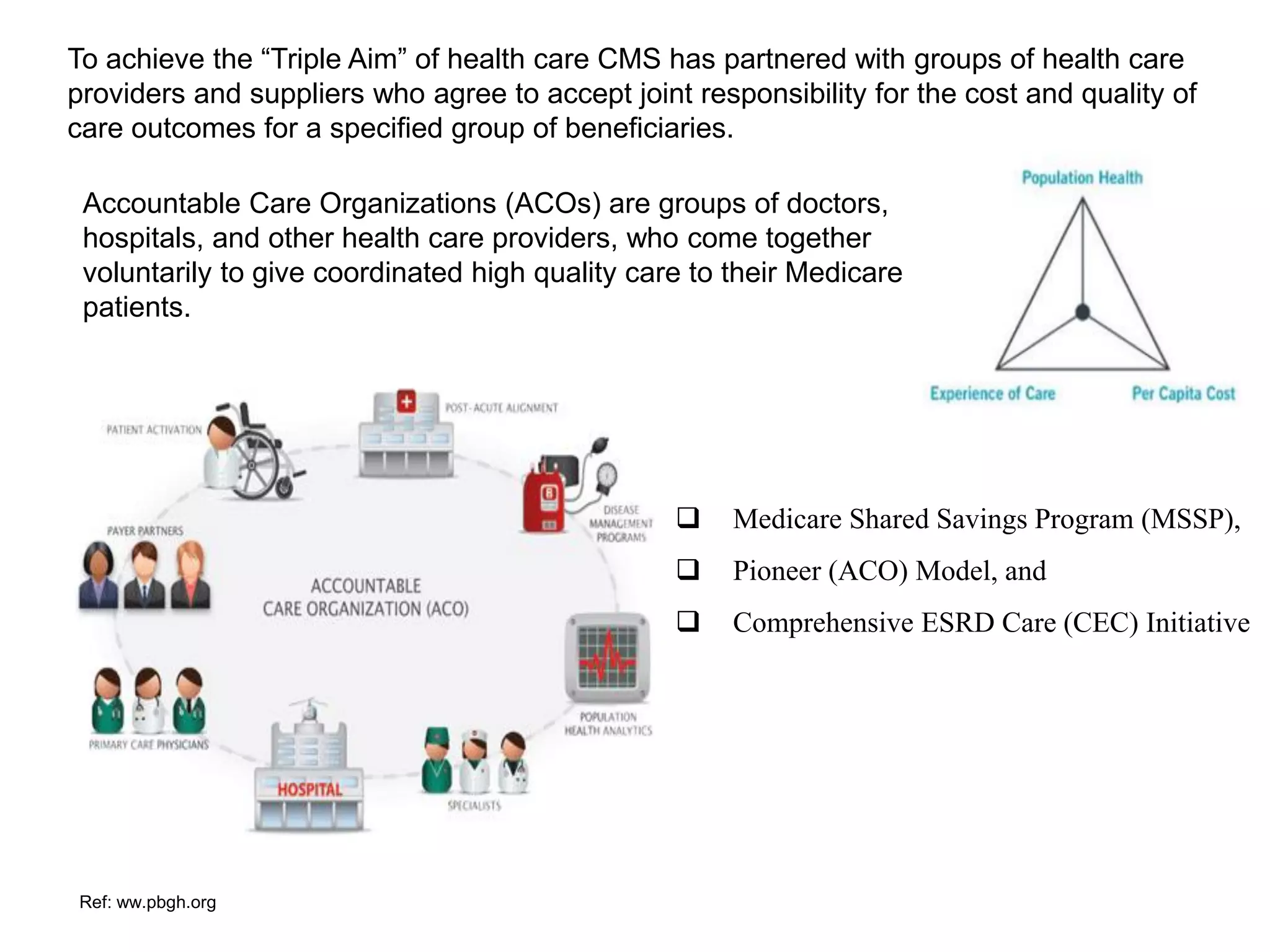
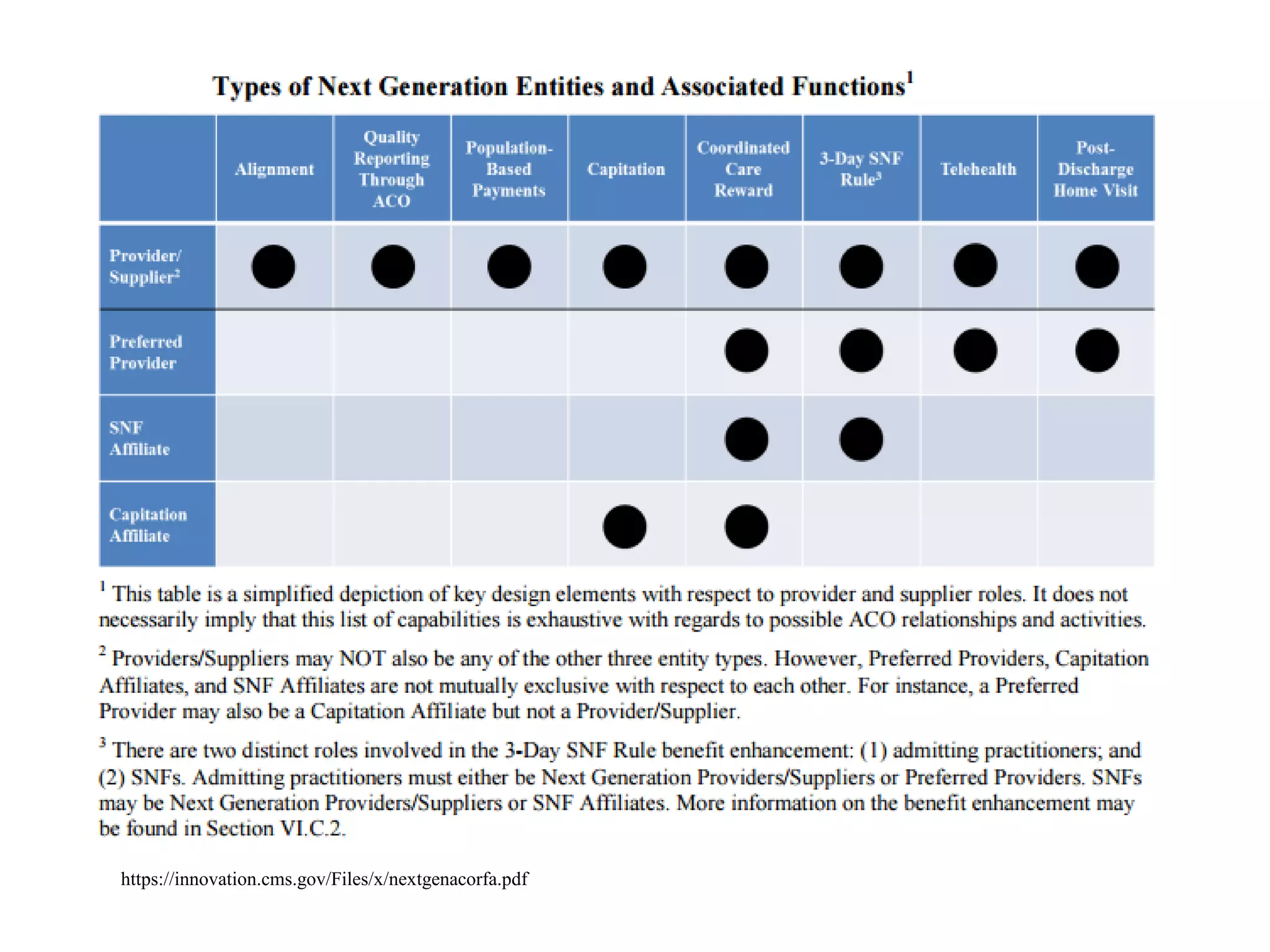
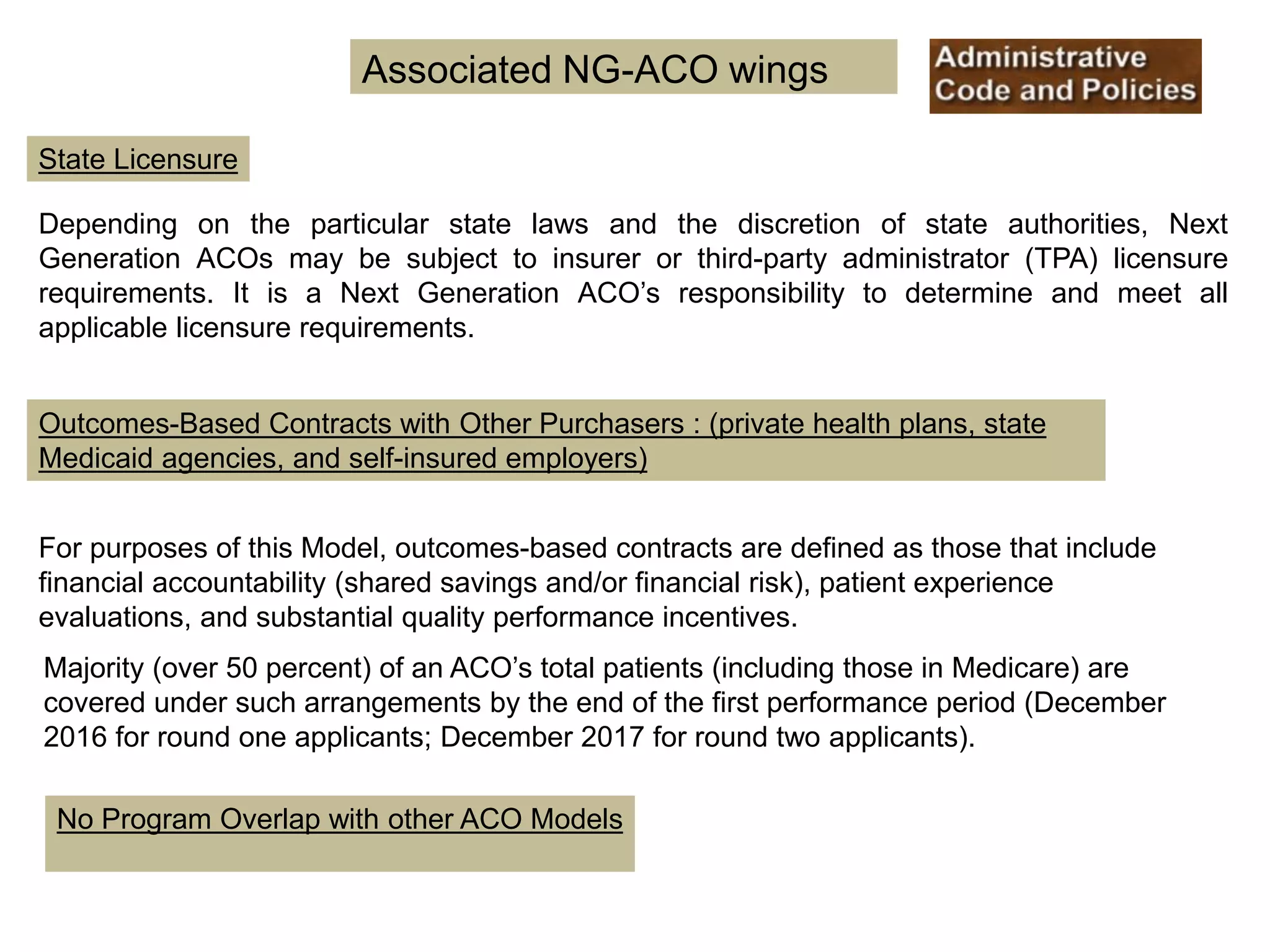
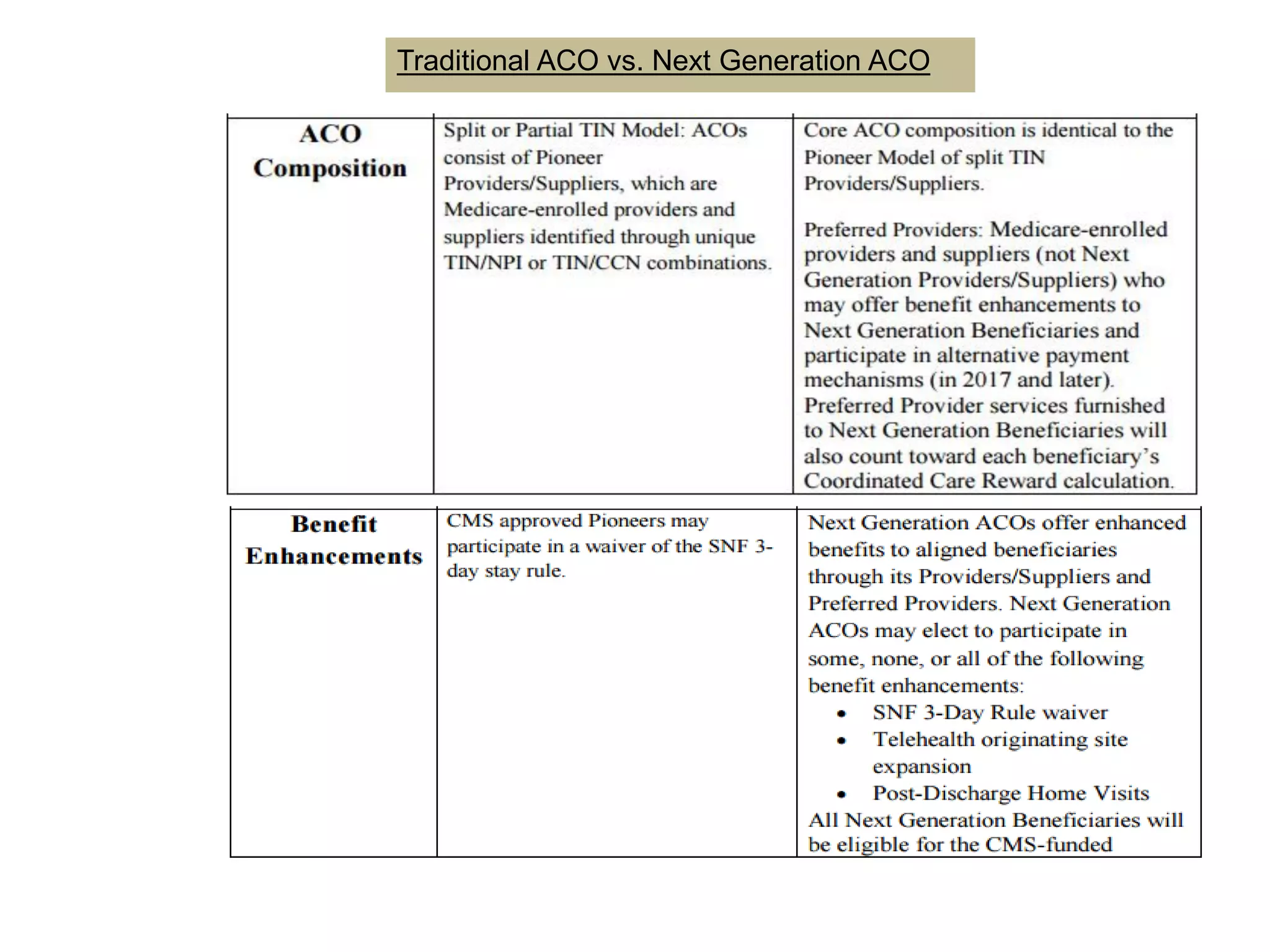
