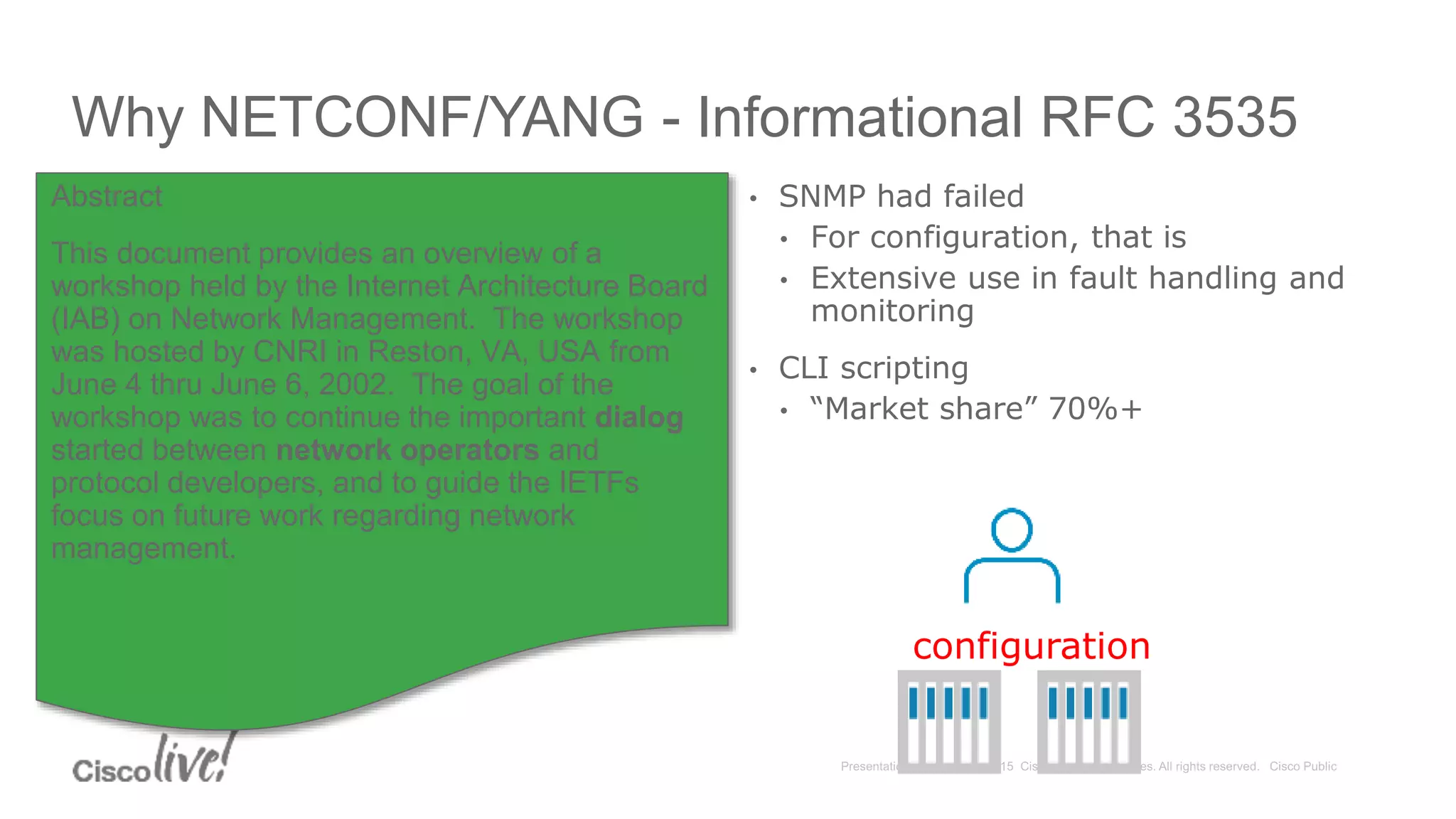
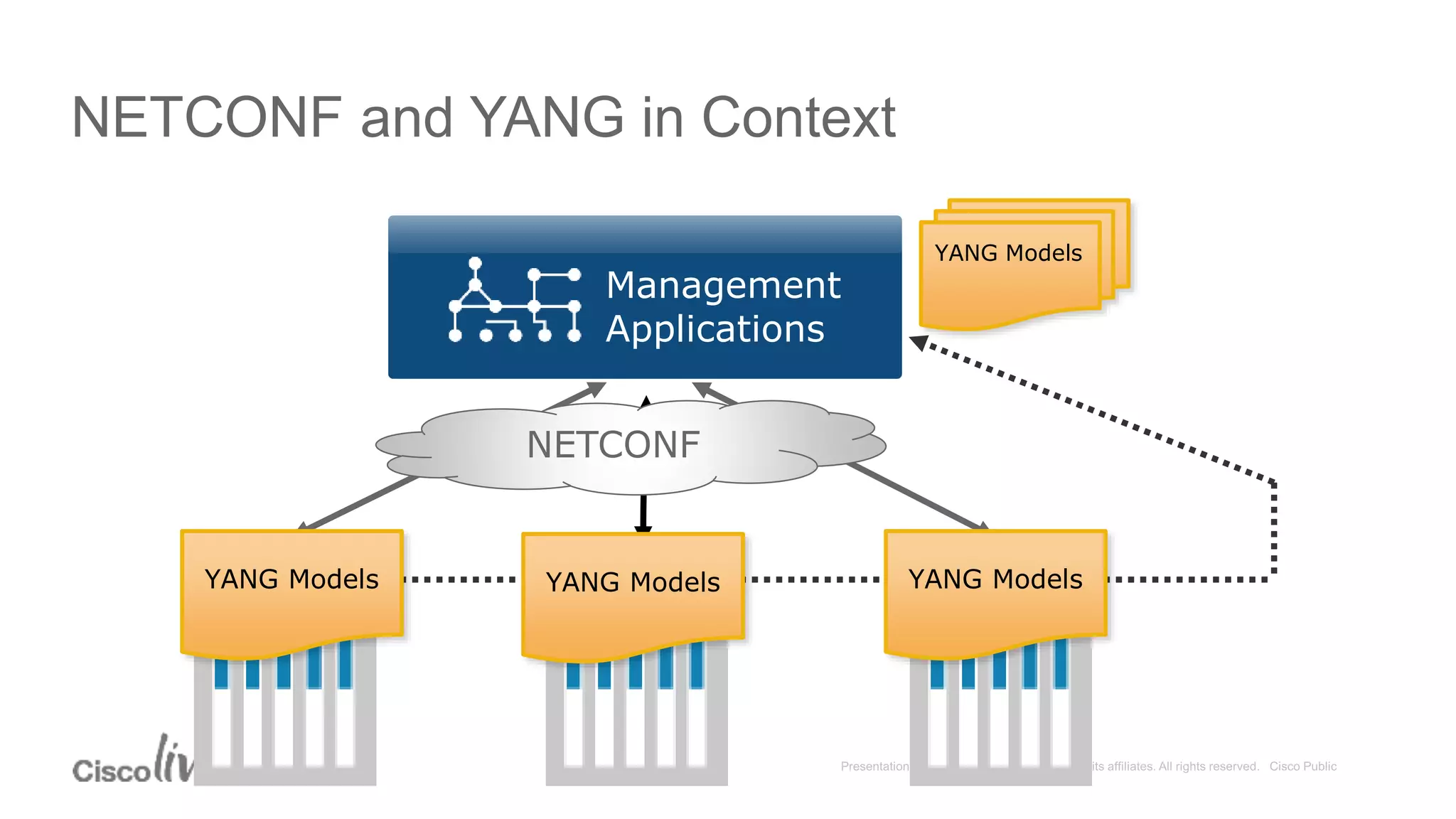
