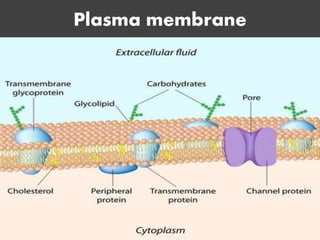
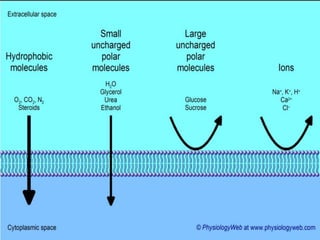
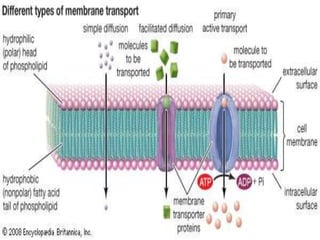
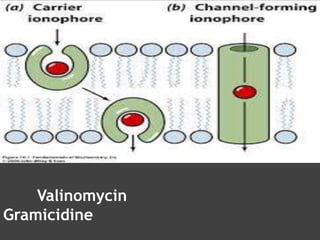
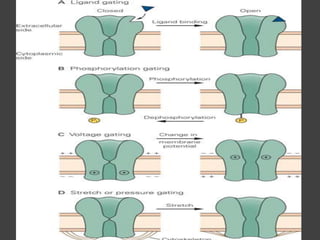
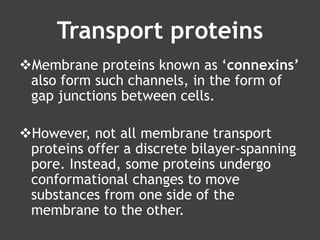
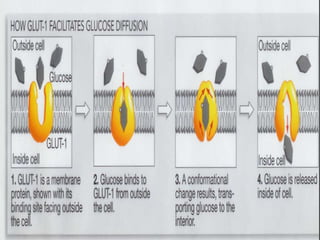
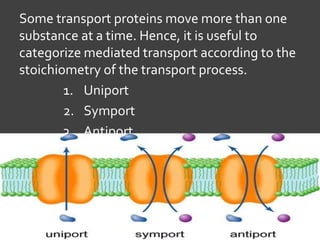
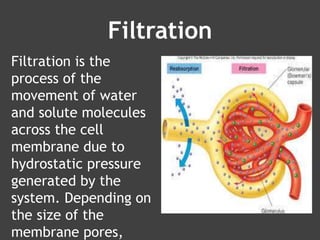
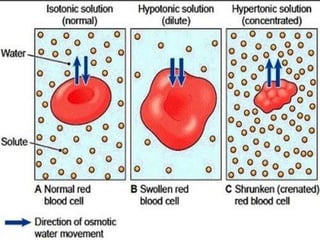
The document discusses various mechanisms of membrane transport, including passive transport, ionophores, porins, ion channels, aquaporins, transport proteins, filtration, and osmosis. Passive transport uses integral membrane proteins to transport larger molecules across cell membranes without energy. Ionophores increase membrane permeability to ions and can exert antibiotic effects. Porins form water-filled pores to transport molecules. Ion channels allow rapid ion passage. Aquaporins transport water and small solutes. Transport proteins may form channels or undergo conformational changes. Filtration and osmosis move water and solutes across membranes.
![James Danielle
(1911-1984)
Cell Membrane
“Possibly the decisive step
the origin of life] was the
formation of the first cell,
which chain molecules
enclosed by a
membrane which kept
together but let their food](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/membranetransport-181020083443/85/Membrane-transport-Passive-mediated-2-320.jpg)