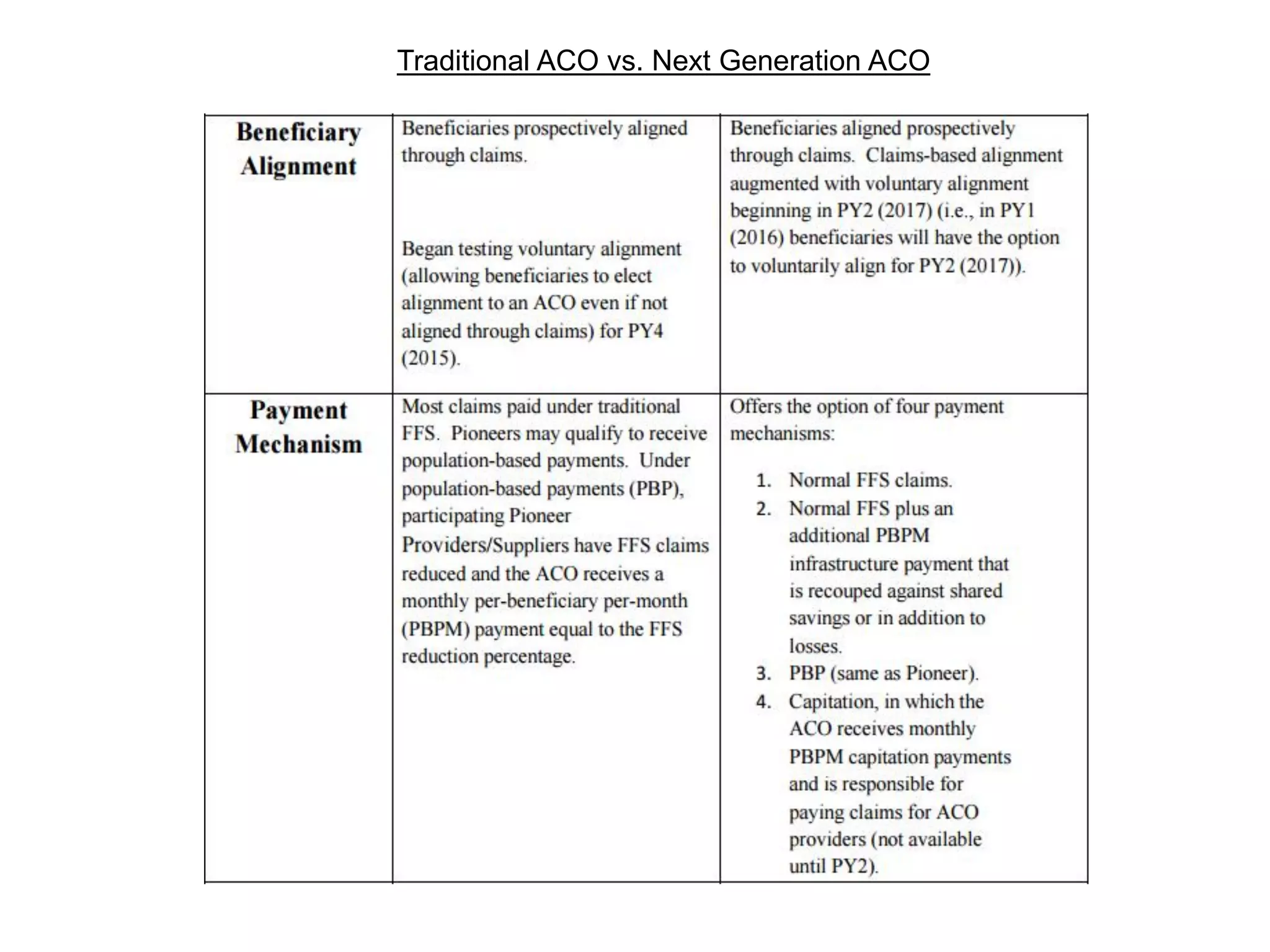
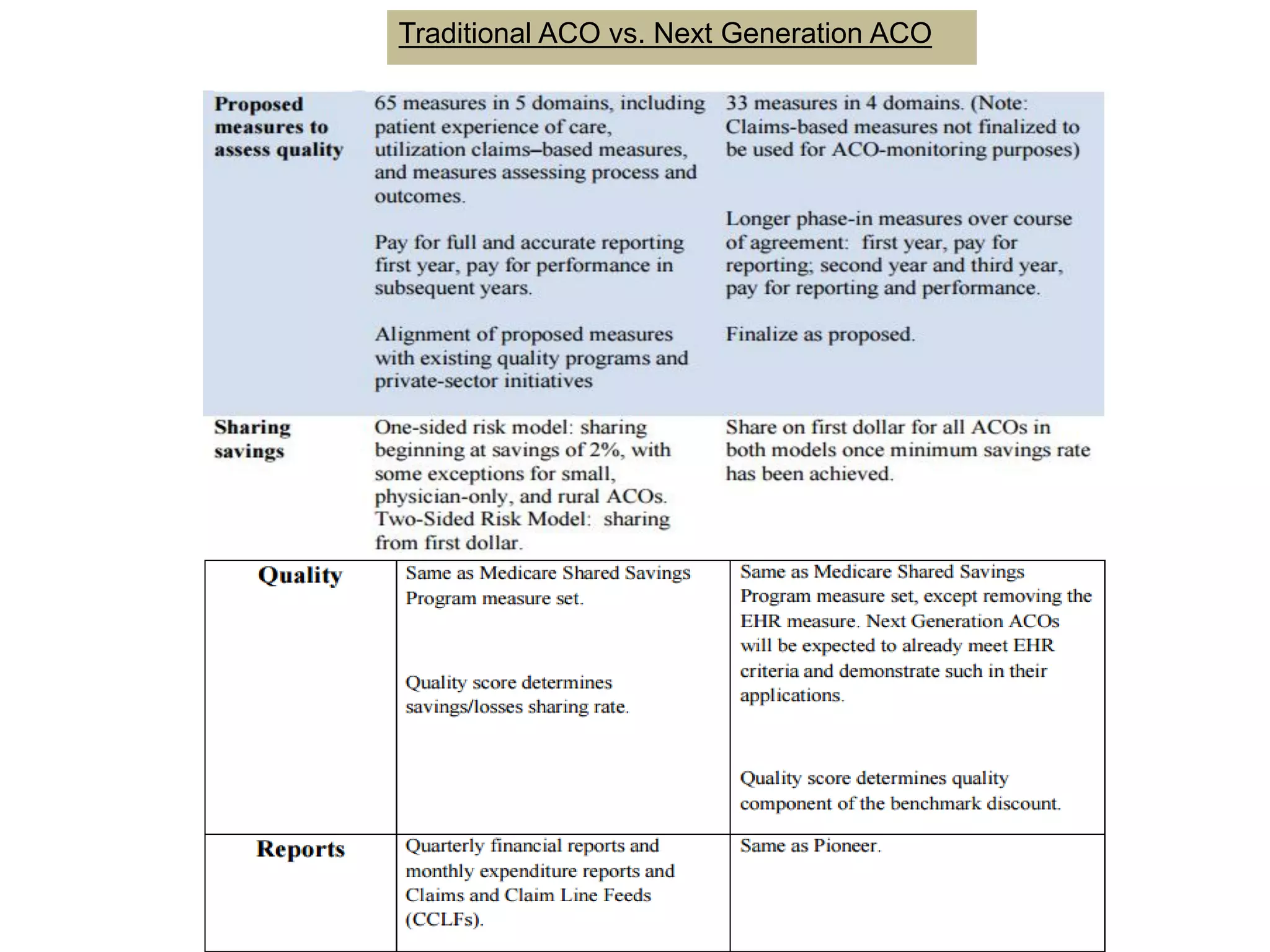
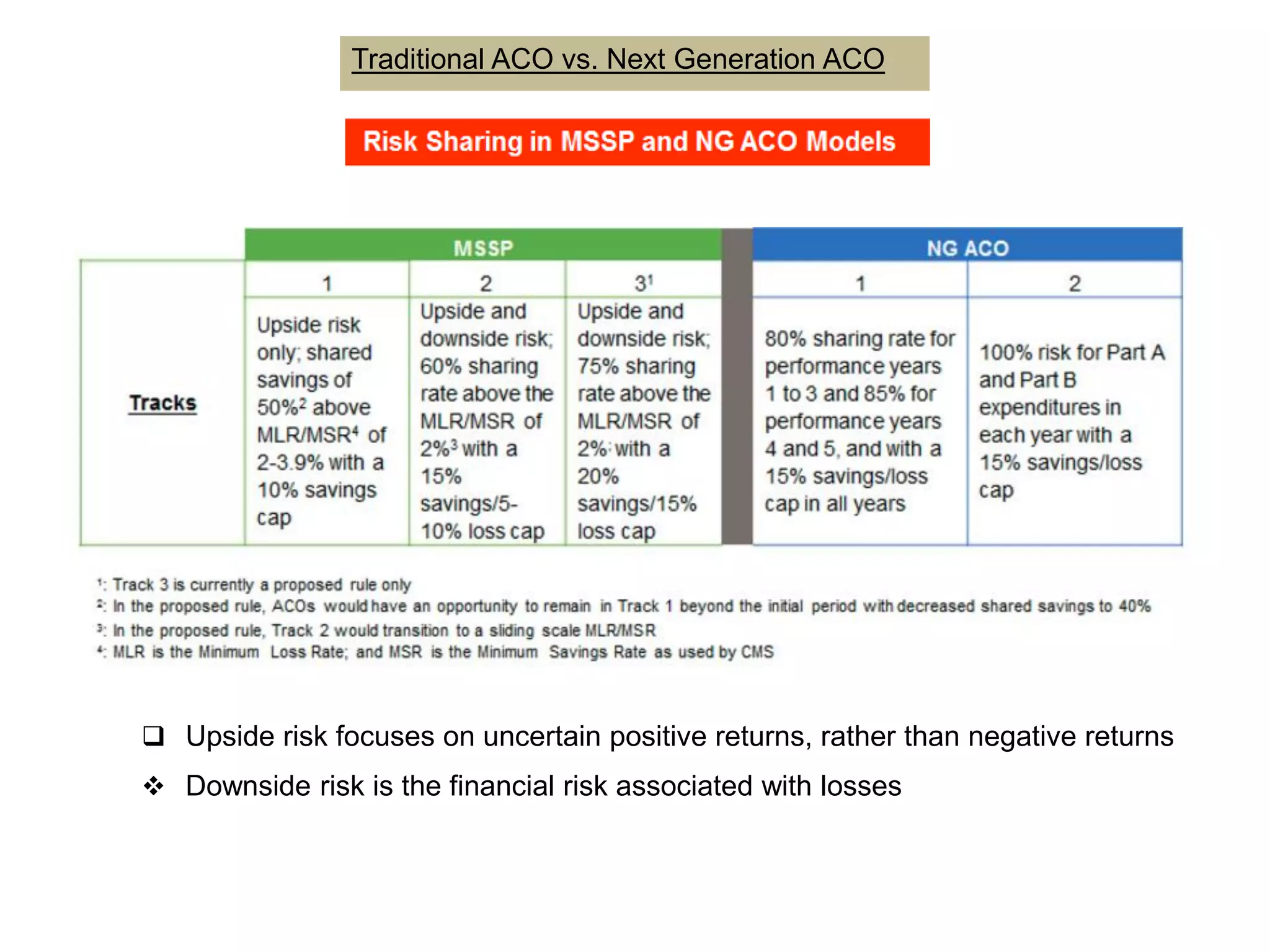
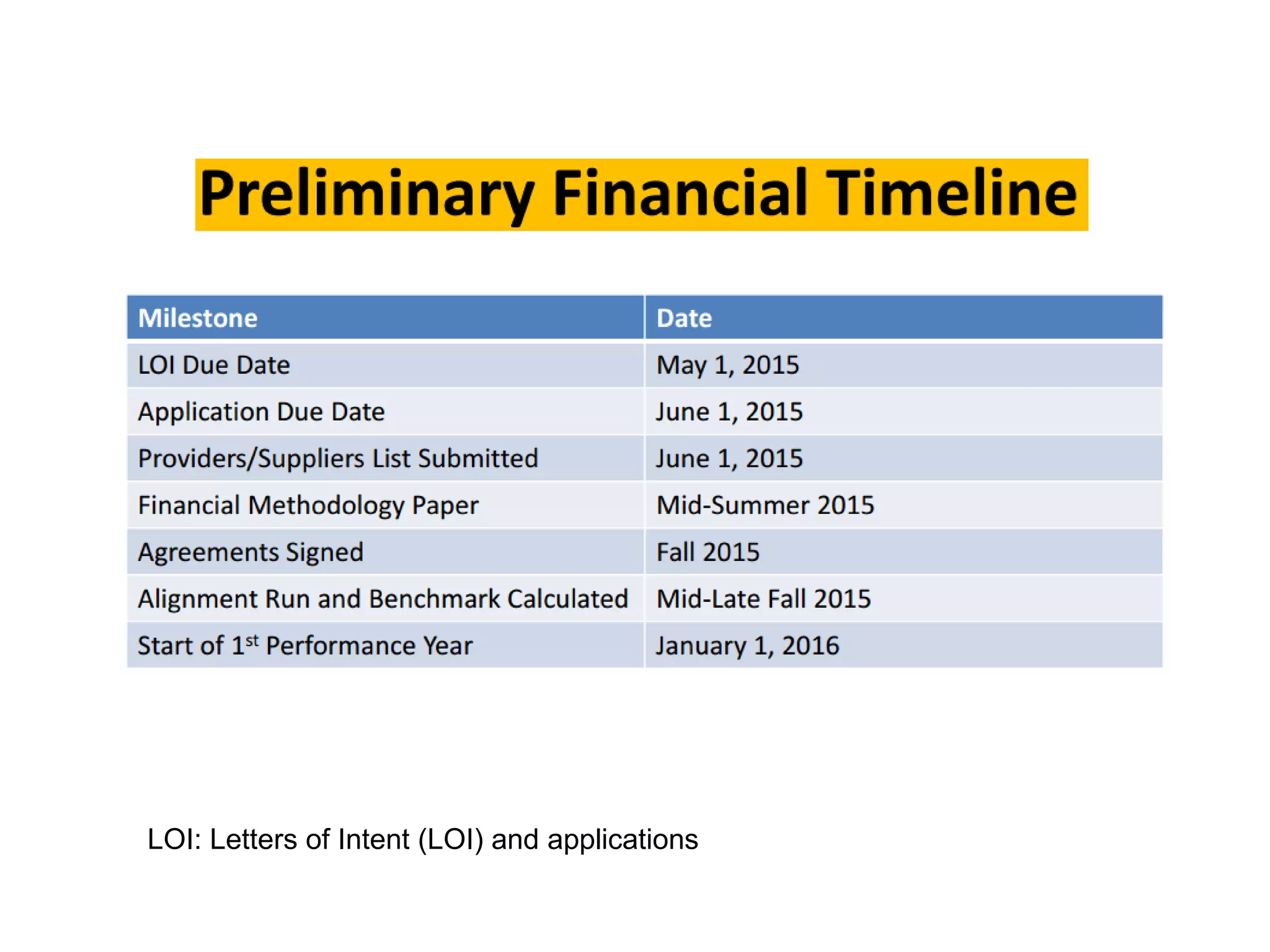