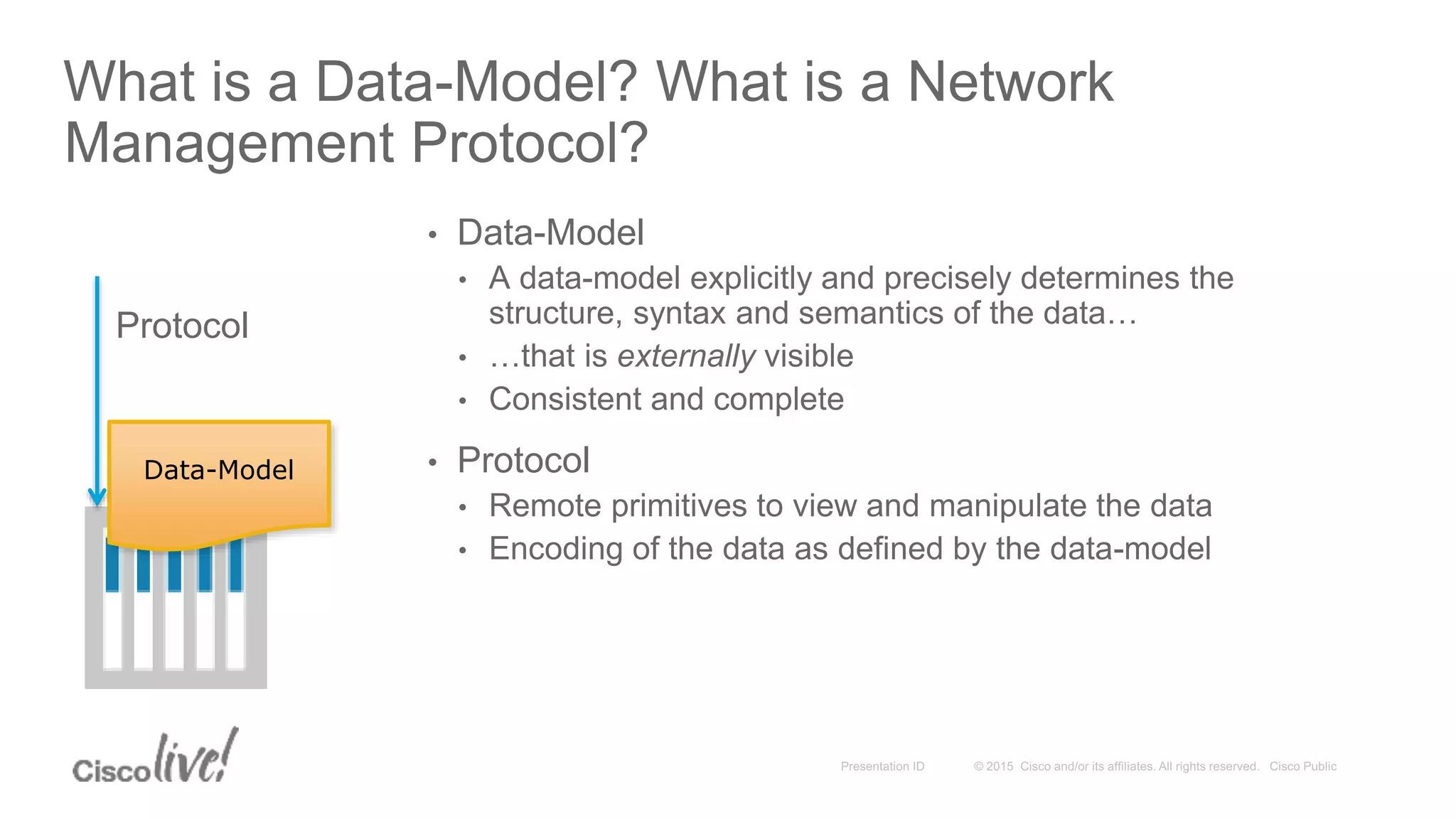
