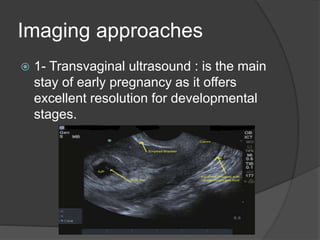
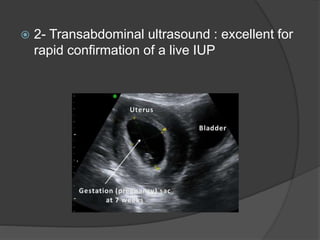
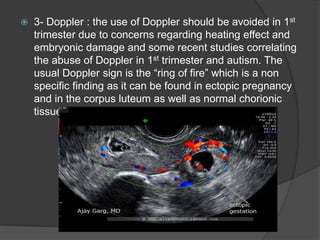
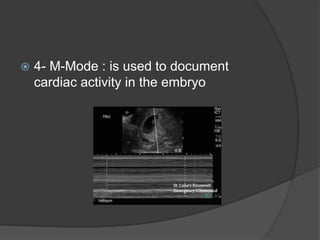
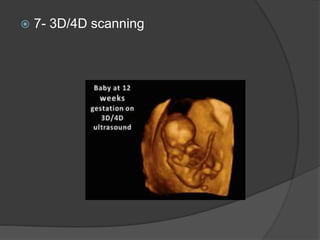
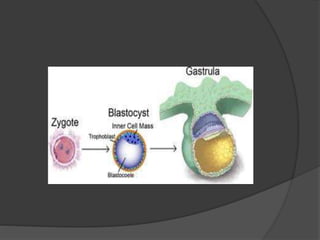
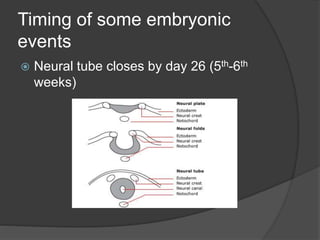
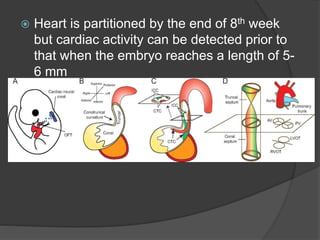
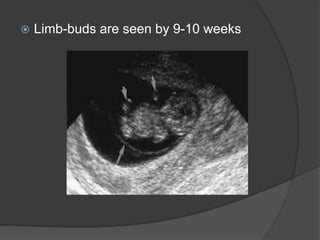
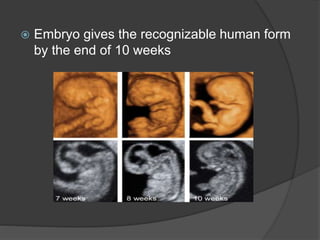
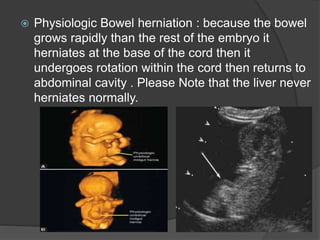
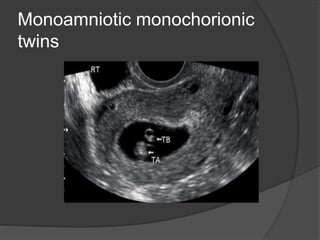
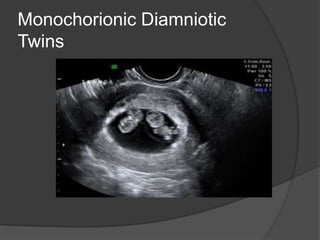
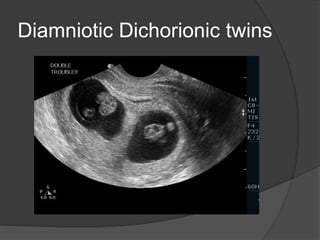
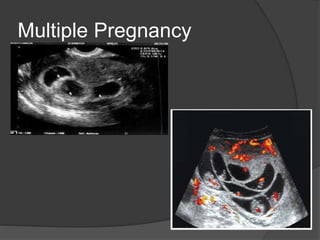
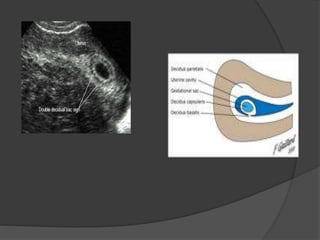
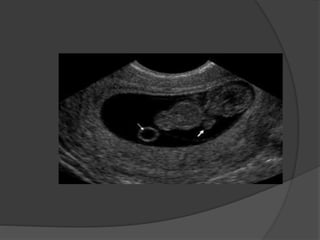
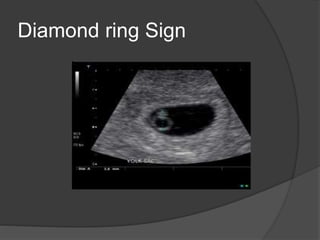
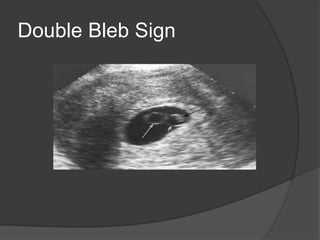
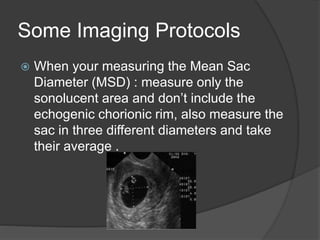
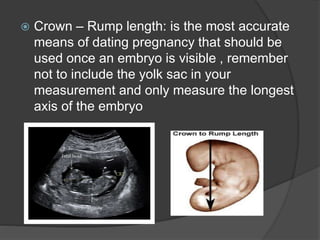