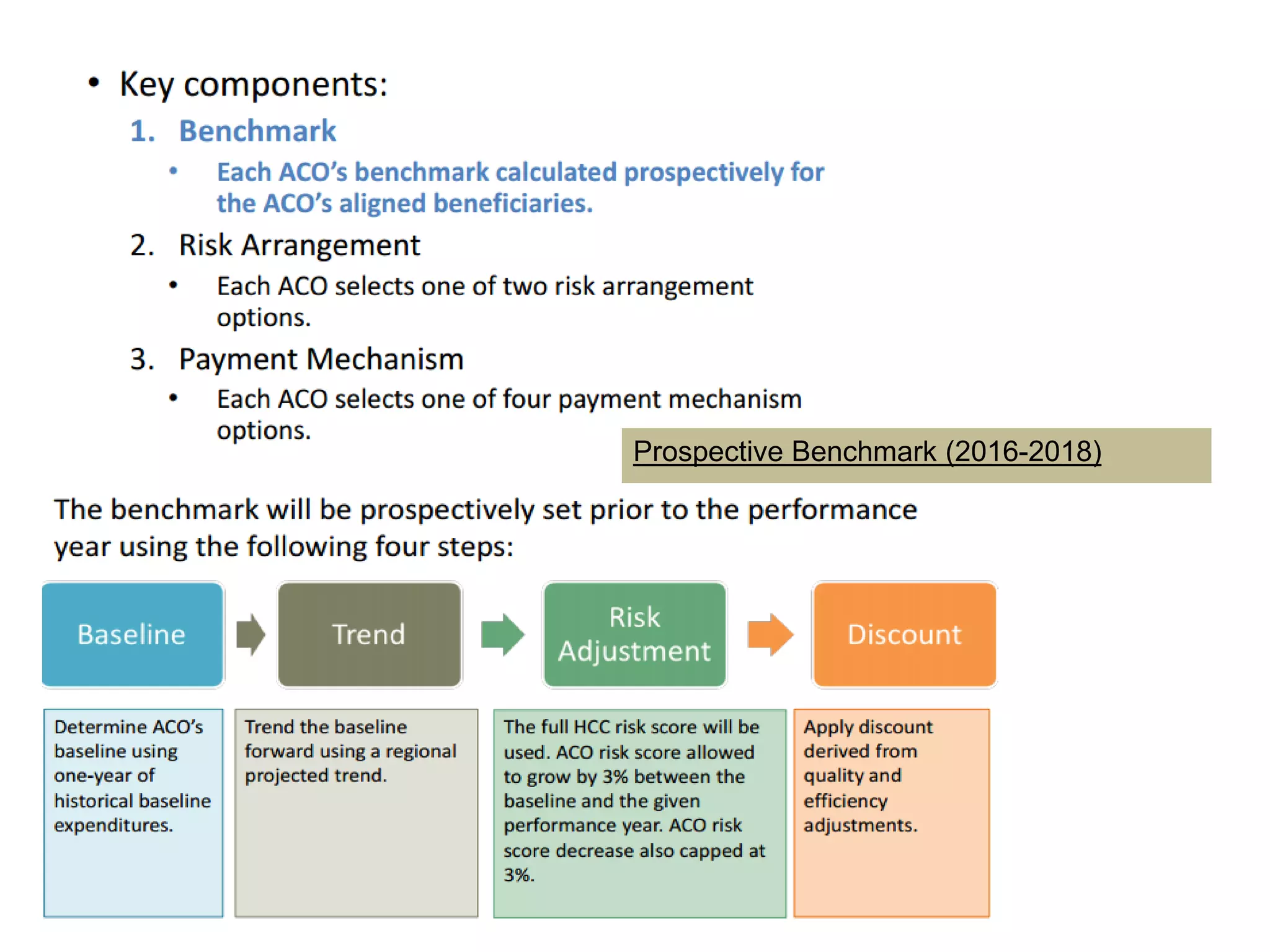
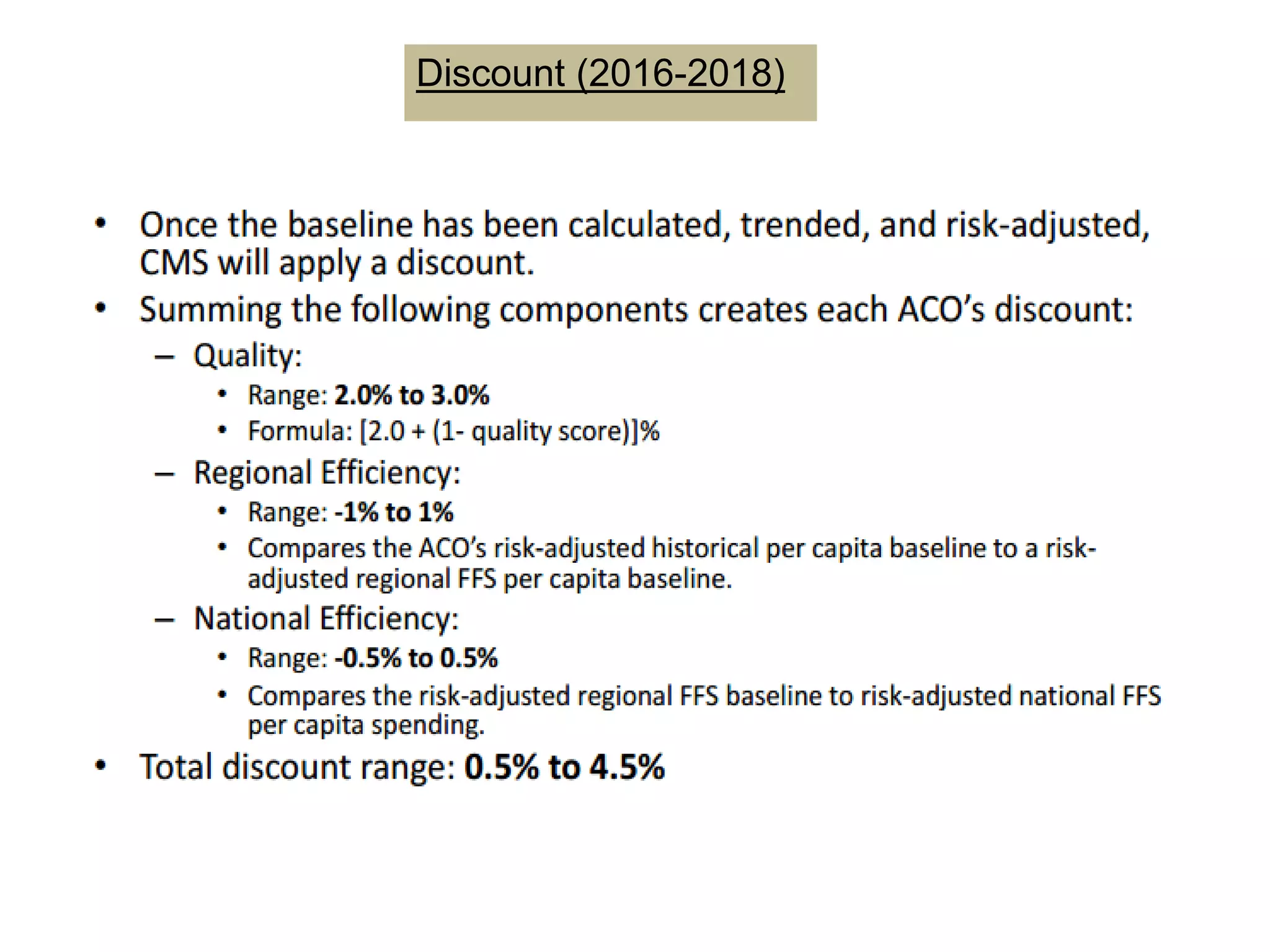
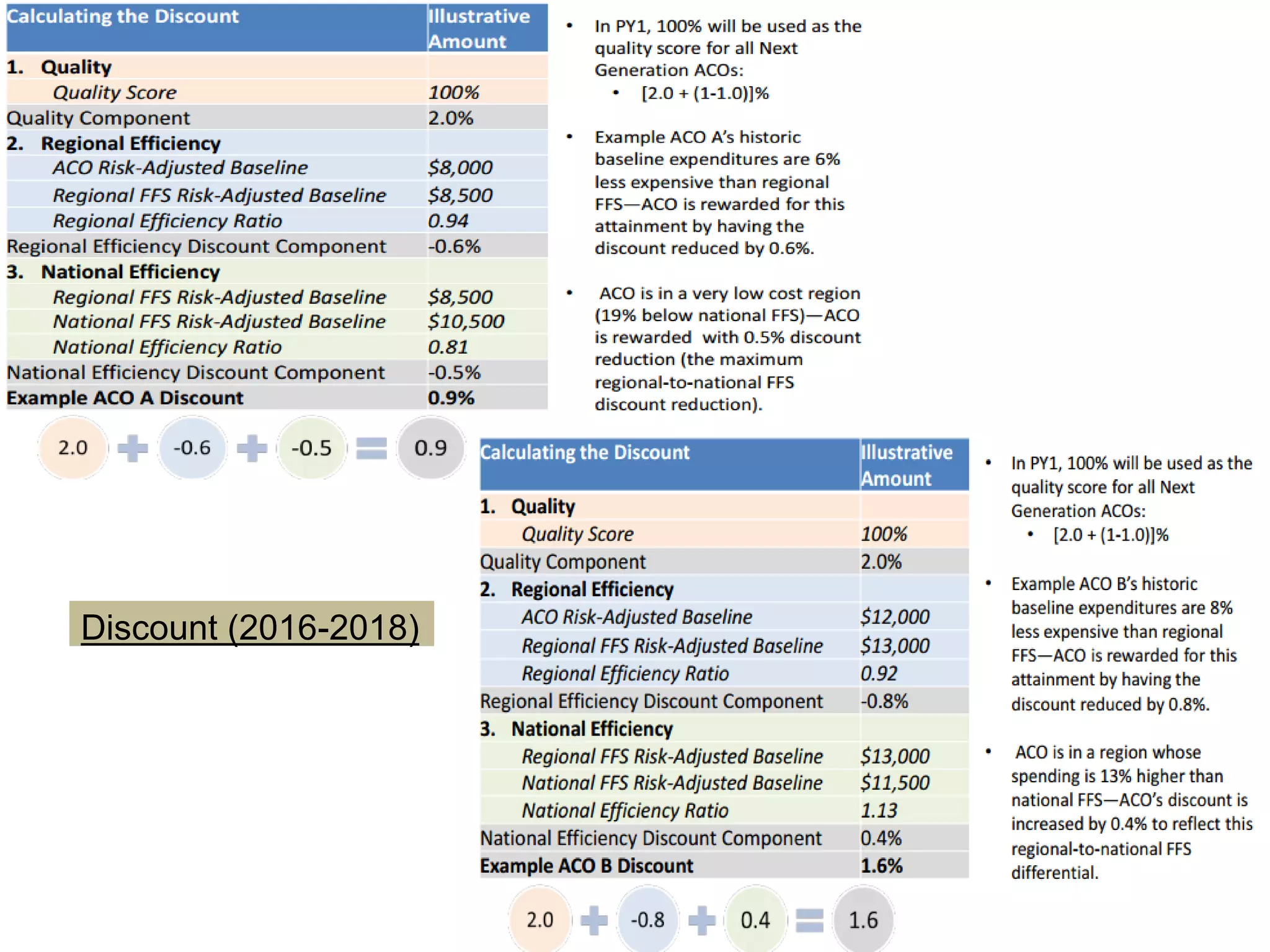
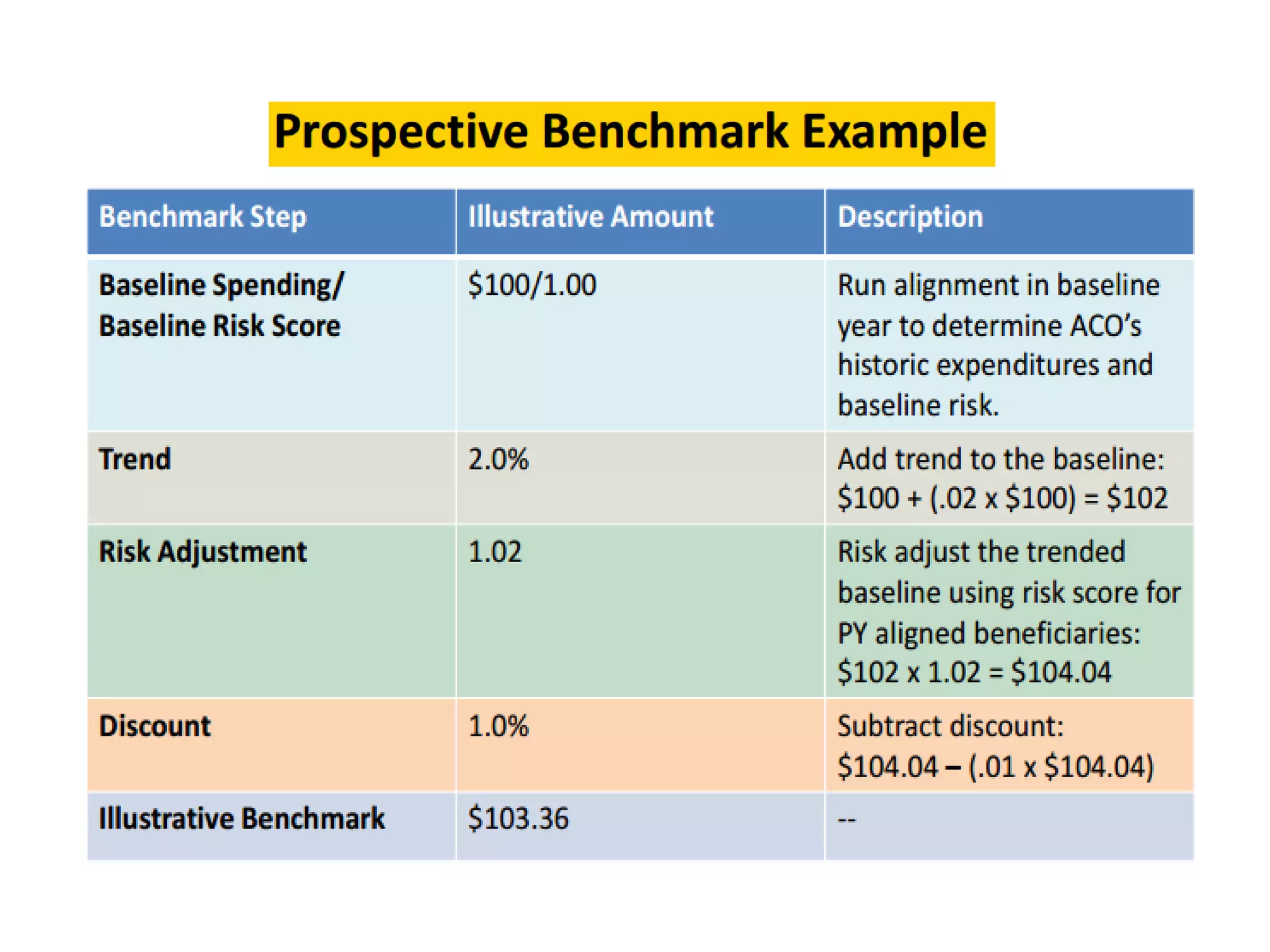