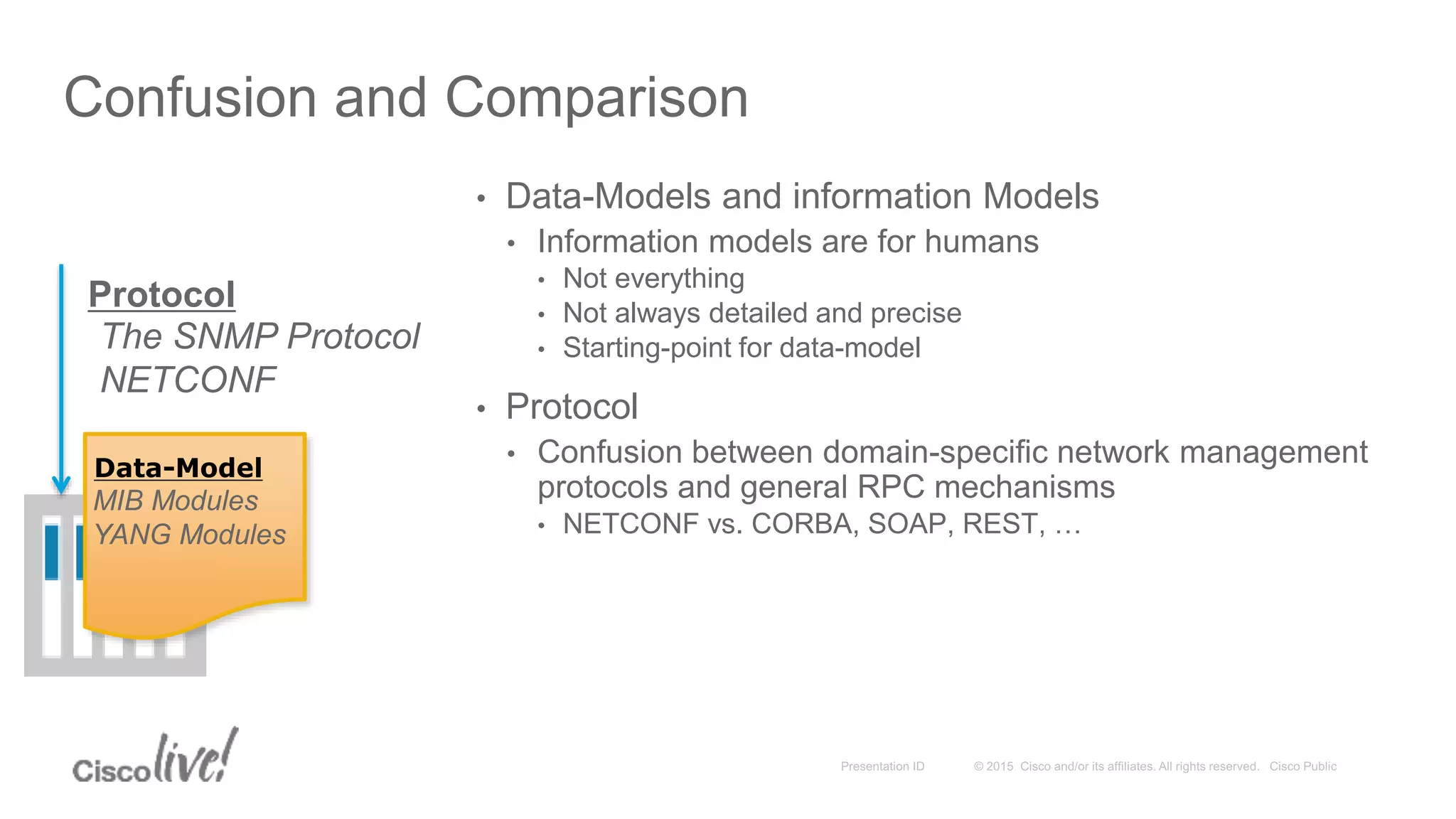
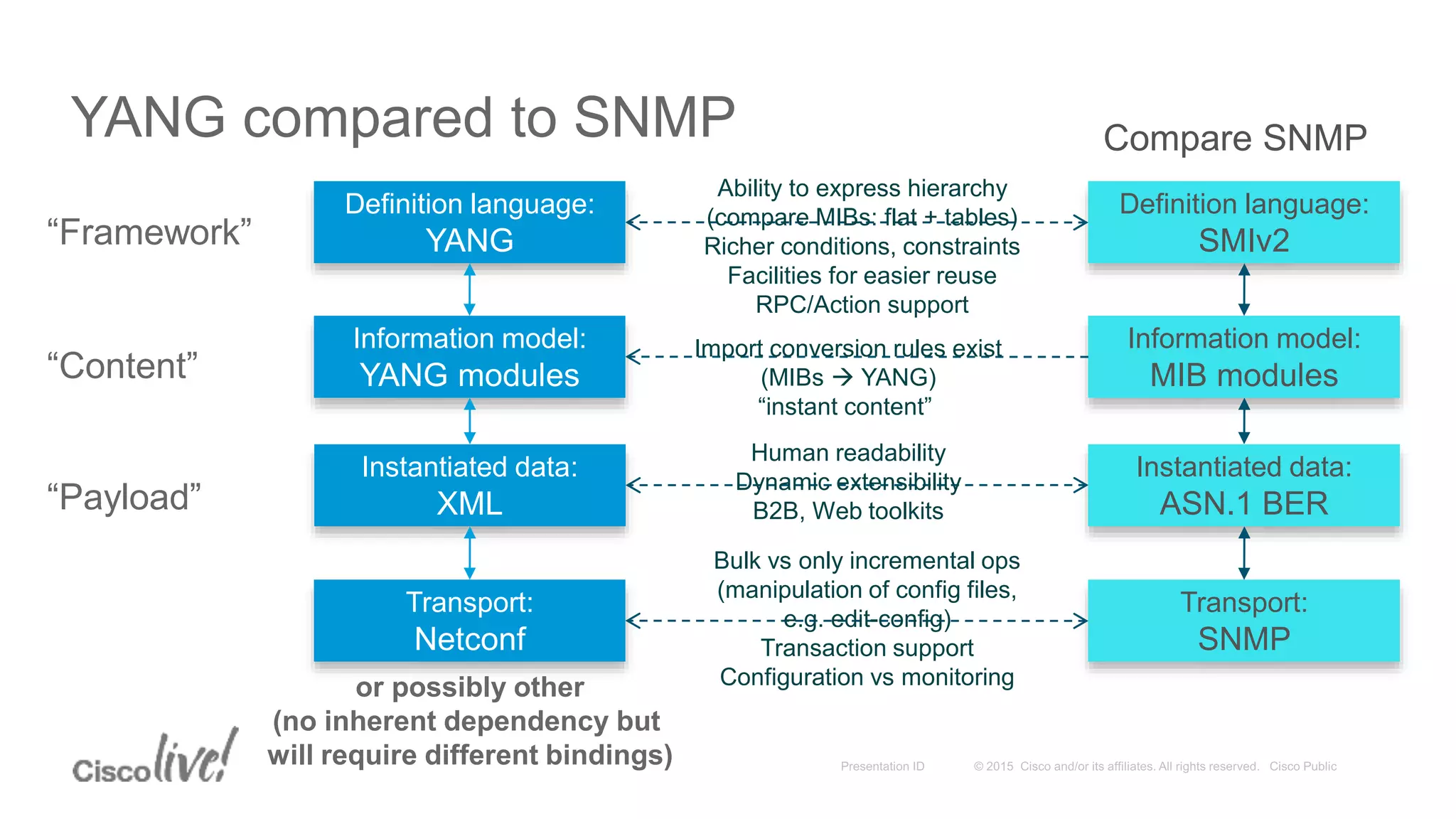
