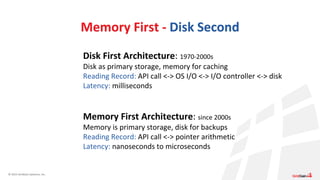
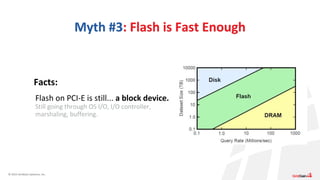
The document discusses the significance and evolution of in-memory computing as a transformative approach that impacts application design and vendor strategies. It outlines myths surrounding in-memory computing and provides key use cases, including automated trading, fraud detection, and real-time data analytics. The speaker emphasizes that memory-first architectures offer significantly reduced latency compared to traditional disk-based systems.