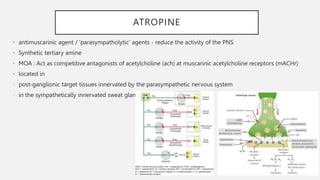
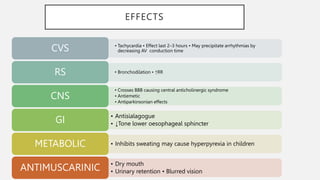
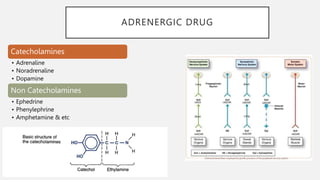
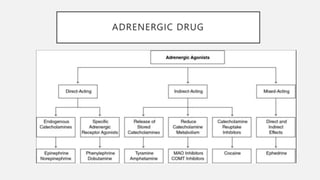
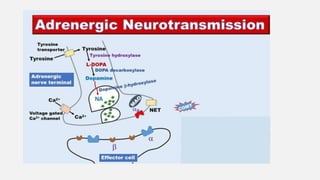
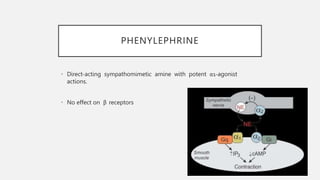
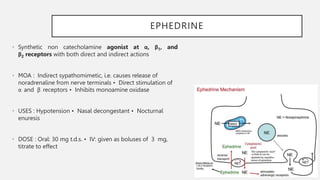
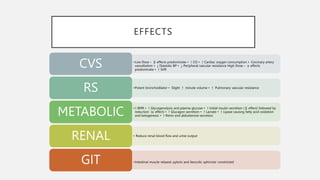
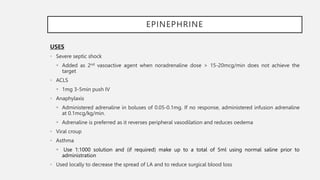
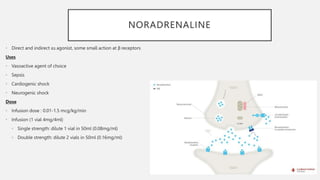
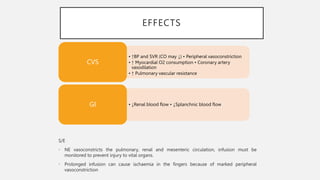
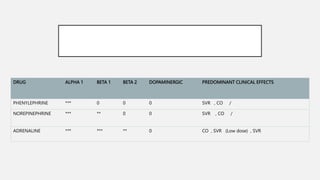
This document summarizes several emergency drugs used in anesthesia - atropine, phenylephrine, ephedrine, adrenaline, and norepinephrine. It provides details on the mechanism of action, effects, dosing, and metabolism for each drug. Atropine is an antimuscarinic agent that acts as a competitive antagonist of acetylcholine. Phenylephrine is a direct-acting alpha-1 agonist with potent vasoconstrictive effects. Ephedrine has actions at alpha, beta-1, and beta-2 receptors and causes release of norepinephrine. Adrenaline and norepinephrine are both catecholamines that stimulate alpha and beta receptors, with adrenaline having more pronounced beta effects and