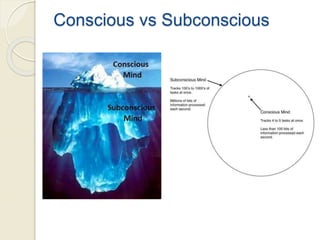
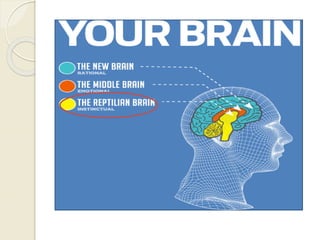
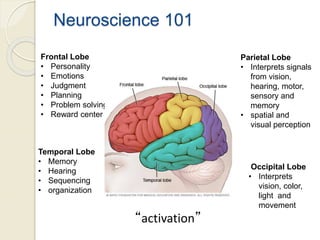
The document discusses neuromarketing, where neuroscience intersects with marketing, covering how brain functions influence consumer behavior. It highlights various brain regions involved in decision-making and provides examples of neuromarketing applications and tools like EEG and fMRI to measure consumer responses. The text concludes by emphasizing the importance of appealing to the 'reptilian brain' for effective marketing strategies.