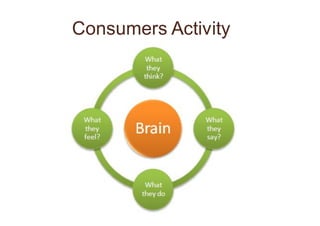
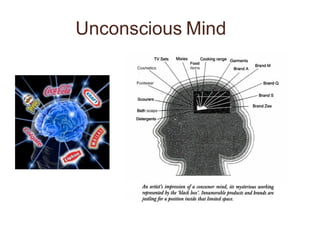
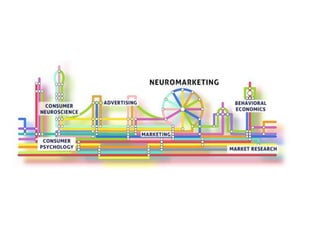
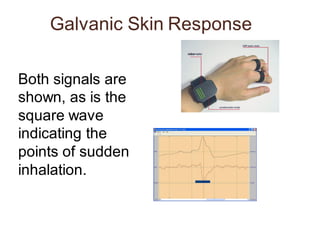
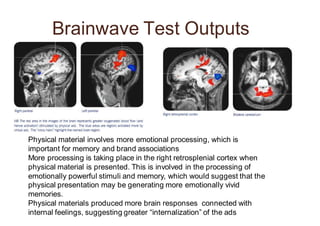
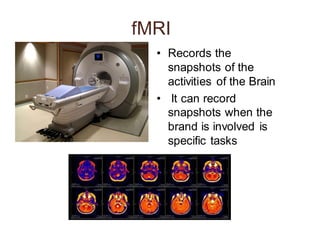
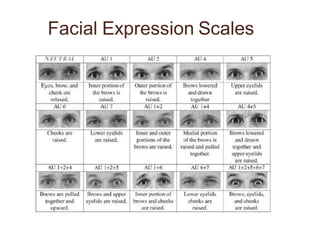
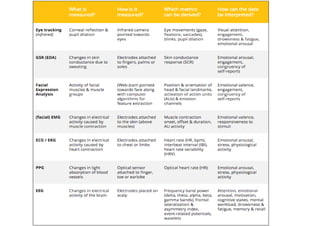
Neuromarketing uses tools from neuroscience like EEG, fMRI, eye tracking and analysis of facial expressions and physiological responses to understand consumers' unconscious emotional and cognitive responses to marketing. This helps optimize products, ads and shelf placement. Traditional methods like surveys are limited since consumers may not consciously understand their own preferences. Neuromarketing tools provide objective data on how the brain processes brands and marketing messages. This helps improve marketing effectiveness and reduce the high failure rate of new products and campaigns. As the field advances, it seeks to better understand cultural differences in how societies relate to marketing.