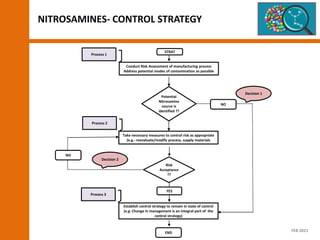
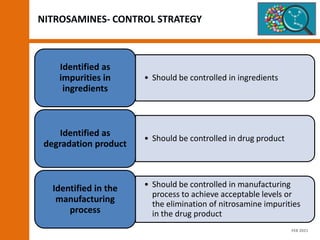
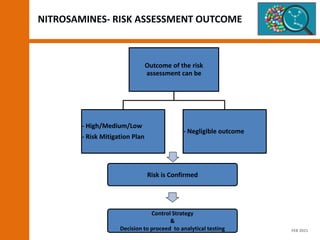
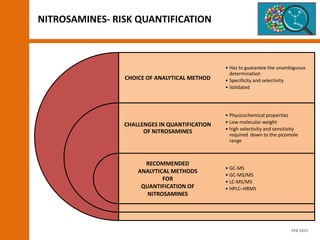
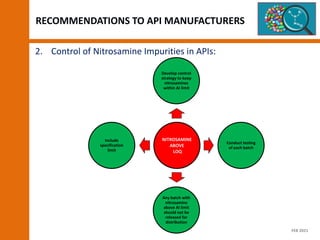
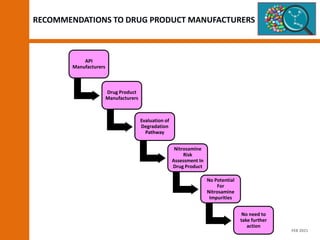
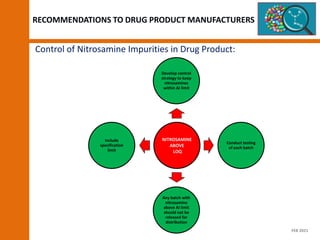
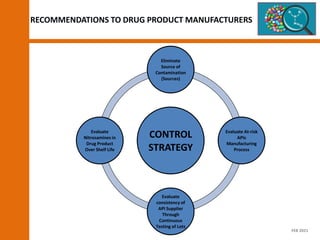
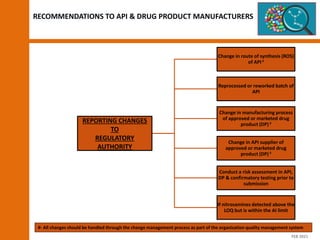
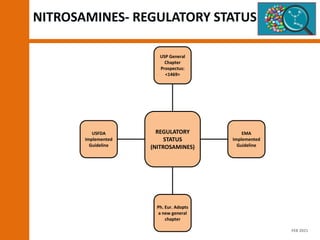
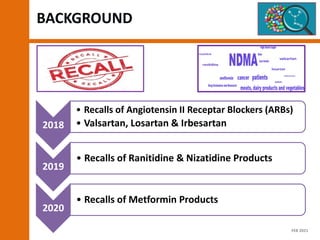
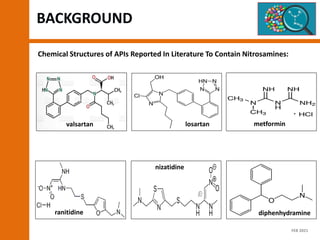
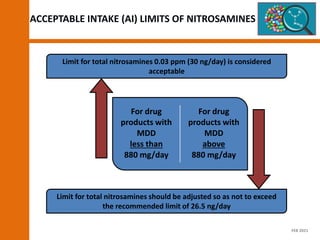
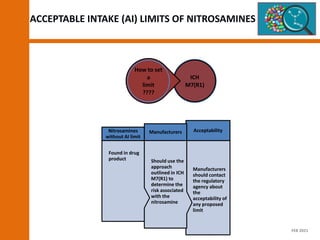
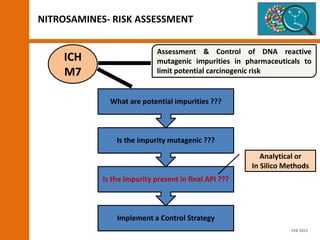
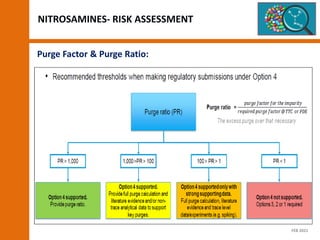
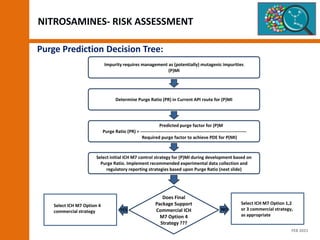
The document discusses the risks and regulatory frameworks surrounding nitrosamines in human medicinal products, highlighting their potential presence, risks of cancer, and regulatory limits set by entities like the EMA and FDA. It outlines the measures that manufacturers should undertake to assess and mitigate the presence of nitrosamines, including risk assessments, confirmatory testing, and compliance with acceptable intake limits. Additionally, it details the various sources and pathways through which nitrosamines can contaminate pharmaceuticals, urging manufacturers to implement control strategies accordingly.









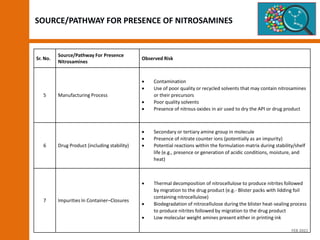
![SOURCE/PATHWAYS FOR PRESENCE OF NITROSAMINES
Sr. No.
Source/Pathway For Presence
Nitrosamines
Observed Risk
1 Impurities In Solvents
Presence of residual dialkyl amines or tri-substituted amines that can
degrade to form dialkyl amines (e.g., triethylamine)
Presence of nitrites (NaNO2) or other nitrosating agents
Presence of acid
Limited controls/specification limits for recycled solvents
Poor quality water or solvents
2 Impurities In Water
Presence of residual dialkyl amines or tri-substituted amines that can
degrade to form dialkyl amines (e.g., triethylamine)
Presence of nitrites (NaNO2) or other nitrosating agents
Presence of acid
3 Impurities In Excipients Presence of nitrites or other nitrosating agents
4 Impurities In Drug Substance/API
Use of sodium azide and nitrite for azide quenching in the synthesis in
acid media
Use of di- or tri-alkylamines and amides (e.g., dimethylformamide
[DMF], dimethylamine [DMA], triethylamine [TEA], N-
methylpyrrolidone [NMP]) in the presence of nitrites and acid media
Use of recycled solvents that may contain nitrosamines or their
precursors
Use of sanitized water (e.g., chloramines)
Need of additional purification steps (e.g., crystallization)
FEB 2021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nitrosaminesinhumanmedicinalproducts05-02-2021-210211132634/85/Nitrosamines-In-Human-Medicinal-Products-37-320.jpg)