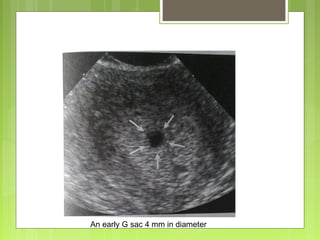
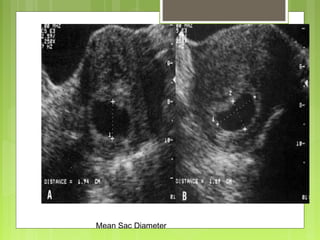
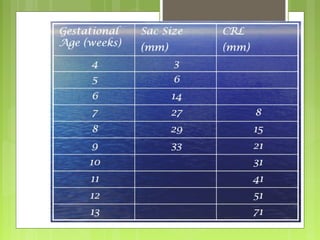
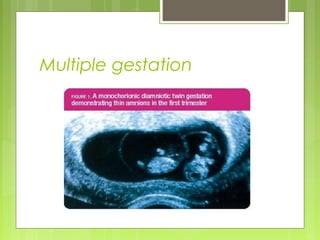
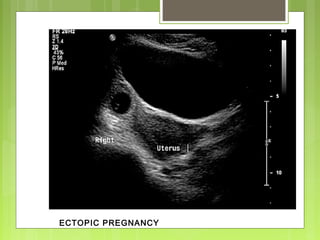
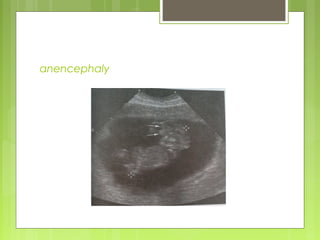
This document discusses the role and components of first trimester ultrasounds. It begins by providing background on the history and development of ultrasound technology. It then describes the mechanics of ultrasounds and their safety. The document outlines the standard exam components including gestational sac, yolk sac, fetal pole, cardiac activity and crown rump length. It discusses the uses of first trimester ultrasounds such as dating the pregnancy and screening for abnormalities. The document also covers topics like failed pregnancies, abortion, invasive procedures, ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, nuchal translucency screening, and various fetal abnormalities.