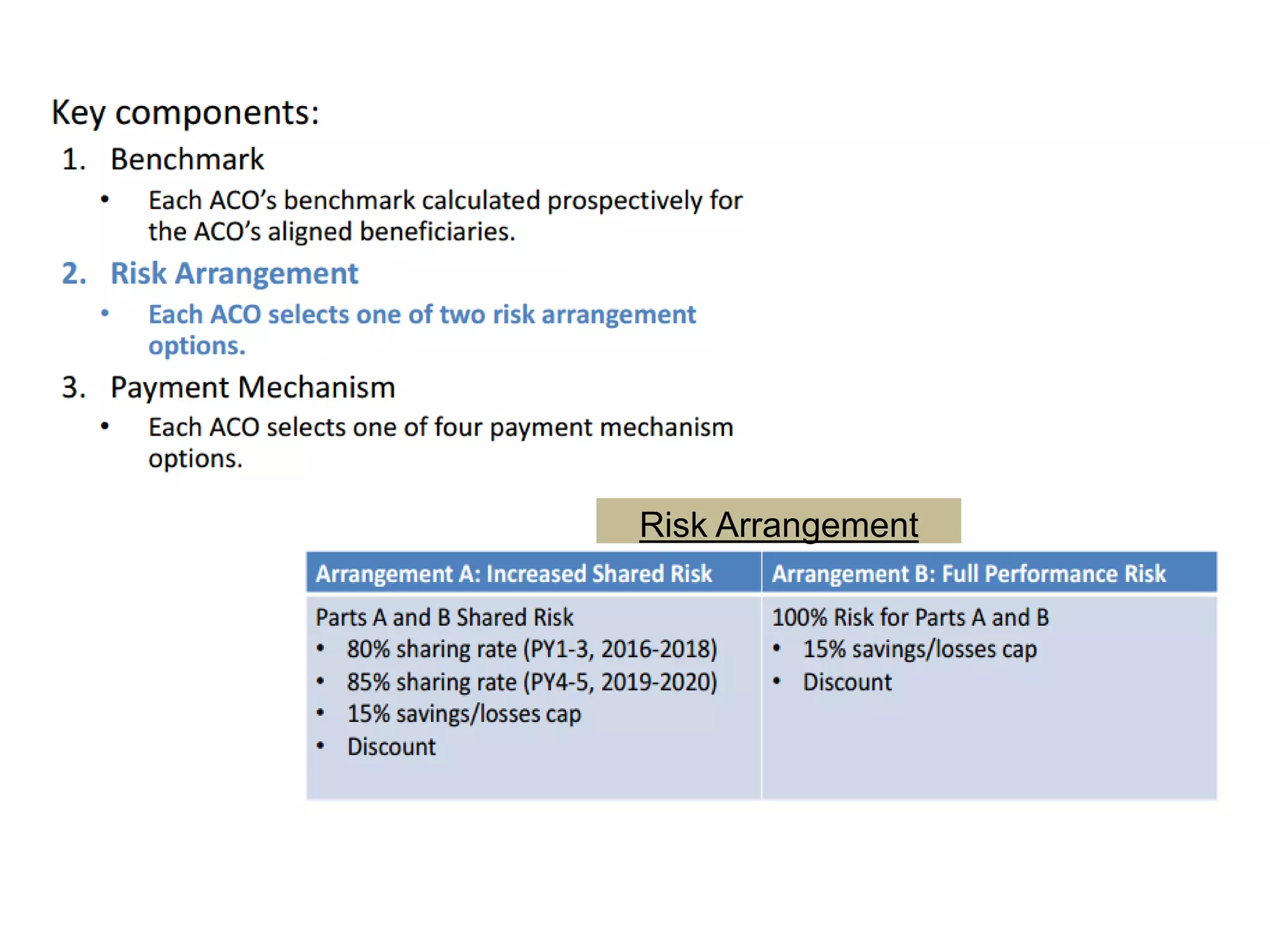
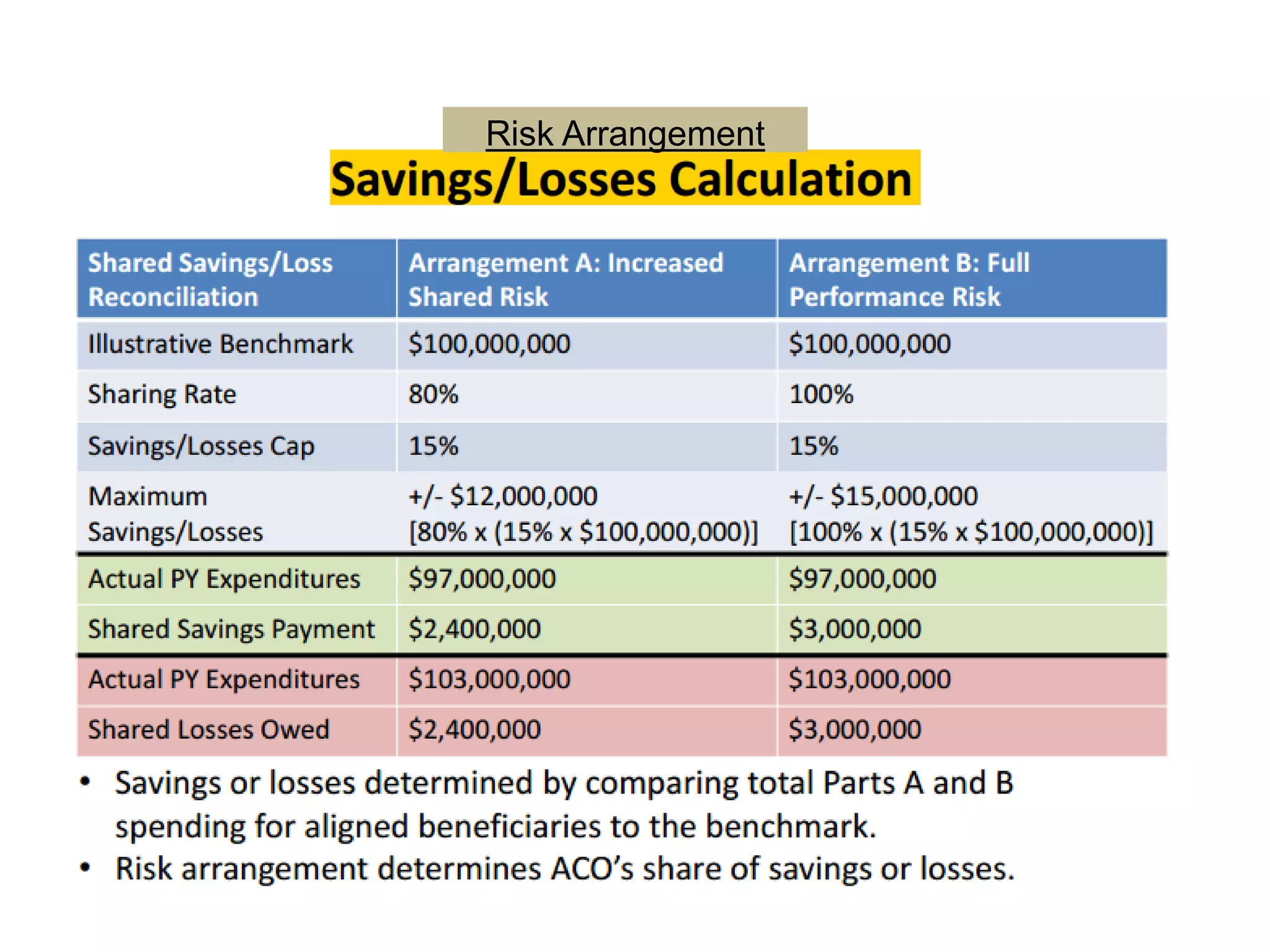
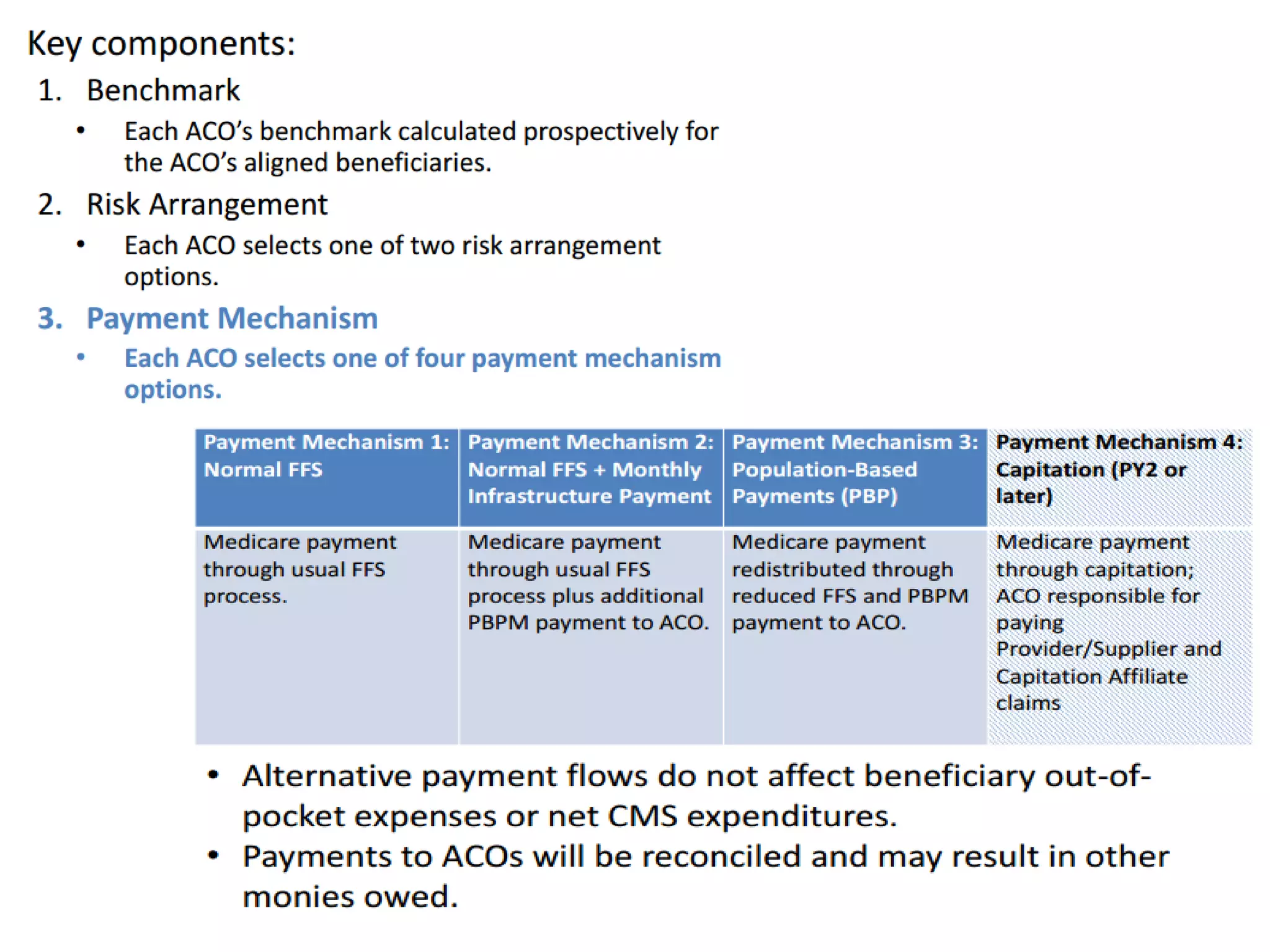
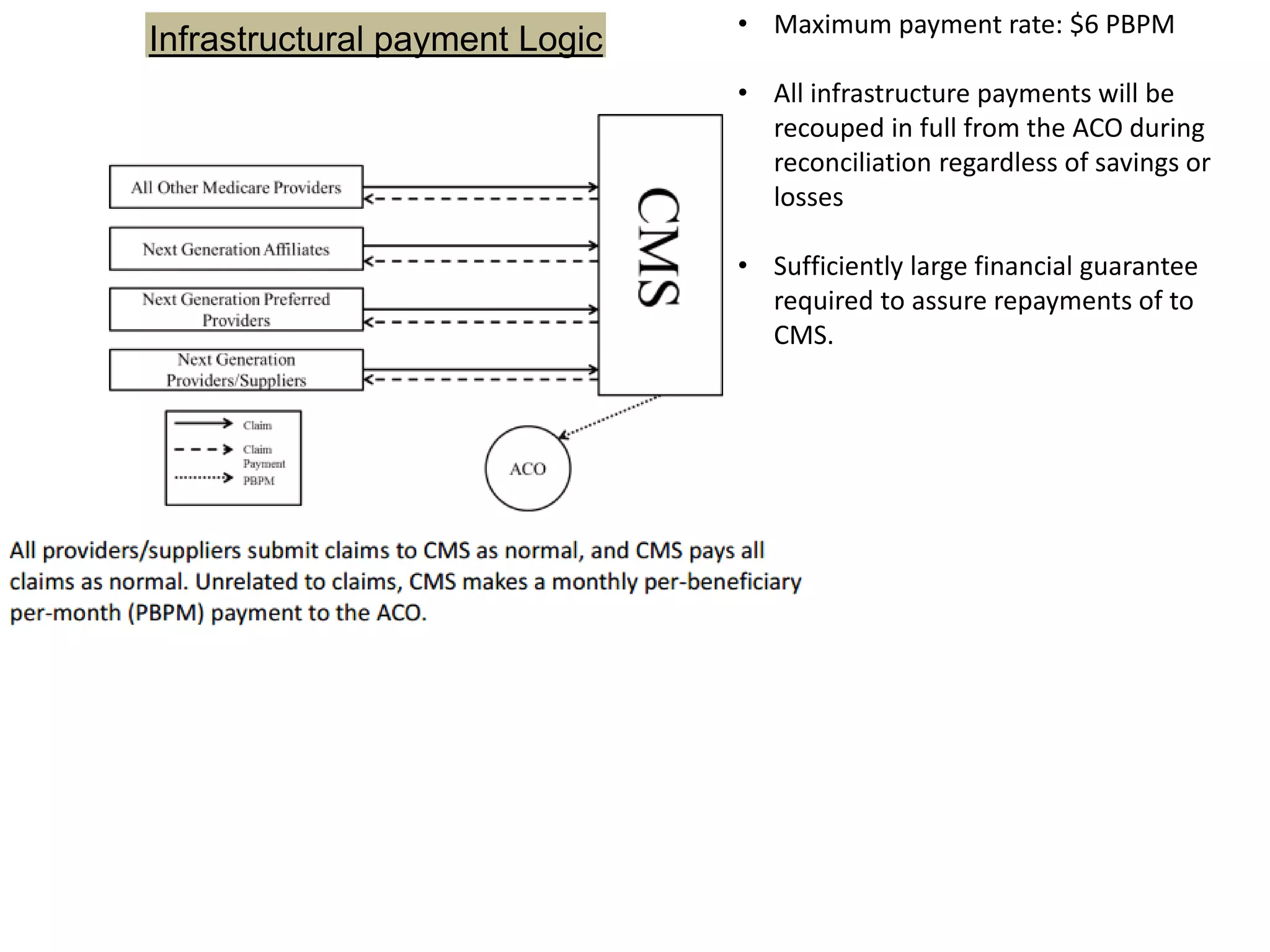
