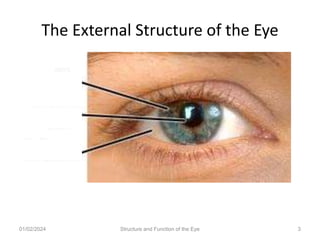
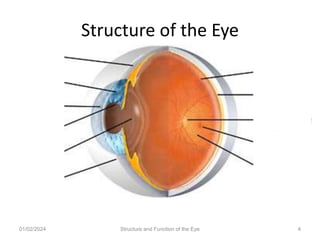
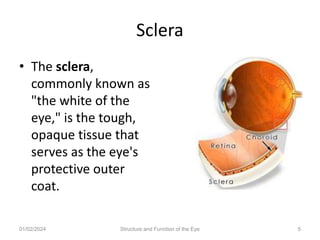
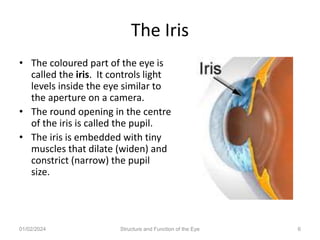
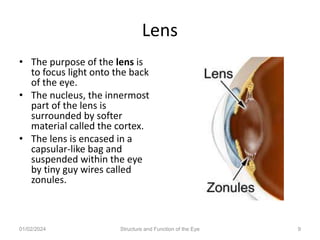
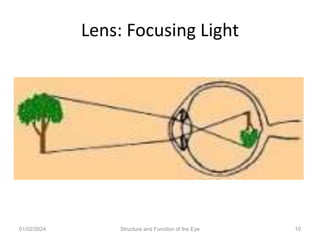
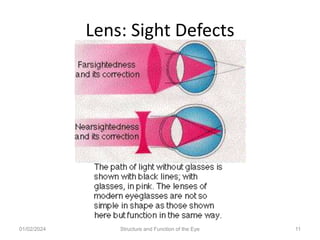
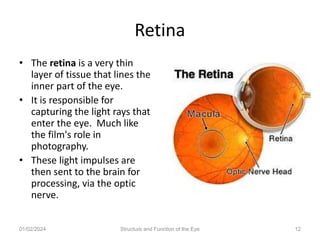
The document discusses the structure and function of the human eye. It describes the external structures like the sclera, iris, cornea, and conjunctiva. Internally, it outlines the lens, retina, and optic nerve. The lens focuses light onto the retina, where light is converted to electrical signals sent by the optic nerve to the brain for processing. The iris controls the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light entering the eye. Together, these structures work to capture light and transmit visual information to the brain.