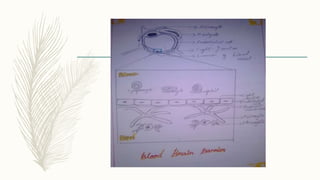
The document discusses the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and its key functions and characteristics. The BBB is formed by cerebral endothelial cells and limits molecular exchange between the blood and brain. It maintains homeostasis in the brain by regulating passage of substances like ions, nutrients, and toxins. Transport across the BBB occurs primarily through passive diffusion, carrier-mediated transport, and active transport mechanisms. The BBB and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier share similarities in selectively controlling molecular movement and protecting the brain microenvironment.






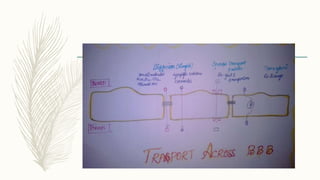


![Transport of macromolecules
alter[Mute].mp4
– Endocytic vesicles- proteins and peptides.
– Vesicular mechanisms-RMT or AMT- transport diverse large
molecules.
Steps involved in transport
1. Internalization
2. Exocytosis
3. Interaction
Peptide specific transporter-facilitate transport.
Function- signaling cascade.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neurochemistry-180123054426/85/Neurochemistry-13-320.jpg)


