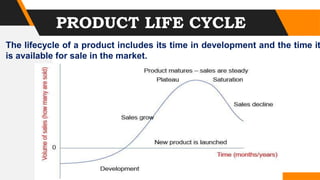
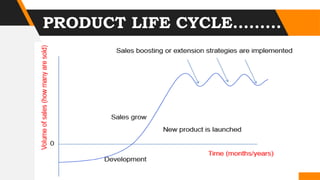
This document outlines the steps in the product development process, including idea generation, concept development and testing, market strategy development, business analysis, product development, market testing, and commercialization. It discusses reasons for new product development like health issues, environmental concerns, convenience, and technological advances. It also covers consumer surveys, advertising effects, product life cycles, and strategies to boost sales at different stages of the cycle. Developing new products is important for business survival and maintaining a competitive advantage.