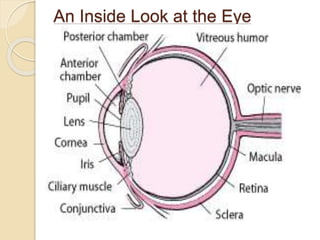
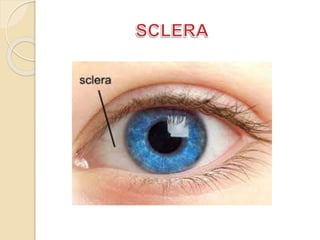
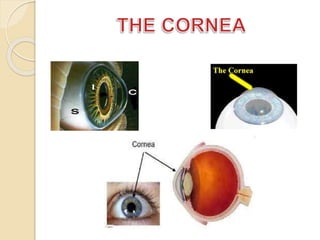
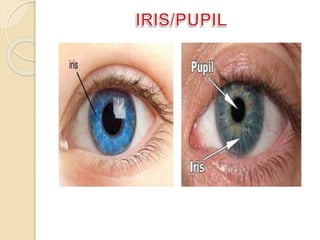
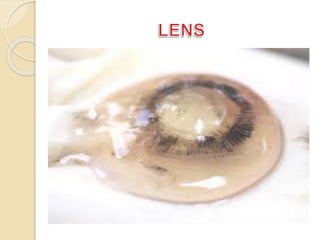
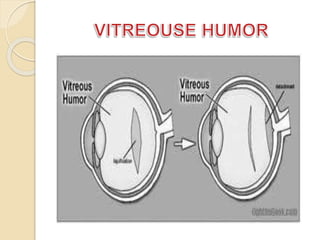
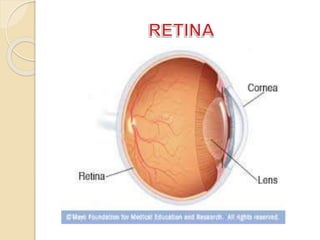
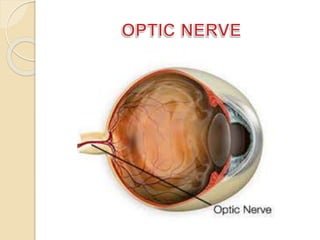
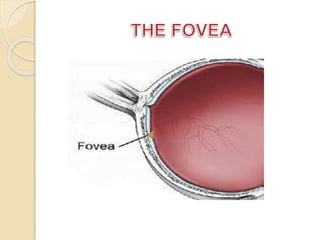
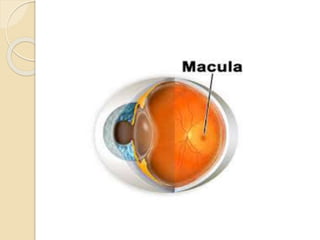
The human eye functions similar to a camera, using a lens to focus light onto the retina. Light passes through the cornea and pupil, and the iris controls the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light. The retina contains light-sensitive cells that transmit visual signals via the optic nerve to the brain. Common structures inside the eye include the sclera, cornea, iris, lens, vitreous humor, and retina, each playing a role in transmitting and focusing light to produce clear vision.