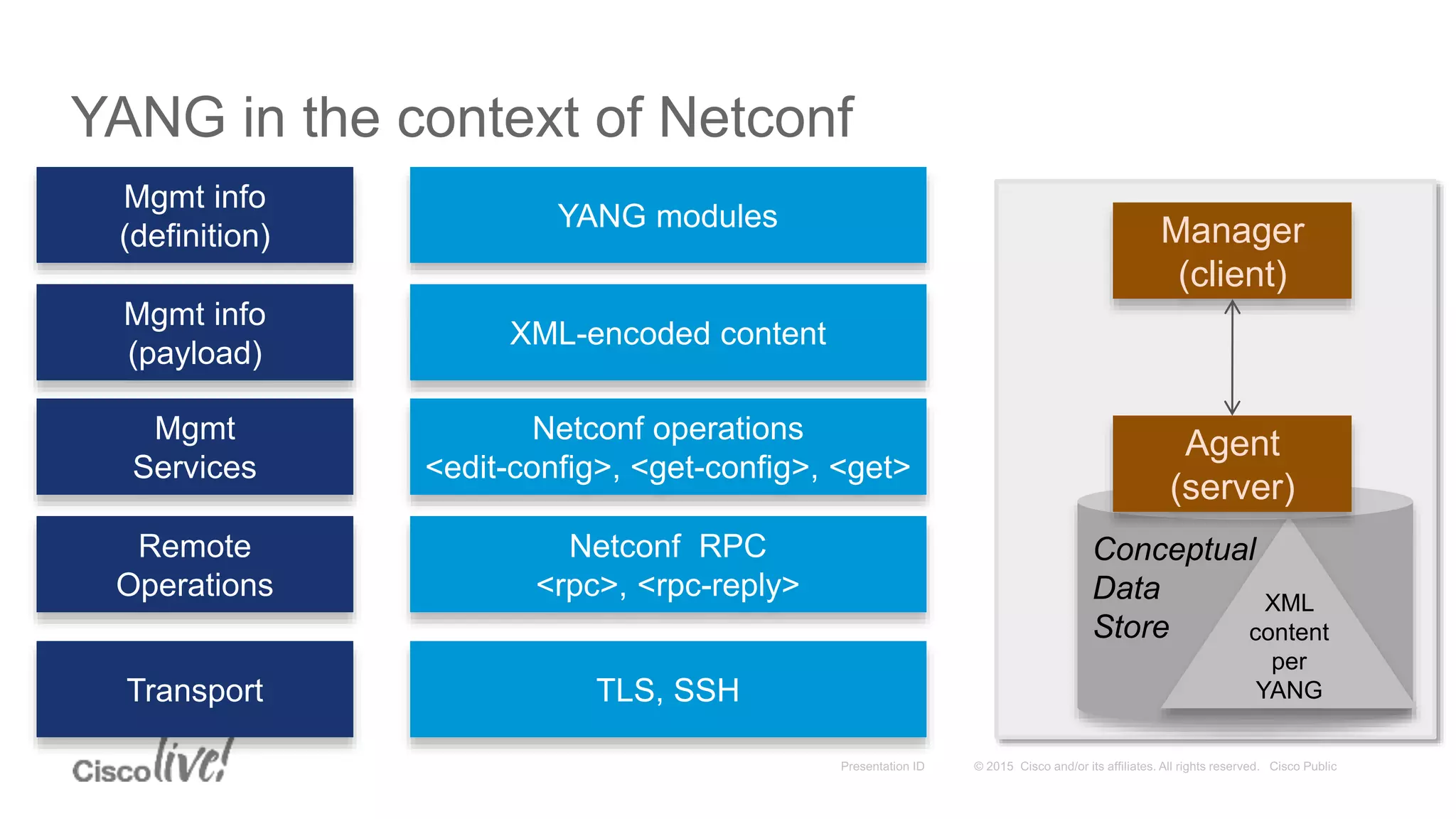
