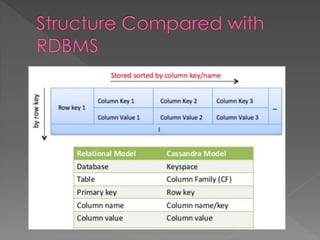
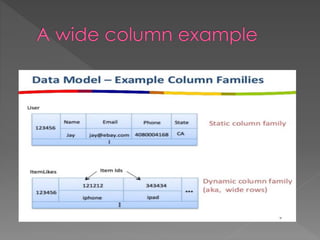
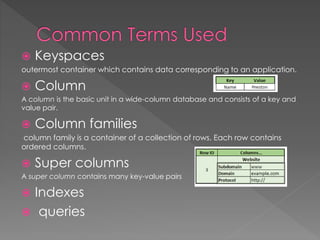
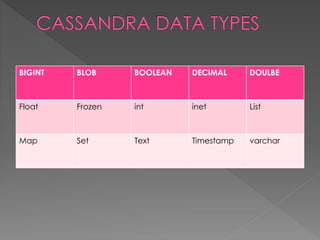
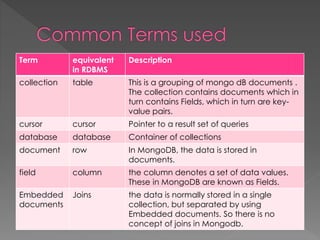
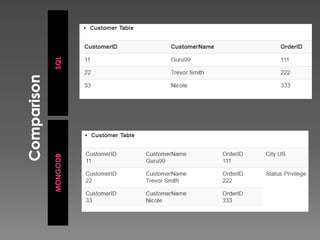
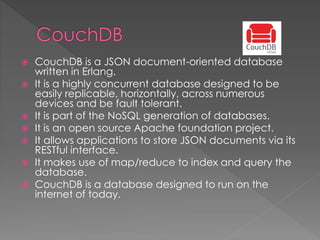
NoSQL databases, which emerged in the late 1960s and gained popularity with web 2.0 companies, offer diverse data models like document, key-value, and column families, providing flexibility, scalability, and higher performance compared to traditional relational databases. Famous NoSQL systems include MongoDB, CouchDB, and Cassandra, each suited for various applications, from big data to real-time analytics, while employing different architectures and query methods. NoSQL databases are particularly advantageous for applications requiring high availability and fault tolerance, with examples of use in large organizations such as Facebook, Twitter, and eBay.











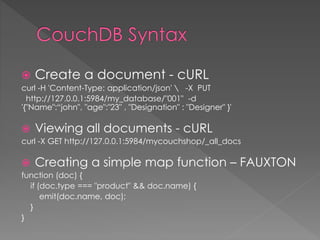
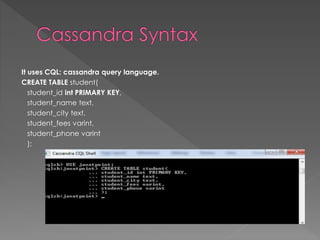
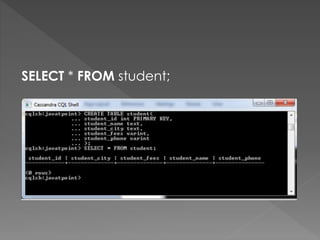
![use javatpoint //create database
db.javatpoint.insert( //insert a document
{
course: "java",
details: {
duration: "6 months",
Trainer: "Sonoo jaiswal"
},
Batch: [ { size: "Small", qty: 15 }, { size: "Medium", qty: 25 } ],
category: "Programming language"
}
)
db.javatpoint.find() //check the inserted document](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqldatabases-180818065846/85/No-sql-databases-16-320.jpg)


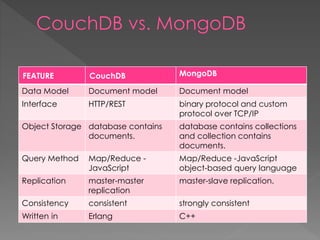
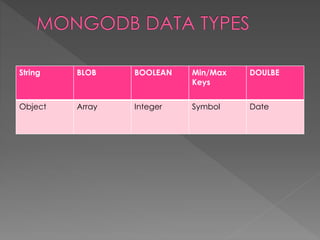
![String Float integer boolean Arrays
Object nulls
{ // a document example
"Subject": "I like Plankton",
"Author": "Rusty",
"PostedDate": "2006-08-15T17:30:12-04:00",
"Tags": [
"plankton",
"baseball",
"decisions"
],
"Body": "I decided today that I don't like baseball. I like plankton."
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqldatabases-180818065846/85/No-sql-databases-22-320.jpg)