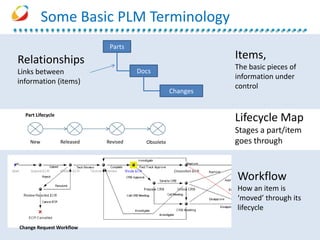
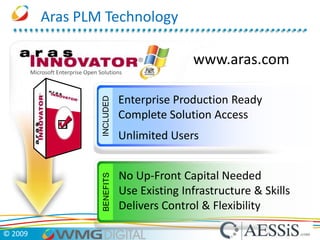
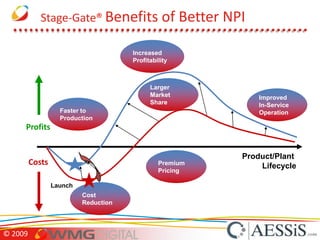
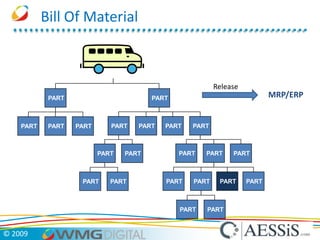
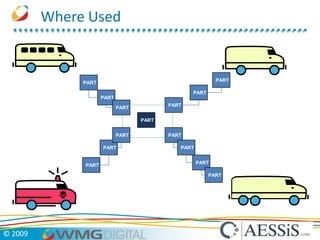
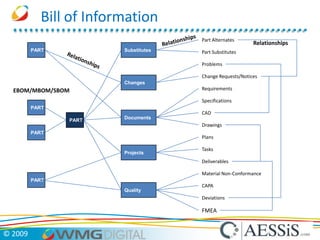
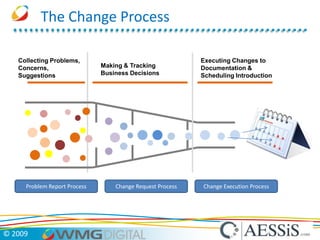
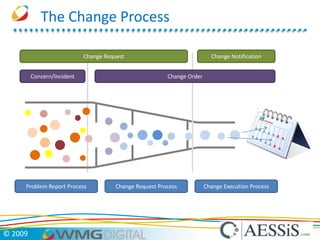
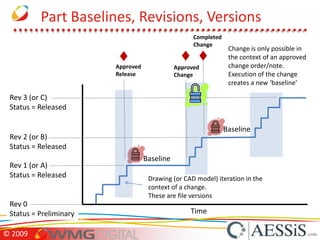
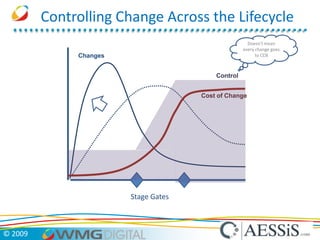
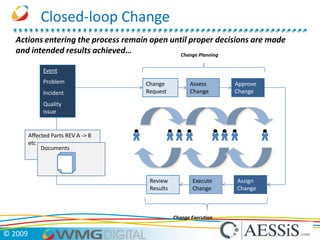
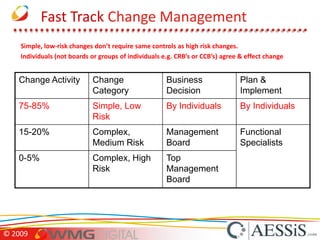
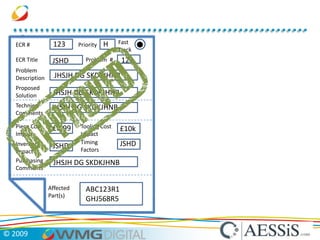
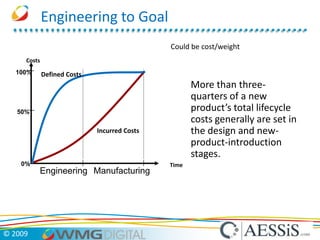
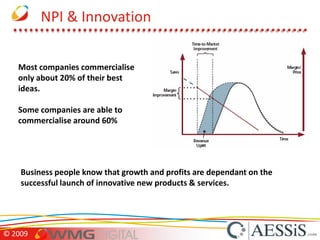
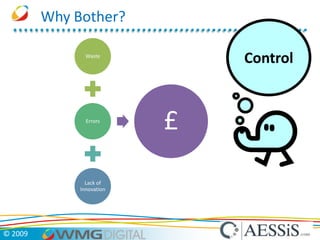
AESSiS is an engineering consultancy that specializes in product lifecycle management (PLM) implementation and process improvement to help manufacturing businesses achieve better performance. PLM is a strategic approach to managing product information throughout the lifecycle from concept to end of life. It aims to provide a single source of truth, configuration management, reduced waste, and increased innovation. PLM tools help manage parts, relationships between parts, documents, changes to parts, and the lifecycle of a part from new to obsolete. Aras is an open source PLM platform that provides an enterprise solution with no upfront costs and uses existing IT infrastructure and skills.