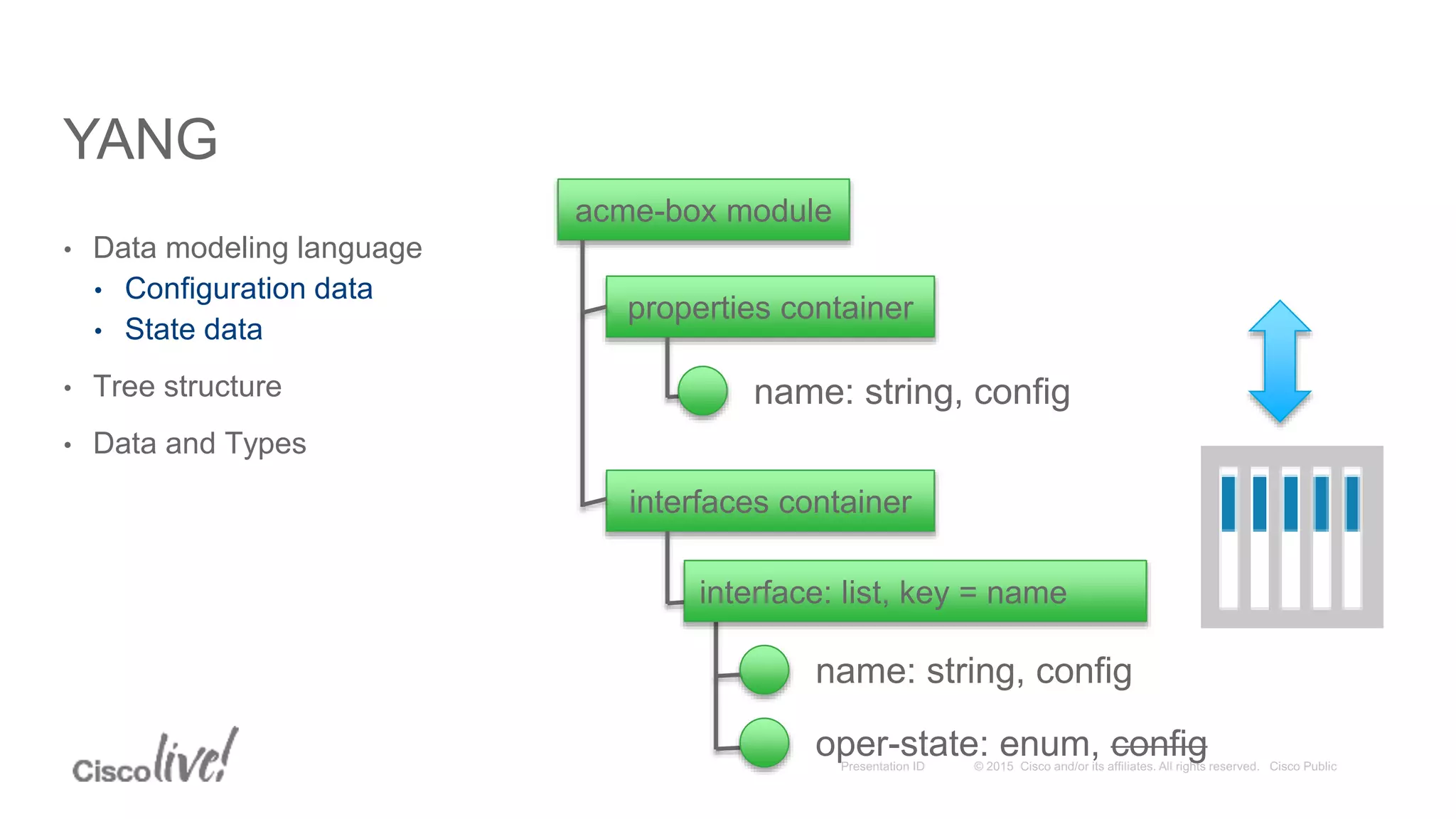
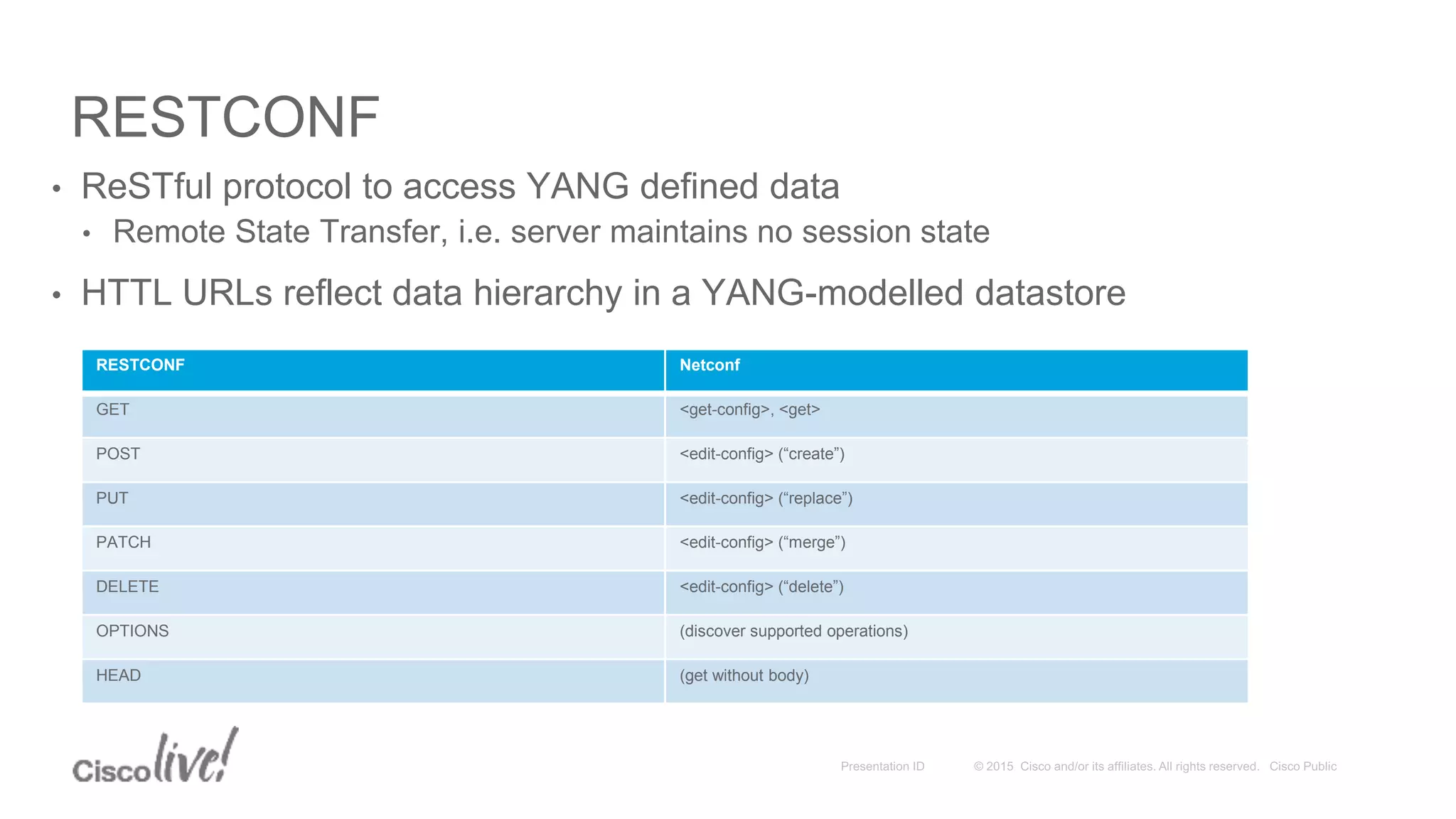
