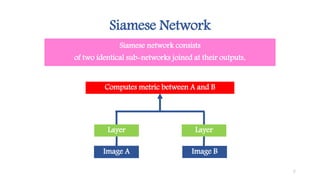
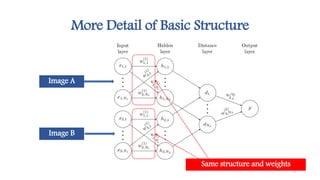
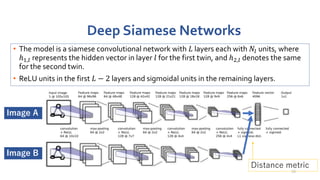
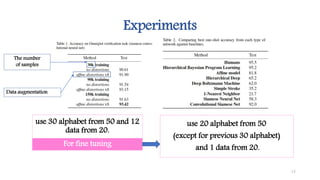
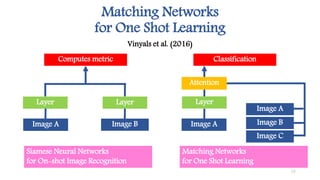
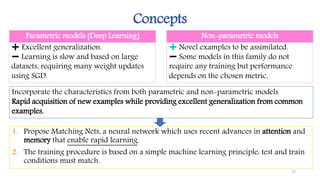
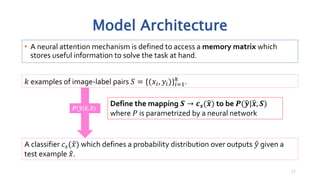
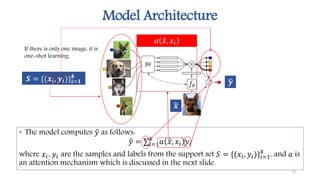
This document discusses methods for one-shot learning using siamese neural networks. It provides an overview of several key papers in this area, including using siamese networks for signature verification (1993) and one-shot image recognition (2015), and introducing matching networks for one-shot learning (2016). Matching networks incorporate an attention mechanism into a neural network to rapidly learn from small datasets by matching training and test conditions. The document also reviews experiments demonstrating one-shot and few-shot learning on datasets like Omniglot using these siamese and matching network approaches.








![𝐿: Possible label sets
• 𝐿 could be the label set {𝑐𝑎𝑡𝑠, 𝑑𝑜𝑔𝑠}.
𝑇: Distribution over 𝐿.This is the train data.
1. Sample 𝐿 from 𝑇.
2. Sample 𝑆 and 𝐵 from 𝐿.
3. Minimize the error predicting the labels in the batch 𝐵 conditioned on the
support set 𝑆.
Definition
Learning Step
Objective Function
𝜃 = arg max 𝜃 𝔼 𝐿∼𝑇[𝔼 𝑆∼𝐿,𝐵∼𝐿[
𝑥,𝑦 ∈𝐵
log 𝑃 𝜃 𝑦 𝑥, 𝑆 ]]
Simulate the task of one shot learning only from train data.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralnetorksmatching-180720053054/85/Neural-netorksmatching-20-320.jpg)
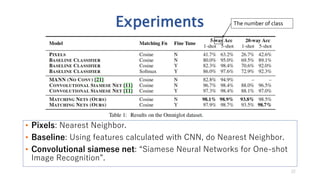
![Experiments
N-way k-shot learning
• Pick 𝑁 unseen character classes, independent of alphabet, as
𝐿.
• Provide the model with one drawing of each of the 𝑁
characters as 𝑆~𝐿 and a batch 𝐵~𝐿.
21
𝜃 = arg max 𝜃 𝔼 𝐿∼𝑇[𝔼 𝑆∼𝐿,𝐵∼𝐿[
𝑥,𝑦 ∈𝐵
log 𝑃 𝜃 𝑦 𝑥, 𝑆 ]]
Objective Function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralnetorksmatching-180720053054/85/Neural-netorksmatching-21-320.jpg)