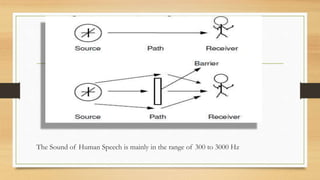
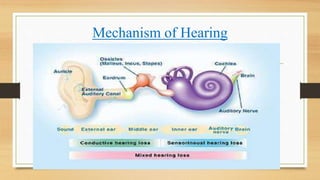
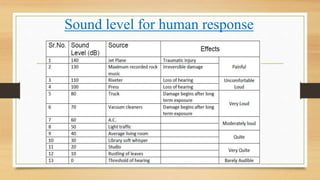
Noise pollution arises from various sources like vehicles, construction machinery, and household appliances. It is defined as unwanted sound that disrupts human or animal activity. Sound is measured in frequency (cycles/second), intensity (sound energy/second), and decibel level which is a logarithmic ratio of measured to reference intensity. The human ear can detect sounds from 20-20,000 Hz. Noise pollution has physiological effects like hearing loss, and psychological effects like sleep disturbances and annoyance. Control methods include using mufflers and insulation to reduce sound transmission, and ear protection for those working in noisy environments.