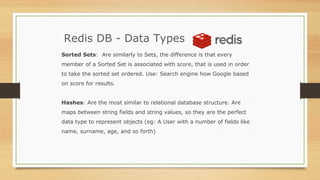
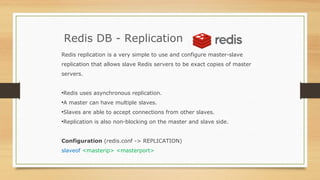
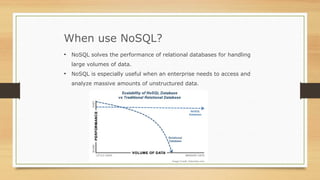
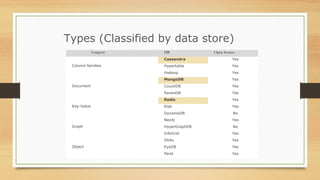
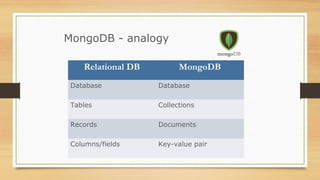
NoSQL databases were developed to handle large volumes of data and optimize for read/write operations better than relational databases. Popular NoSQL databases include MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, and Neo4j. MongoDB is a document database where data is stored in collections as documents with dynamic schemas. Redis is an in-memory key-value store that also supports data structures like lists, sets, and hashes. Both MongoDB and Redis can scale horizontally and offer high availability through replication.







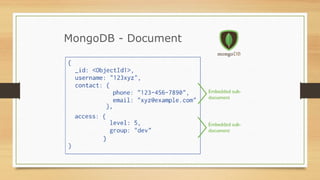
![MongoDB - Document
{
title: "MongoDB: The Definitive Guide",
author: [ "Kristina Chodorow", "Mike Dirolf" ],
published_date: ISODate("2010-09-24"),
pages: 216,
language: "English",
publisher: {
name: "O'Reilly Media",
founded: 1980,
location: "CA"
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nosqlbycab-propio-150119101953-conversion-gate01/85/NoSQL-Databases-12-320.jpg)