1) The document outlines an innovative lesson plan about the structure of the eye presented by teacher T.C. Nijina.
2) The plan includes learning objectives, content analysis, facts about the eye, and teaching activities involving models, charts, and worksheets.
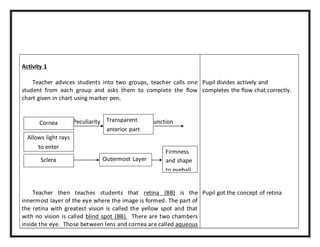
3) Key parts of the eye are taught such as the sclera, cornea, iris, pupil, lens, aqueous and vitreous chambers, retina, and blind spot.