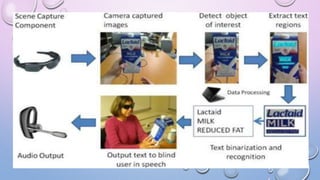
This document proposes a portable camera-based system to assist blind persons in reading text labels on products. The system uses a camera to capture images of objects held by the user, detects the region of interest containing text, recognizes the text using OCR, and outputs the text verbally to the user. It aims to enhance independent living for the blind by allowing them to identify product labels and packages. Future work includes improving text localization for various text orientations and sizes and enhancing the user interface.














![ World Health Organization. (2013). 10 facts about blindness and visual
impairment [Online]. Available:
www.who.int/features/factfiles/blindness/blindness_facts/en/index.html[28]
C. Stauffer and W. E. L. Grim son, “Adaptive background mixture models
for real-time tracking,” presented at the IEEE Computer. Soc. Conf.Comput.
Vision Pattern Recognition., Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5a3-150308030416-conversion-gate01/85/New-Technology-16-320.jpg)

