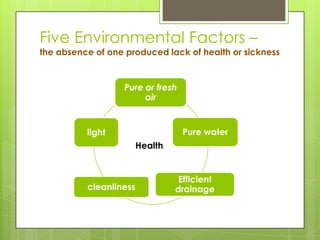
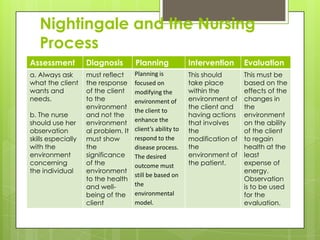
Florence Nightingale developed the environmental theory of nursing in the 1850s based on her experiences as a nurse in the Crimean War. She believed the environment strongly influences health outcomes. Her theory outlined 13 canons focusing on ventilation, light, noise, hygiene and other environmental factors. Nightingale viewed the nurse's role as controlling and manipulating the patient's environment to support recovery. Her theory established the foundations of modern nursing by emphasizing the importance of environmental assessment, intervention and evaluation of outcomes.