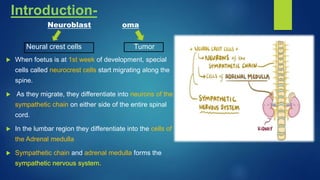
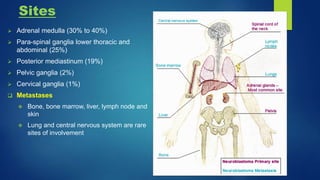
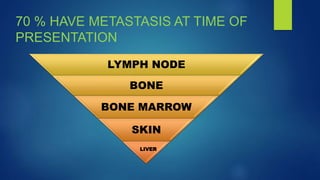
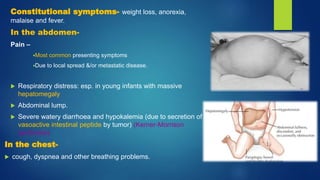
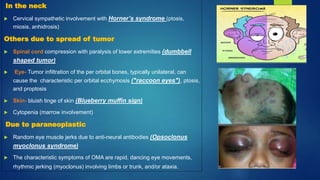
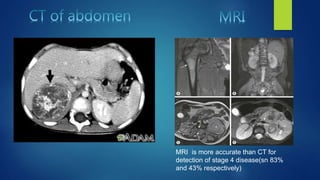
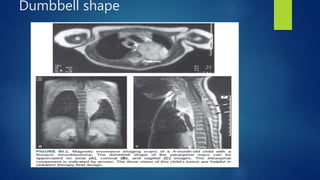
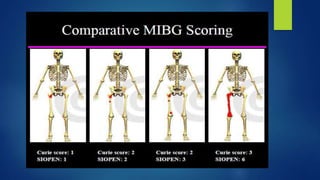
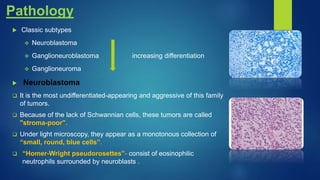
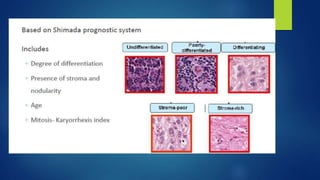
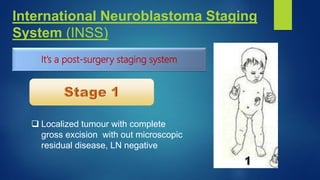
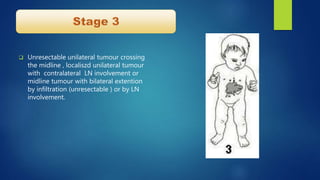
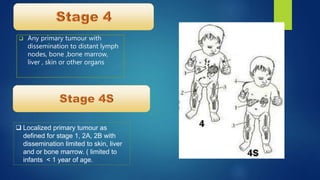
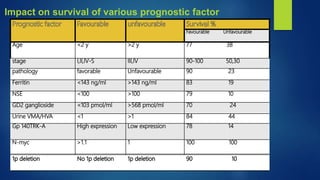
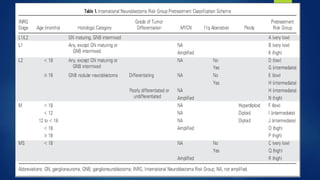
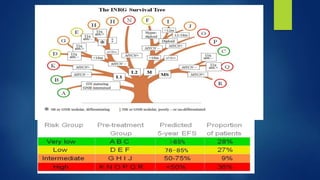
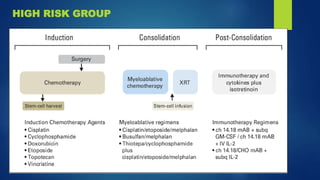
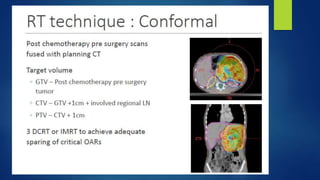
The document provides information on neuroblastoma, including its origin from neural crest cells, sites of occurrence, clinical presentation, diagnosis, staging systems, prognostic factors, and management. It notes that neuroblastoma is the most common extracranial solid tumor in children and occurs most often in children under 5 years old. The diagnosis involves imaging tests like CT/MRI to identify the primary tumor and metastases, biopsy for histopathological examination, and urine and bone marrow tests. Staging systems include the International Neuroblastoma Staging System and International Neuroblastoma Risk Group system. Prognostic factors include the child's age, tumor biology markers like MYCN amplification, and response to initial treatment. Management involves surgery, chemotherapy,