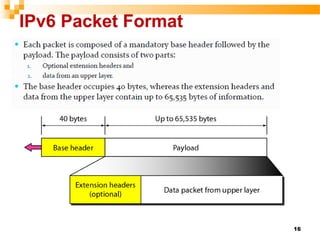
This document discusses next generation IP (IPv6). It covers IPv6 addressing, the IPv6 protocol, and transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6. IPv6 addresses are 128-bit and represented using hexadecimal colon notation. They allow for a much larger address space to accommodate more devices. The document examines IPv6 packet format and compares IPv4 and IPv6 headers. It also outlines different methods for transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6, including dual stack, tunneling, and translation techniques.