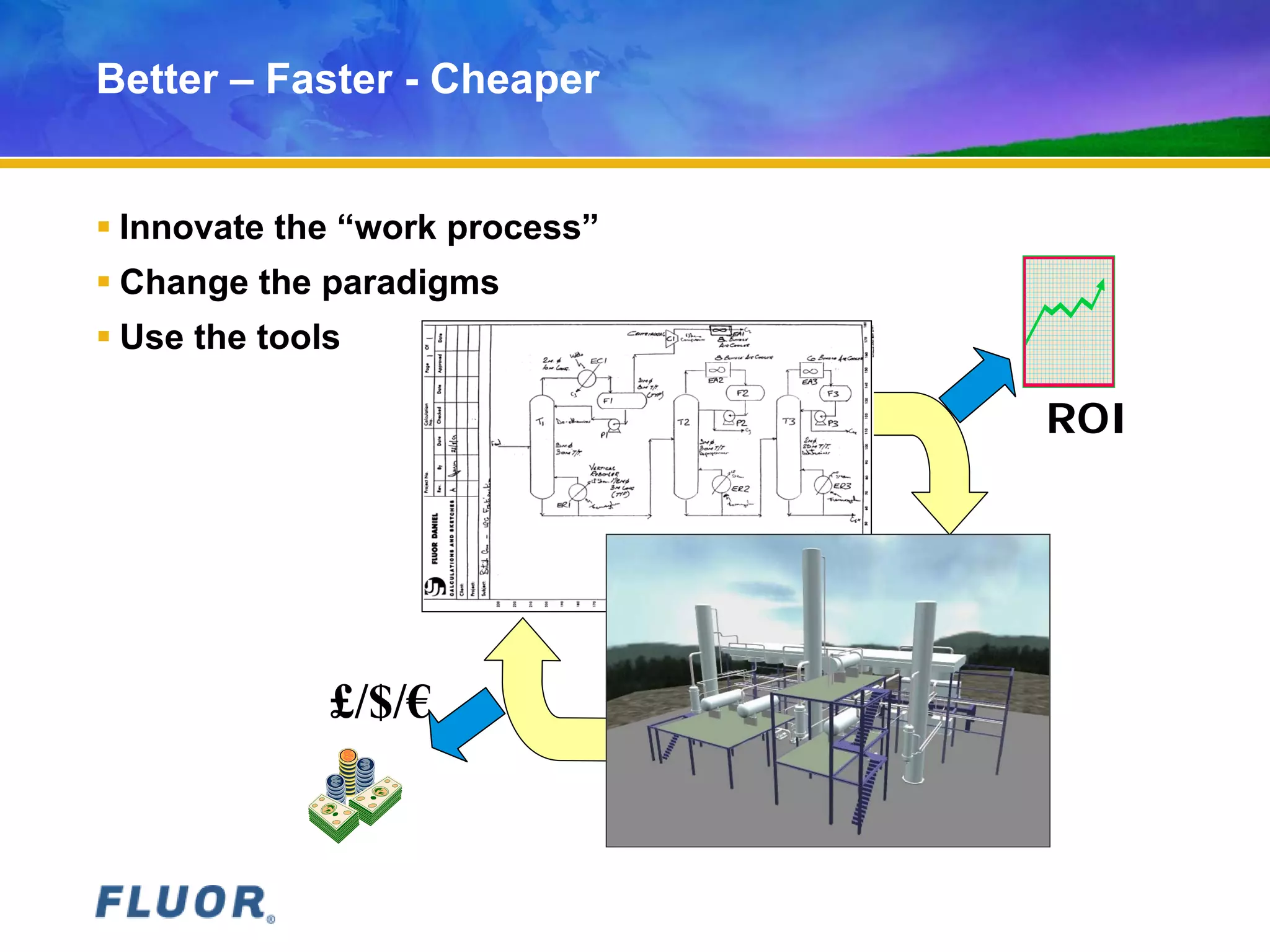
This document discusses innovation and provides examples. It summarizes Fluor's focus on innovation to gain competitive advantages and ensure quality solutions for customers. Real examples are given showing how Fluor has innovated work processes to complete projects better, faster and cheaper through modular construction techniques. While some innovations fail, Fluor emphasizes an environment where employees can challenge conventions and contribute new ideas.