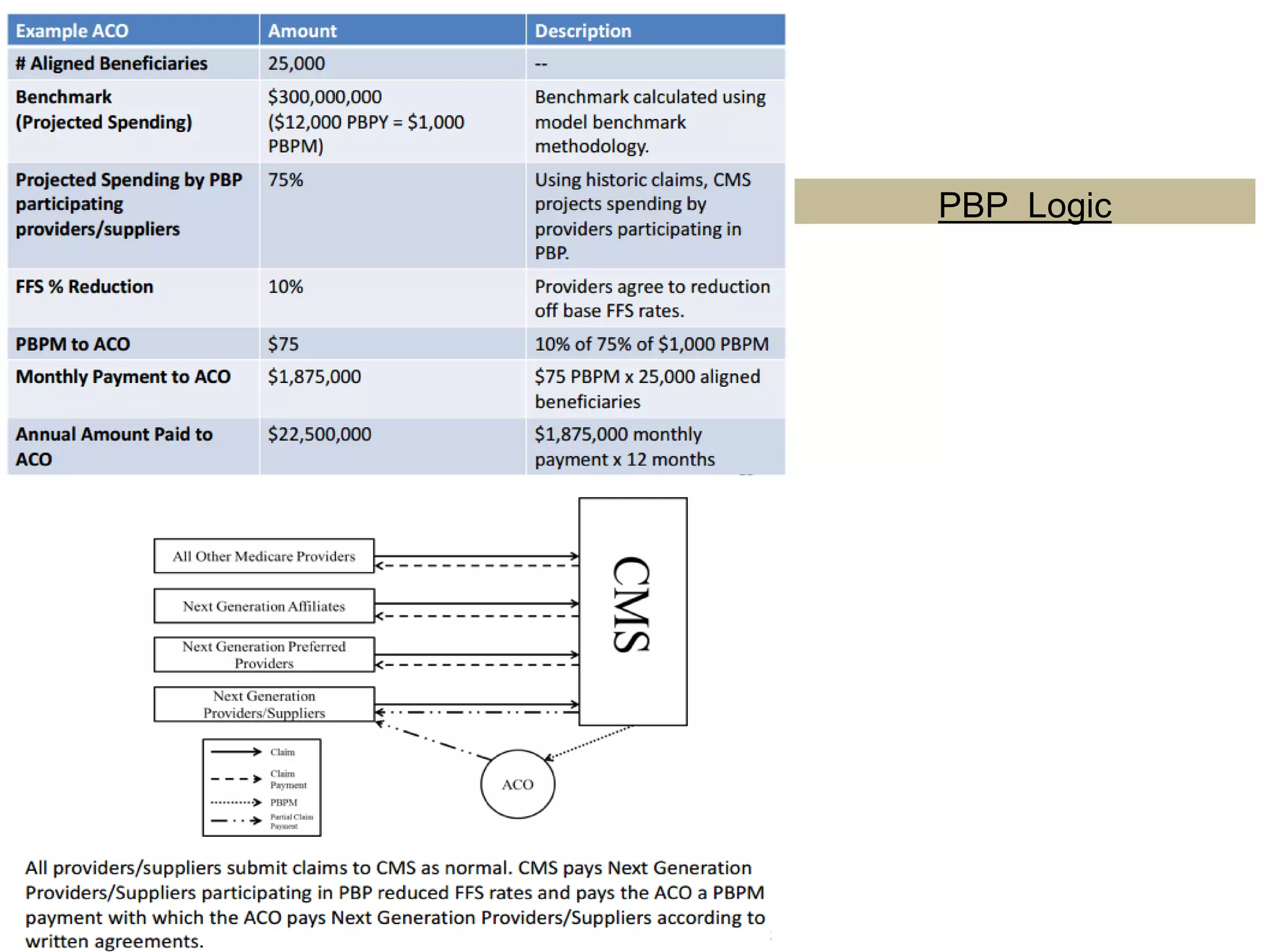
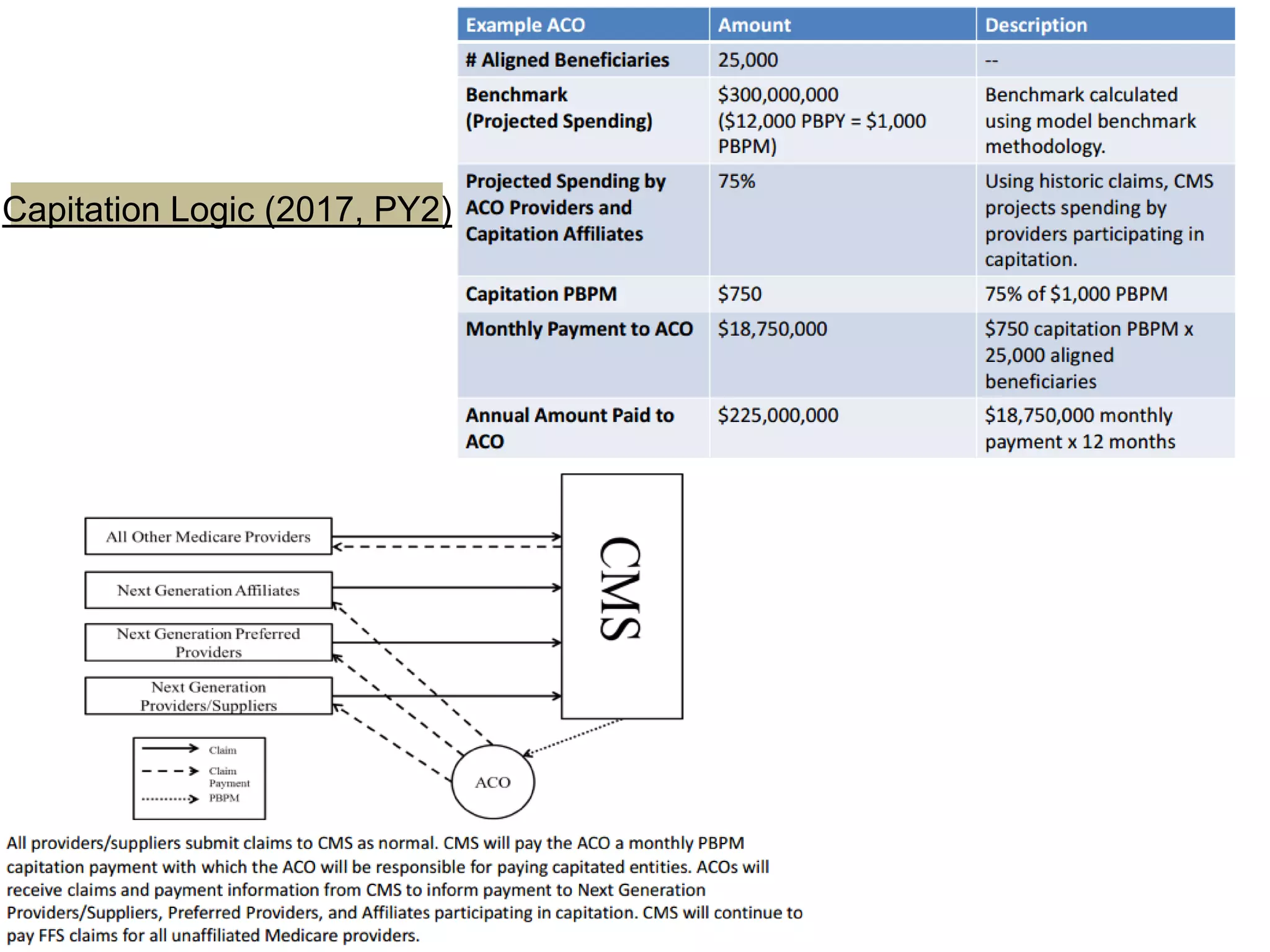
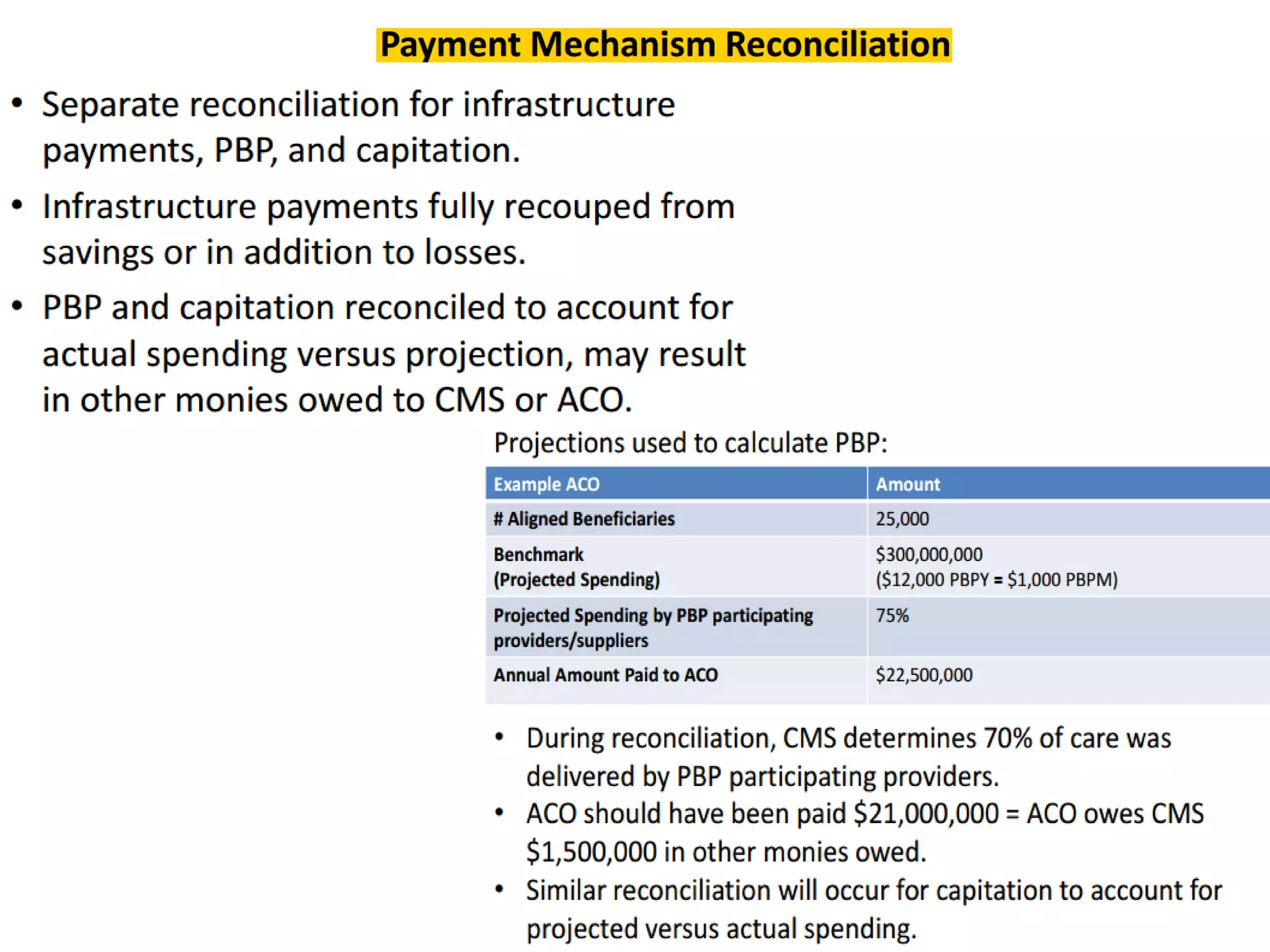
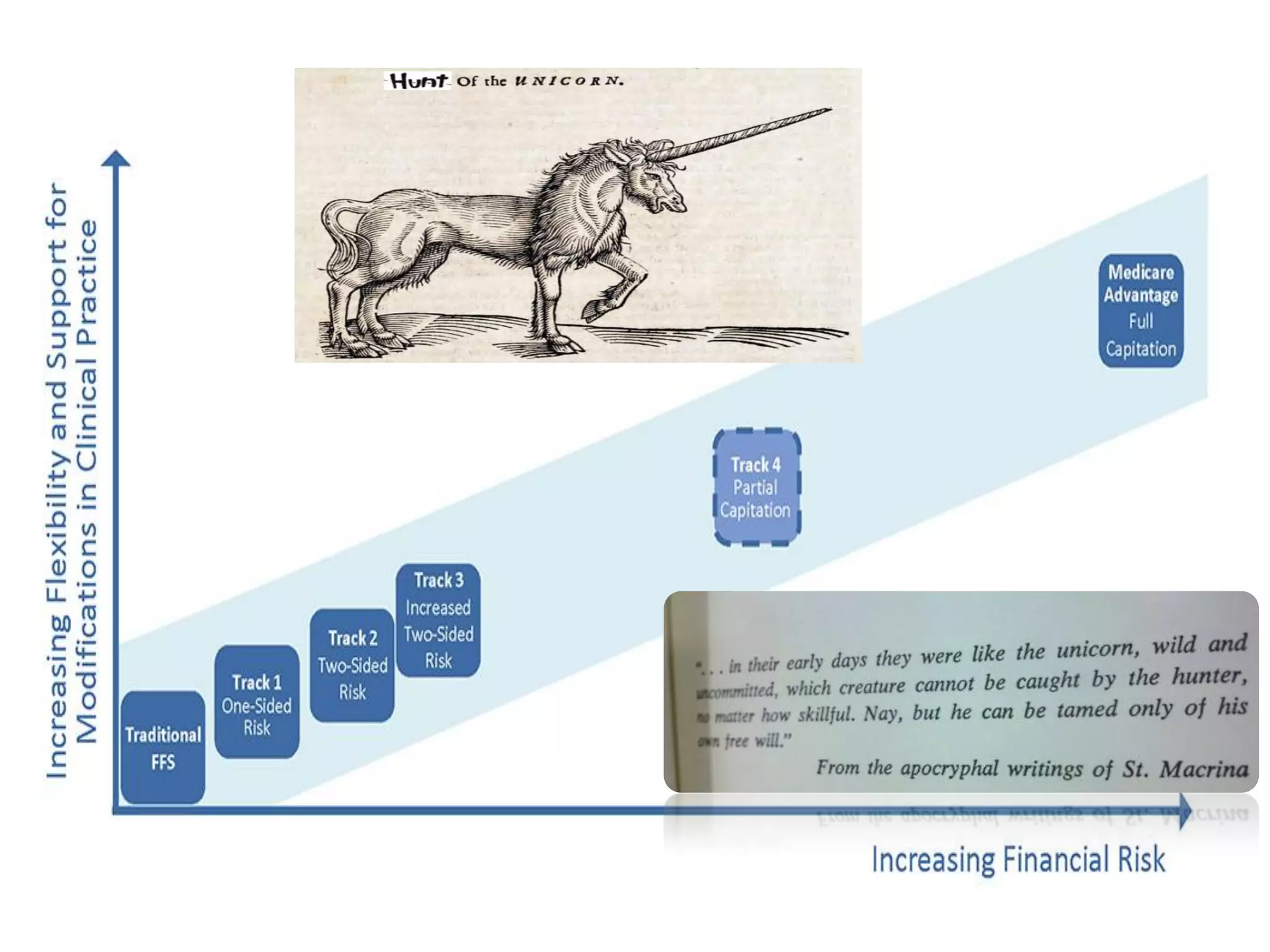
The document provides an overview and agenda for a presentation on Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) and the Next Generation ACO model. It discusses the background and objectives of ACOs, the purpose and components of the Next Generation ACO model, comparisons between traditional and Next Generation ACOs, financial timelines and calculations, risk arrangements, payment mechanisms, and conceptual diagrams. Contact information is provided for follow up.