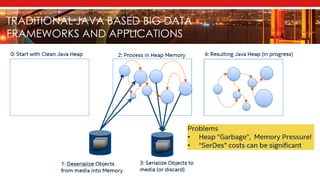
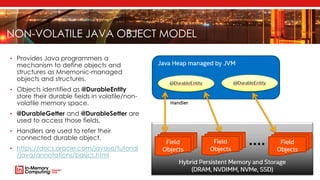
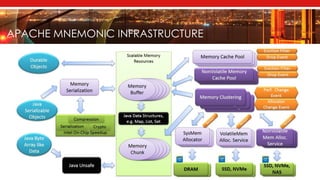
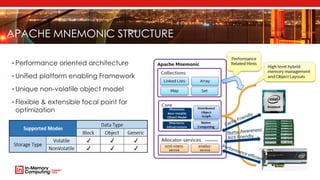
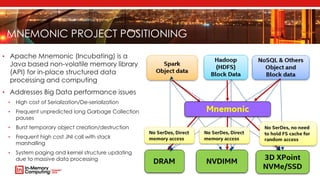
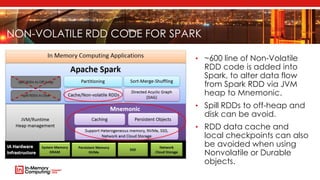
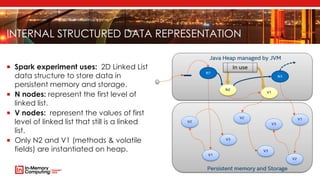
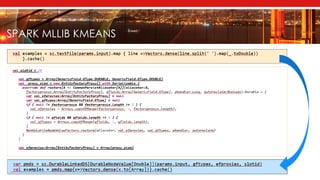
The document introduces Apache Mnemonic, a non-volatile programming model aimed at improving in-memory computing performance for Java applications by leveraging advanced storage media. It focuses on creating a non-volatile object model that allows Java programmers to manage data in place, minimizing serialization costs and improving performance in big data frameworks like Spark. The document also outlines practical use cases and provides insights into performance improvements, particularly in machine learning applications.