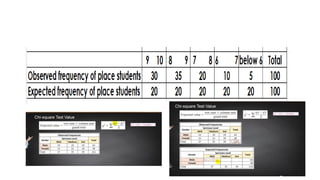
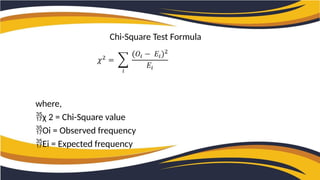
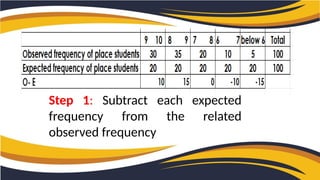
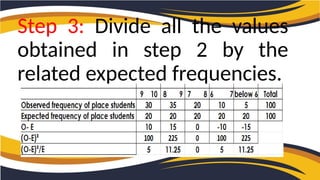
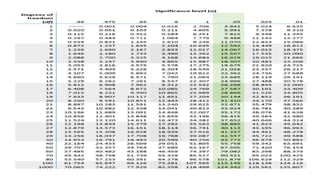
The document explains the chi-square test, a statistical method used to determine the association between two categorical variables. It covers three types: Pearson’s chi-square test, chi-square goodness of fit test, and chi-square test of independence, alongside the formula for calculating the chi-square value. A practical example illustrates how a researcher investigates the relationship between student placement rates and CGPA using the chi-square test.