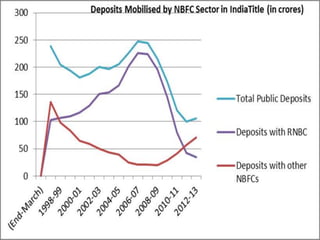
The document discusses the structure and regulations of non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) in India, detailing their services and types. It outlines the regulatory bodies overseeing NBFCs, the various categories of NBFCs as per the Reserve Bank of India, and the specific requirements for each category. Additionally, it addresses growth parameters, performance trends, and suggestions for improving the operational landscape for NBFCs, emphasizing the challenges they face in funding and regulation.