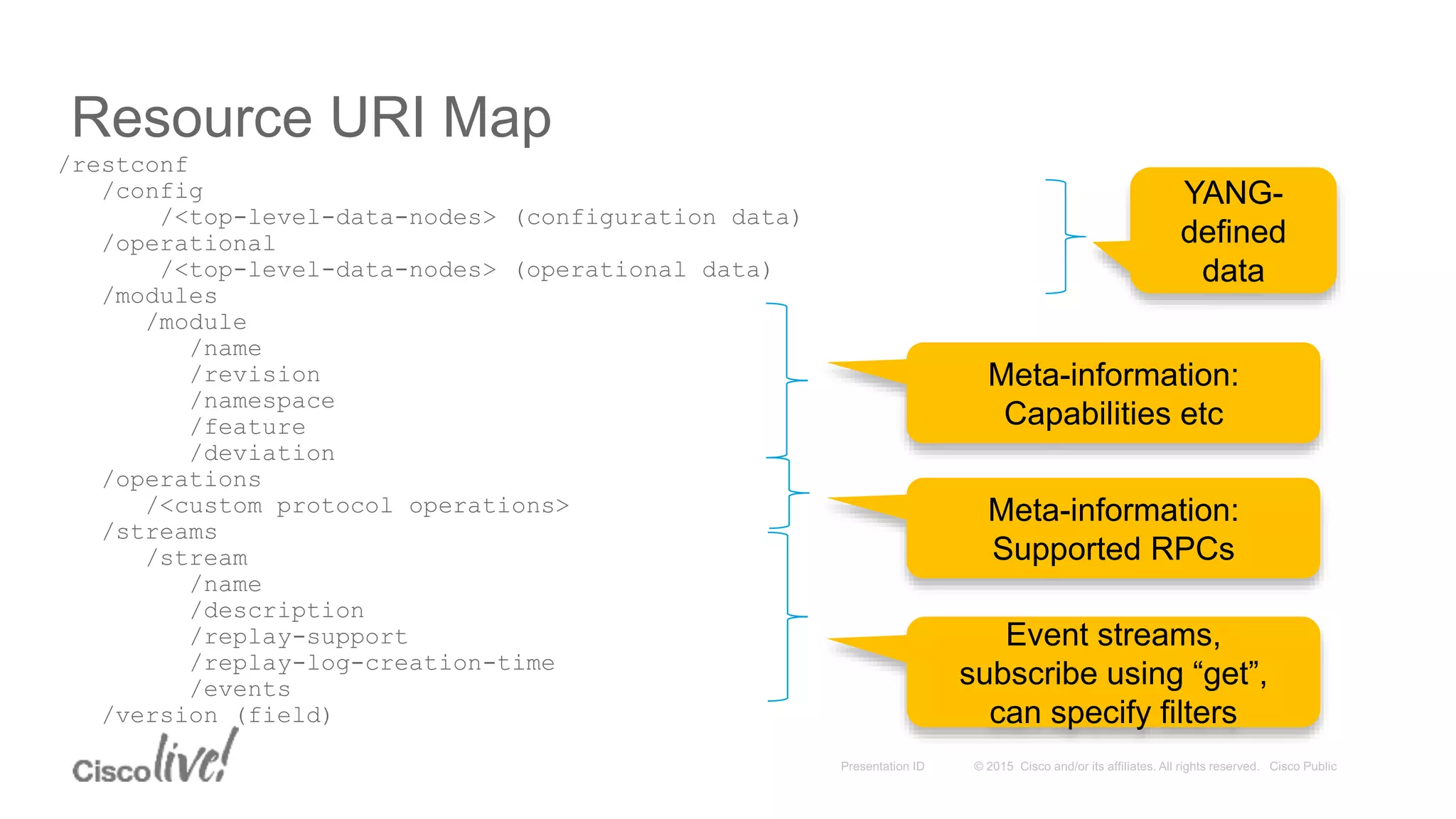
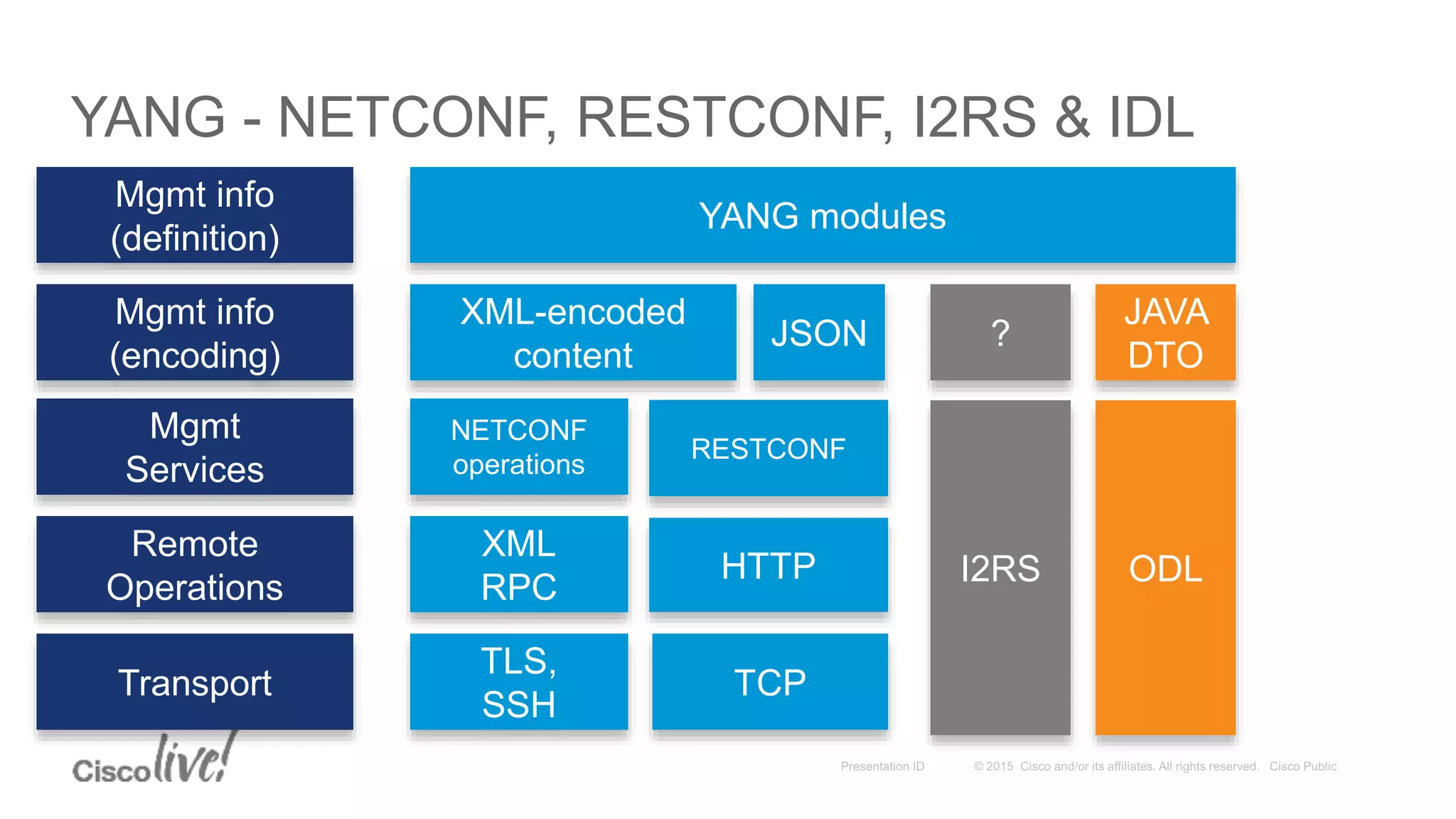
