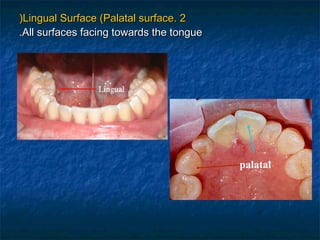
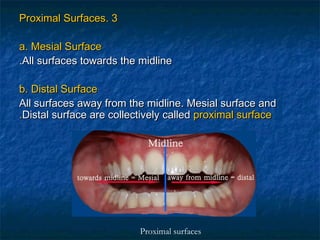
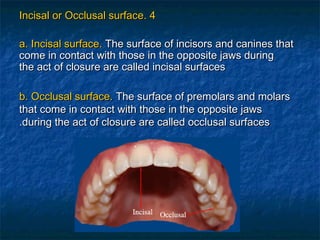
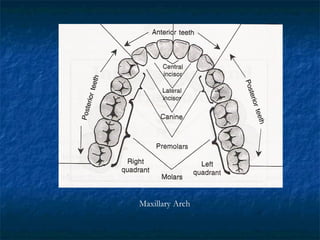
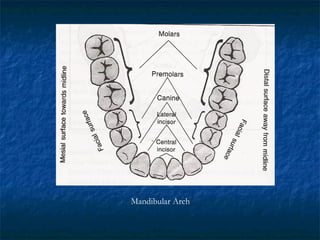
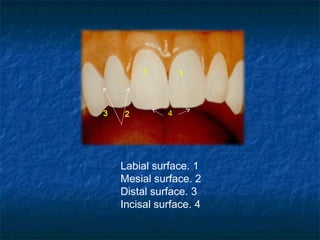
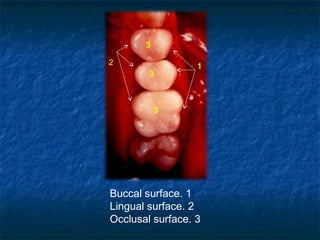
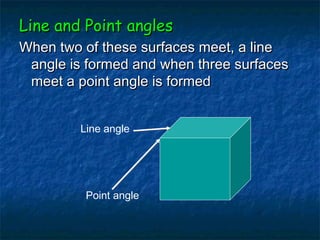
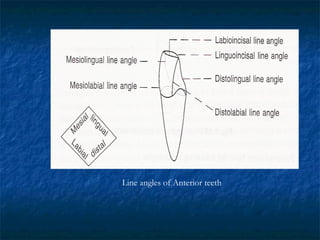
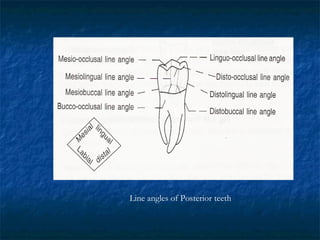
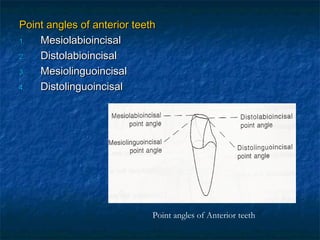
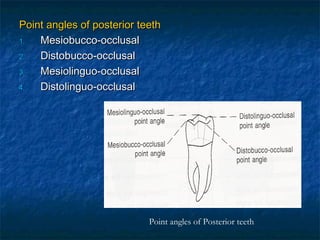
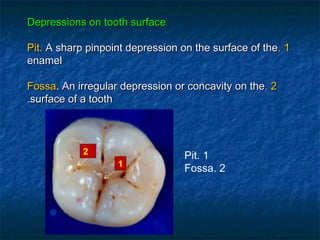
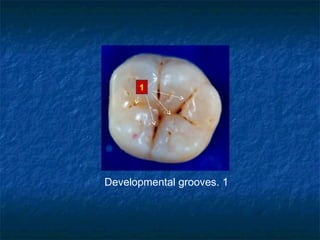
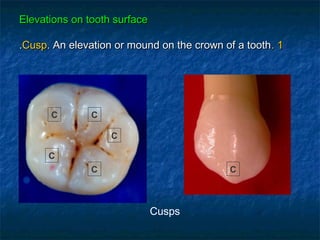
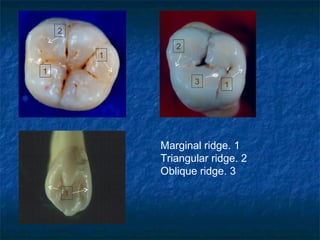
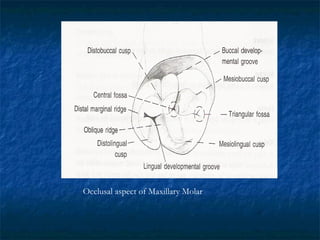
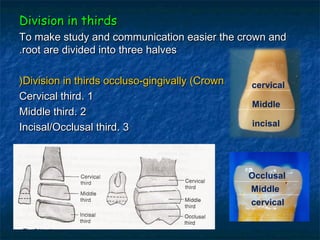
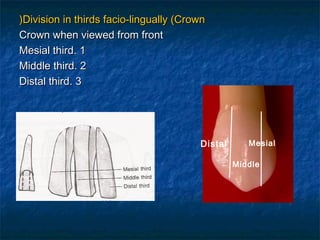
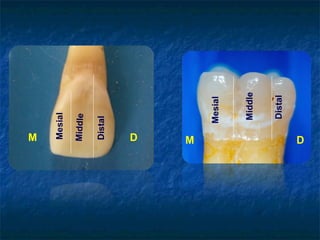
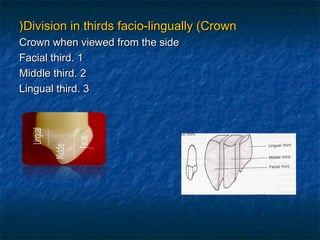
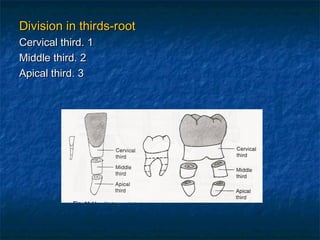
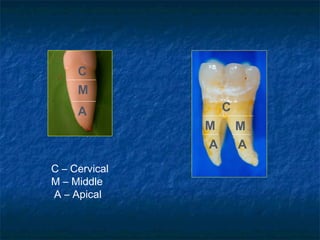
This document provides an overview of dental terminology used to describe the anatomy of teeth. It discusses the surfaces, lines, angles, depressions, elevations, and divisions of teeth. Key terms introduced include crown, root, CEJ, facial surface, lingual surface, proximal surfaces, incisal/occlusal surfaces, line angles, point angles, cusps, fossae, sulci, and the division of teeth into thirds. The objective is to introduce this terminology which is important for understanding dental anatomy and communication.