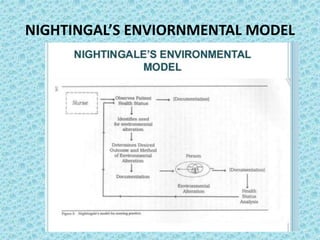
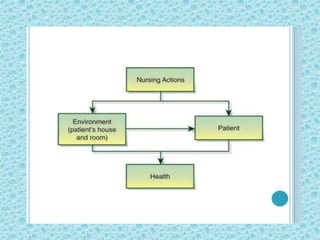
Apply Nightingale's theory in nursing process for this case.
Assessment:
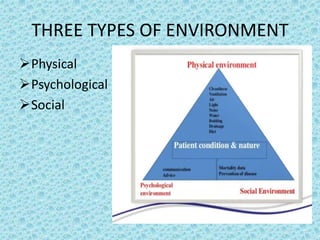
- Physical environment: Clean room, adequate ventilation, lighting and temperature control
- Psychological: Anxious due to fever, unable to sleep
- Social: Married, lives with family
Diagnosis: Acute febrile illness related to infection as evidenced by fever, chills, headache
Planning:
- Ensure cleanliness, adequate ventilation, lighting and comfortable temperature
- Provide comfort measures like back rub, listening ear
- Educate on importance of rest and nutrition
Implementation:
- Maintain clean room and bedding
- Open windows for cross-ventilation
- Dim lights for