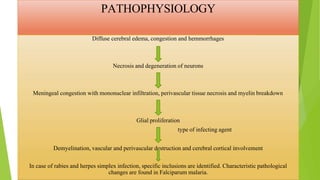
Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain that is usually caused by a viral infection. It can cause symptoms like fever, headache, vomiting, and confusion. While most cases are mild, encephalitis can sometimes be life-threatening. The document discusses the types, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of encephalitis.