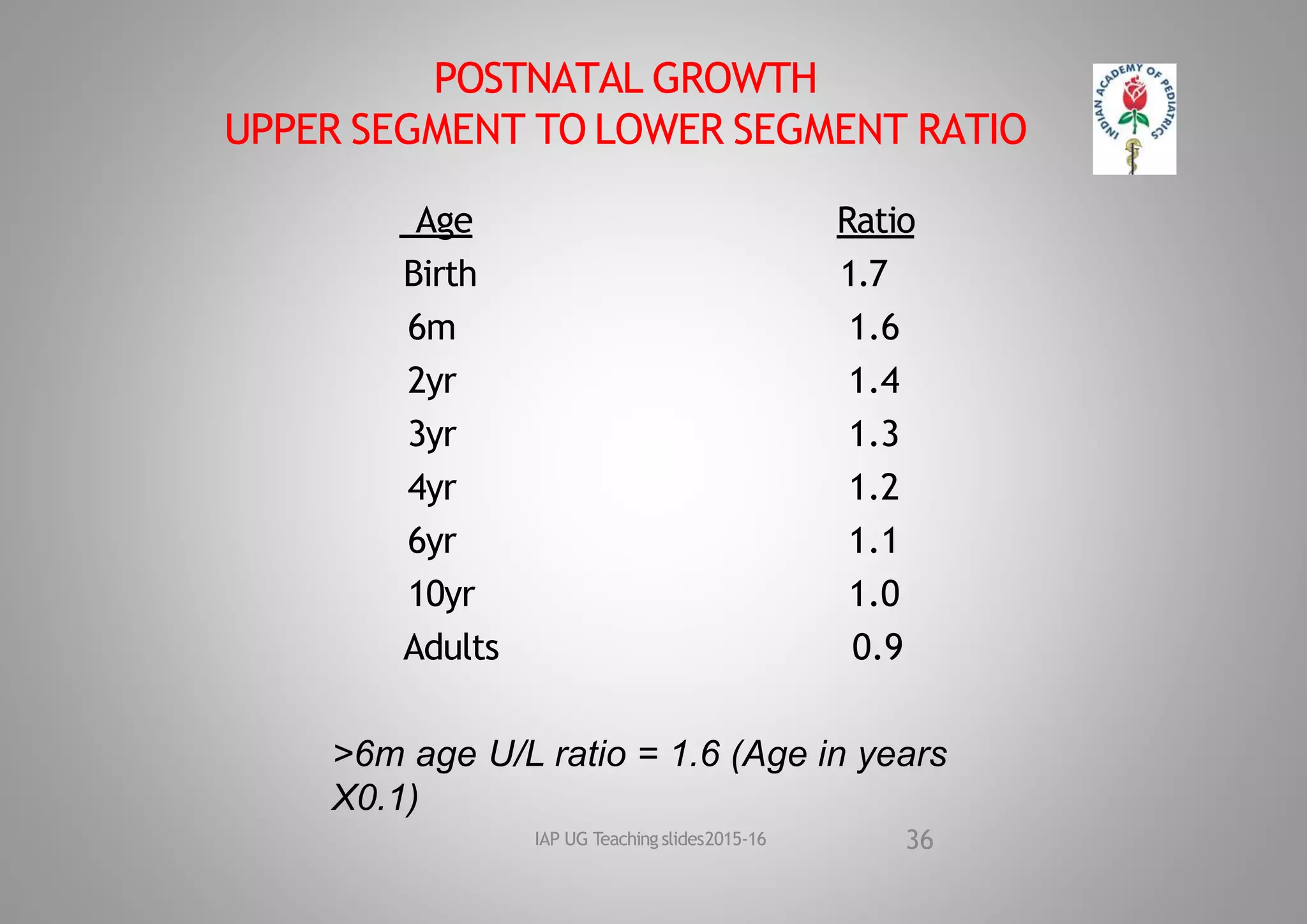
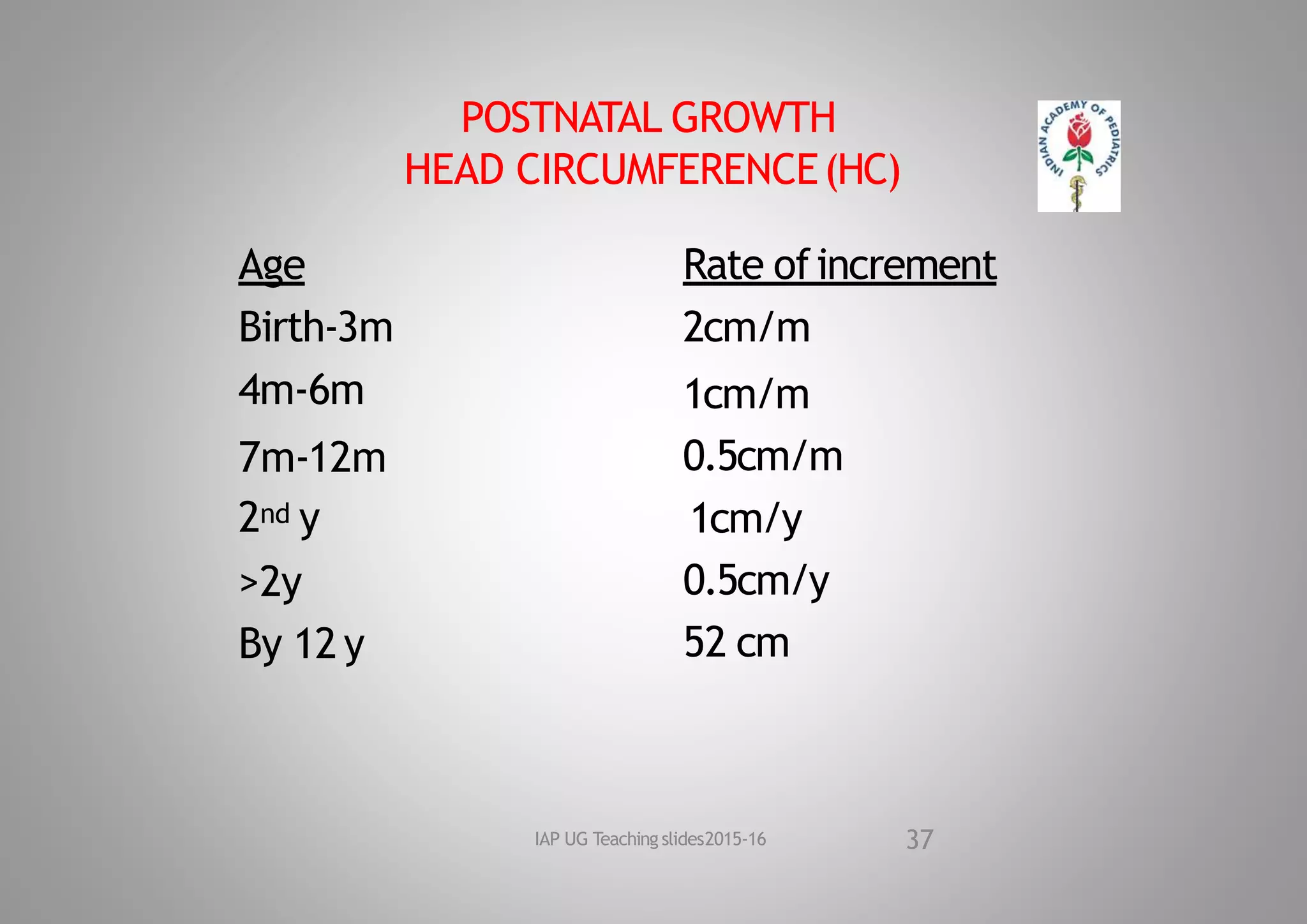
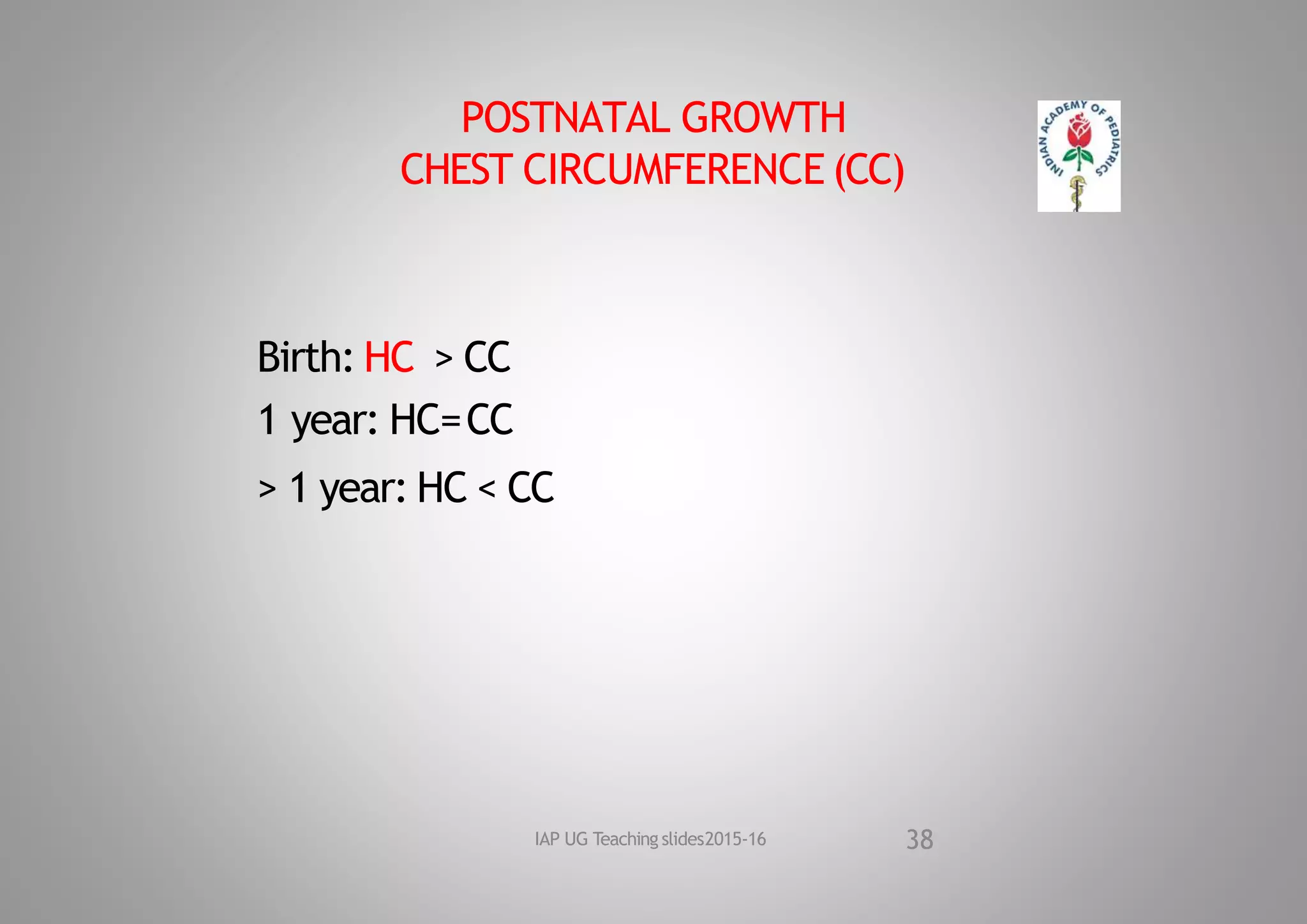
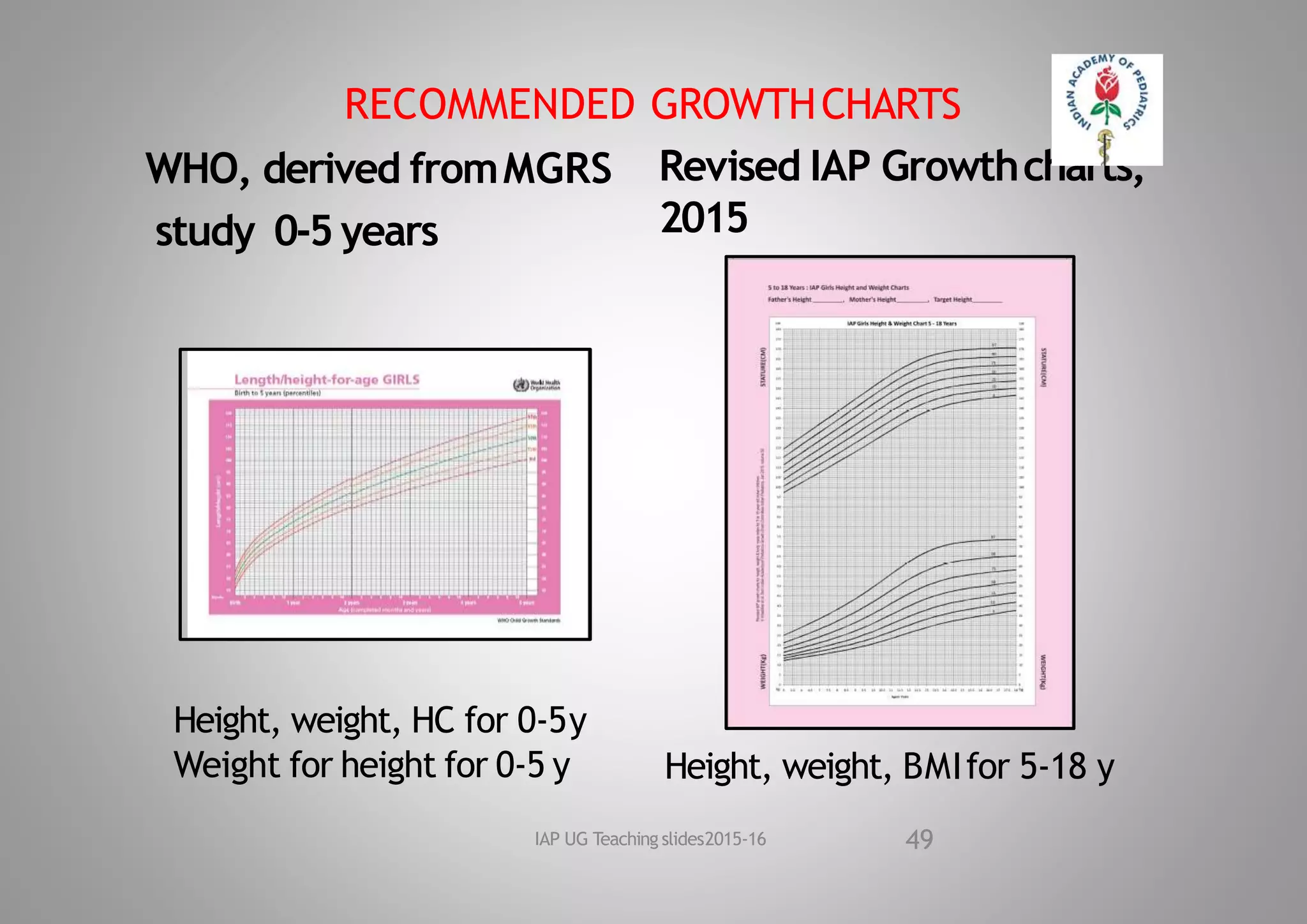
This document discusses normal growth and factors affecting growth. It defines growth and development, and notes the significance of growth. Prenatal and postnatal factors affecting growth are described, including genetic, environmental, hormonal, and social influences. The document outlines periods of growth from prenatal to postnatal, and average growth parameters at birth. It provides details on measuring and standards for weight, length, head circumference, and other growth parameters during infancy, childhood, and adolescence.

























![POSTNATAL GROWTH :WEIGHT
Age group
0‐3 m
4m‐1 yr.
2yr – Pubertal growth spurt*
2‐3 Kg/y
or
Weight gain
25‐30g/day
400g/month
[Wt. in Kg = (Age in years +4) X 2]
• Weight doubles at 5m, triples at 1 y
,quadruples
at 2y
* Boys 12 y
, girls 10 y
.
33
IAP UG Teaching slides2015‐16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/normalgrowthassessmentcharts-211031150610/75/Normal-growth-assessment-charts-33-2048.jpg)