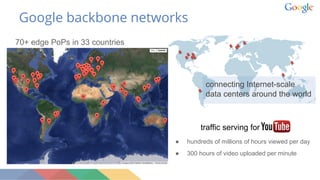
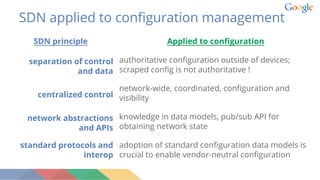
This document discusses bringing SDN principles to network management planes at scale. It outlines challenges of managing large networks including multiple vendors, high configuration changes, and lack of visibility. It proposes applying SDN concepts like centralized control, network abstractions, and standard protocols. The document advocates for model-driven network management using standardized configuration and telemetry models like OpenConfig, which is an industry collaboration to define vendor-neutral models. It describes an intent-based configuration flow using these models and streaming telemetry for network visibility.