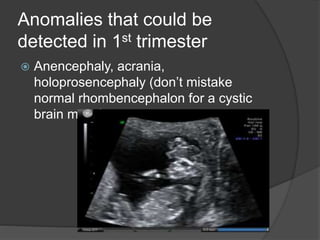
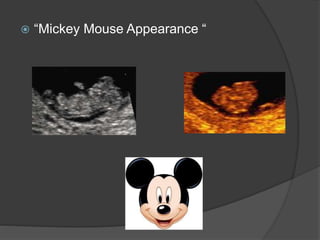
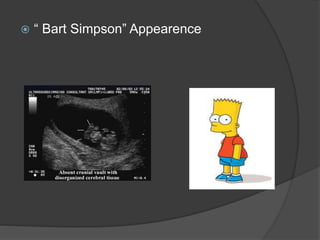
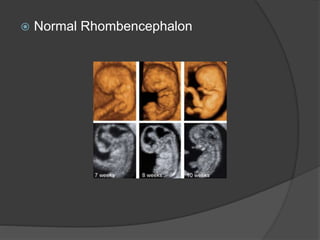
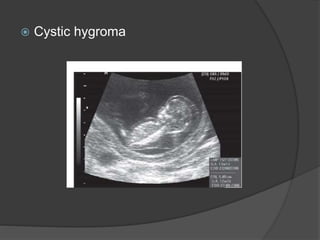
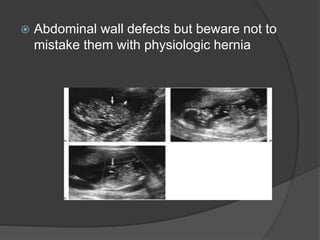
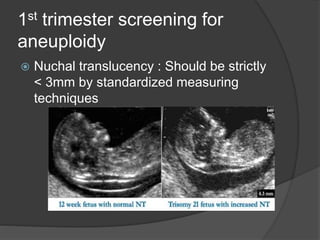
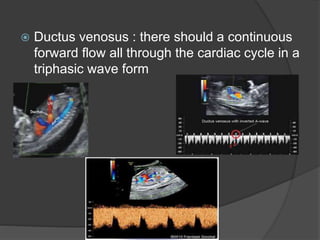
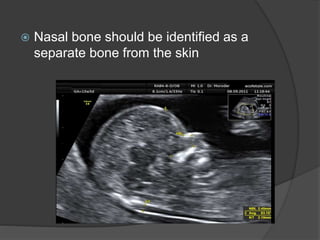
Transvaginal ultrasound is the main imaging approach in the first trimester. The double decidual sac sign appears by 4-5 weeks and confirms an intrauterine pregnancy. By 5-6 weeks, a yolk sac and embryonic heartbeat can be seen when the crown-rump length reaches 5mm. Anomalies like anencephaly can be detected. Nuchal translucency measurement and assessment of ductus venosus flow are used for first trimester aneuploidy screening. An empty uterus with hCG over 2000 suggests ectopic pregnancy or miscarriage.