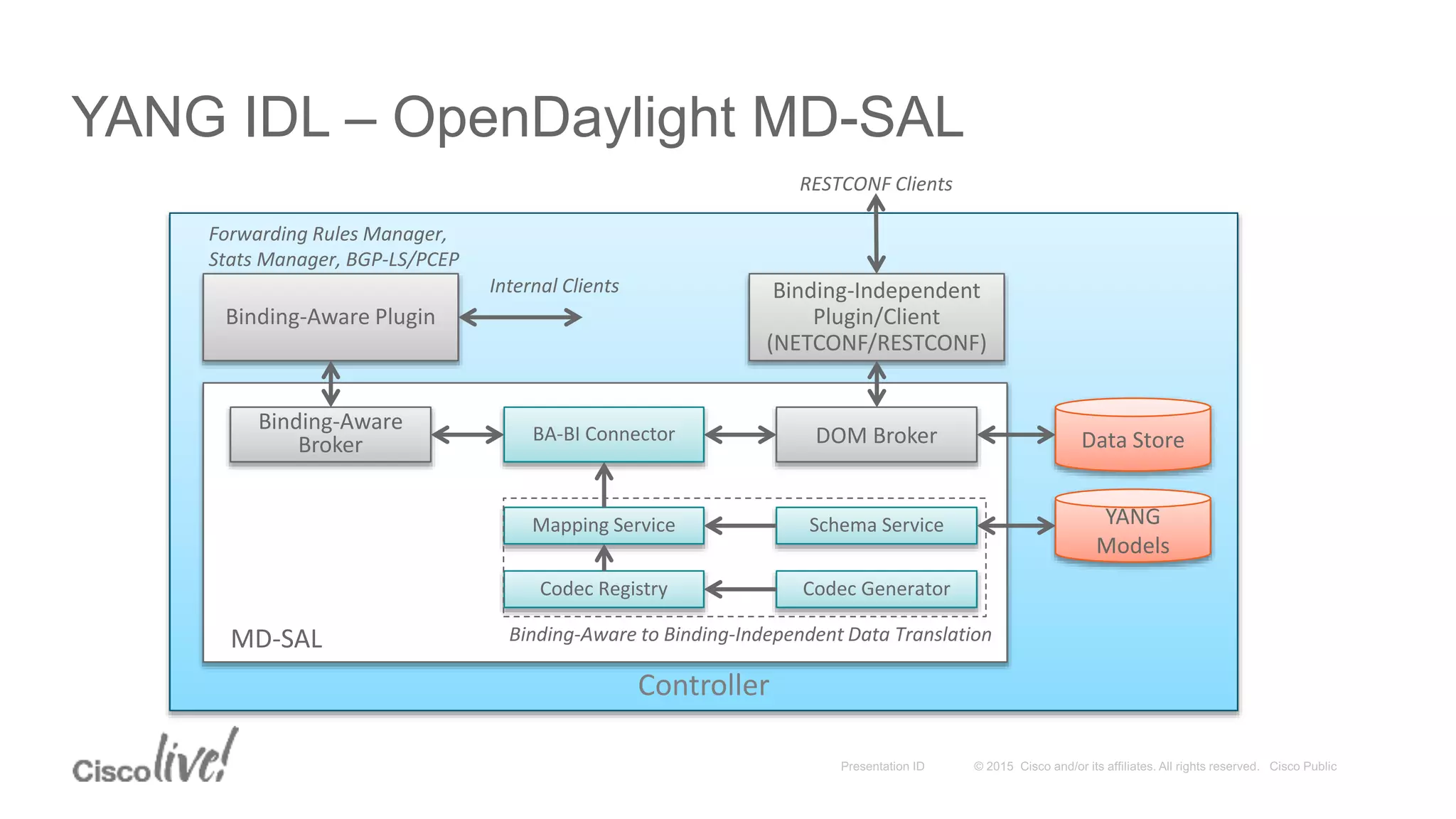
