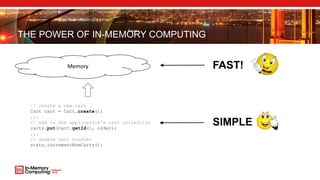
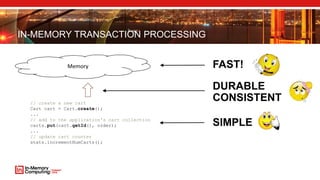
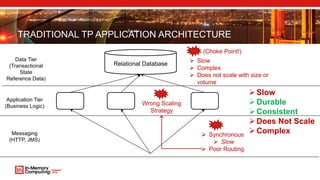
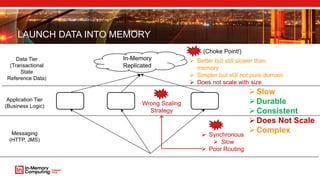
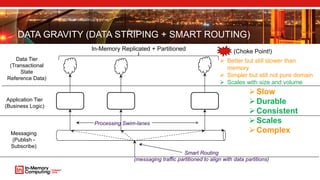
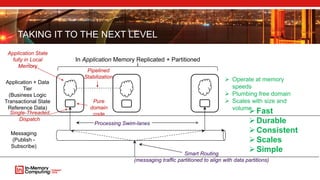
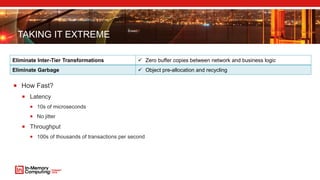
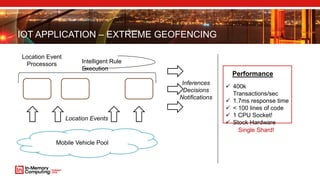
The document discusses extreme transaction processing in a memory-oriented architecture, highlighting its benefits such as fast processing speeds, high throughput, and system reliability without losing simplicity and consistency. It emphasizes a new model that utilizes in-memory computing to handle vast scales of transactions efficiently with minimal latency, outperforming traditional architectures. Real-life use cases demonstrate the practical advantages of this approach in various industries, including e-commerce and finance.