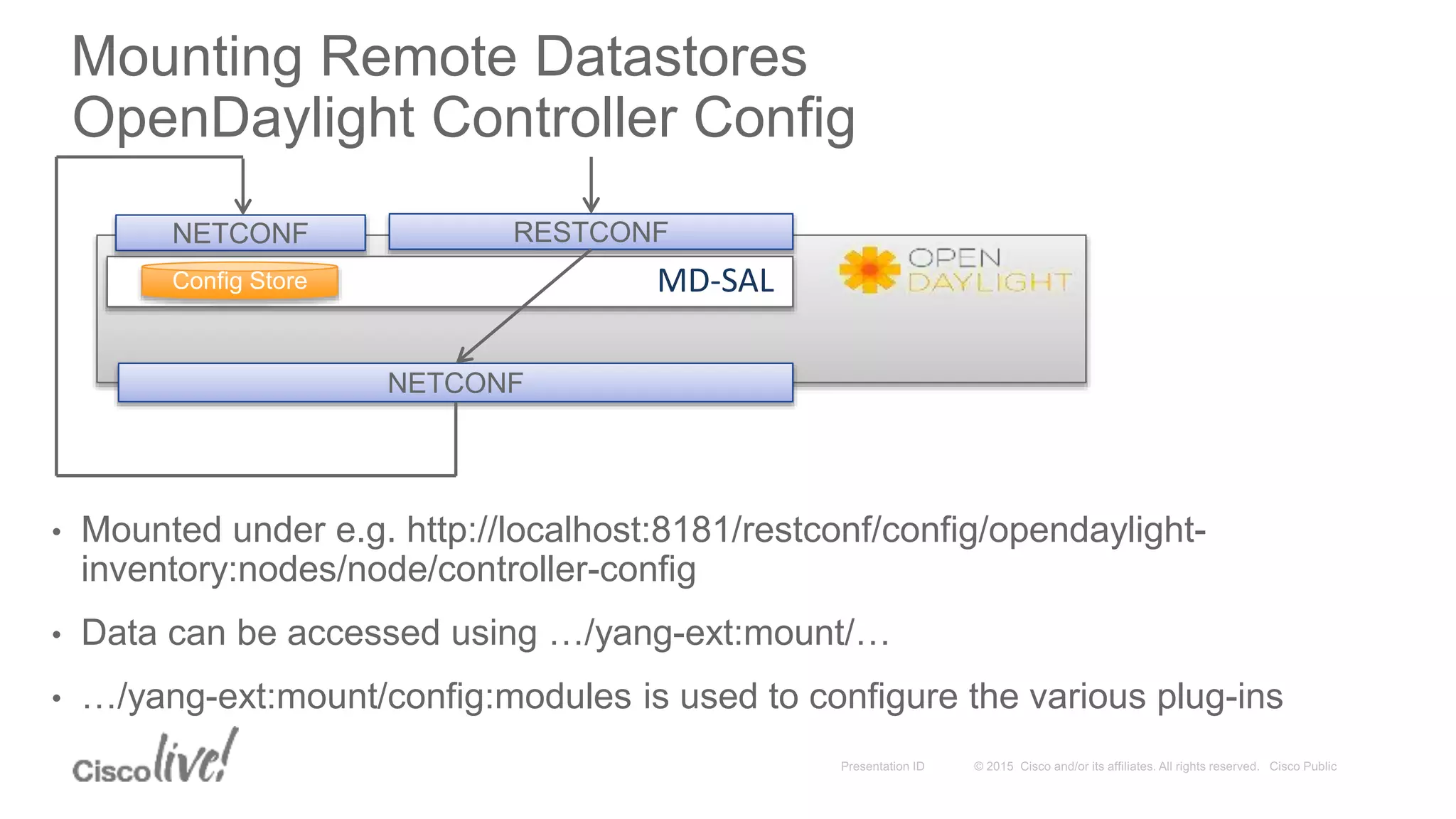
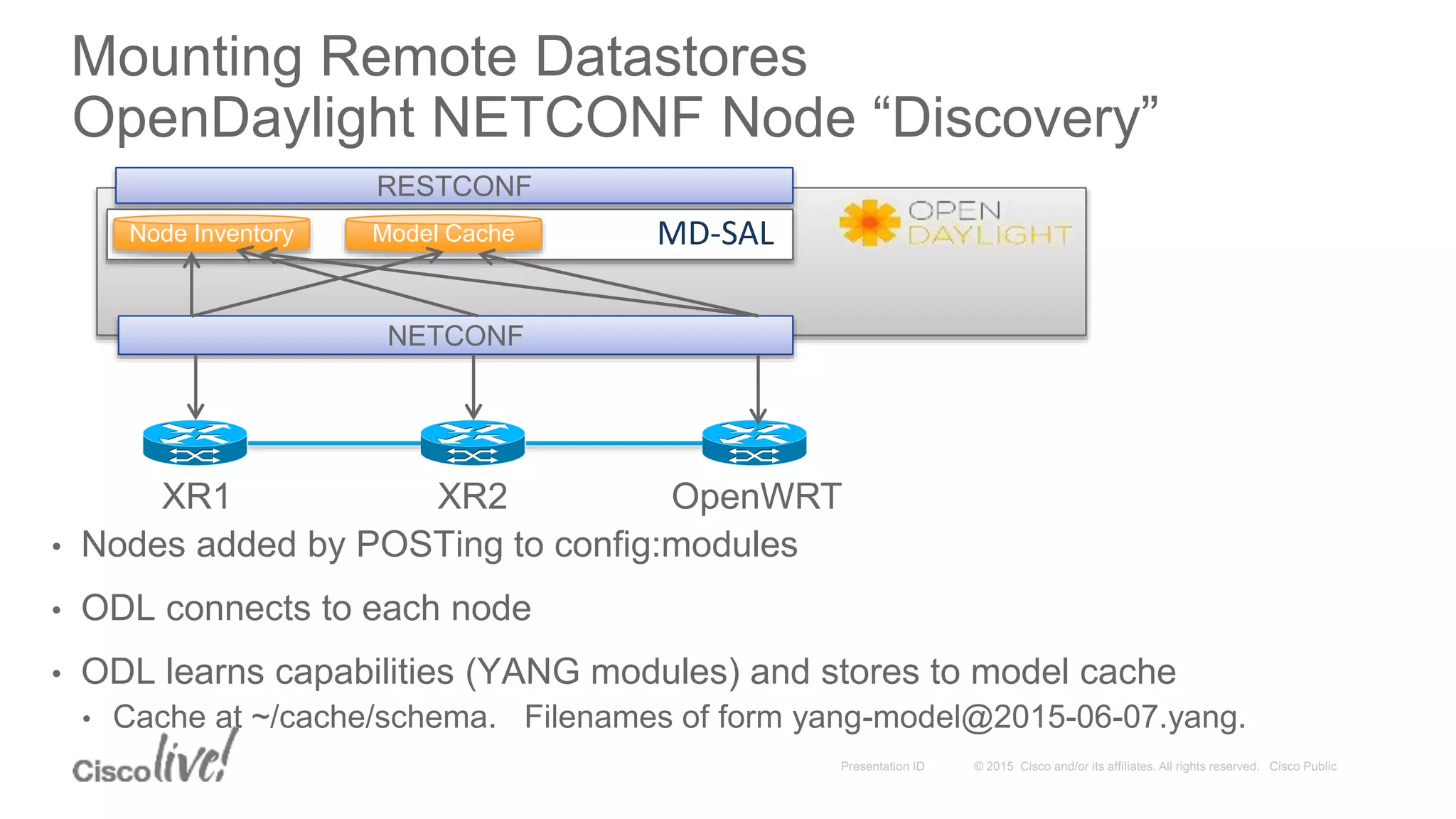
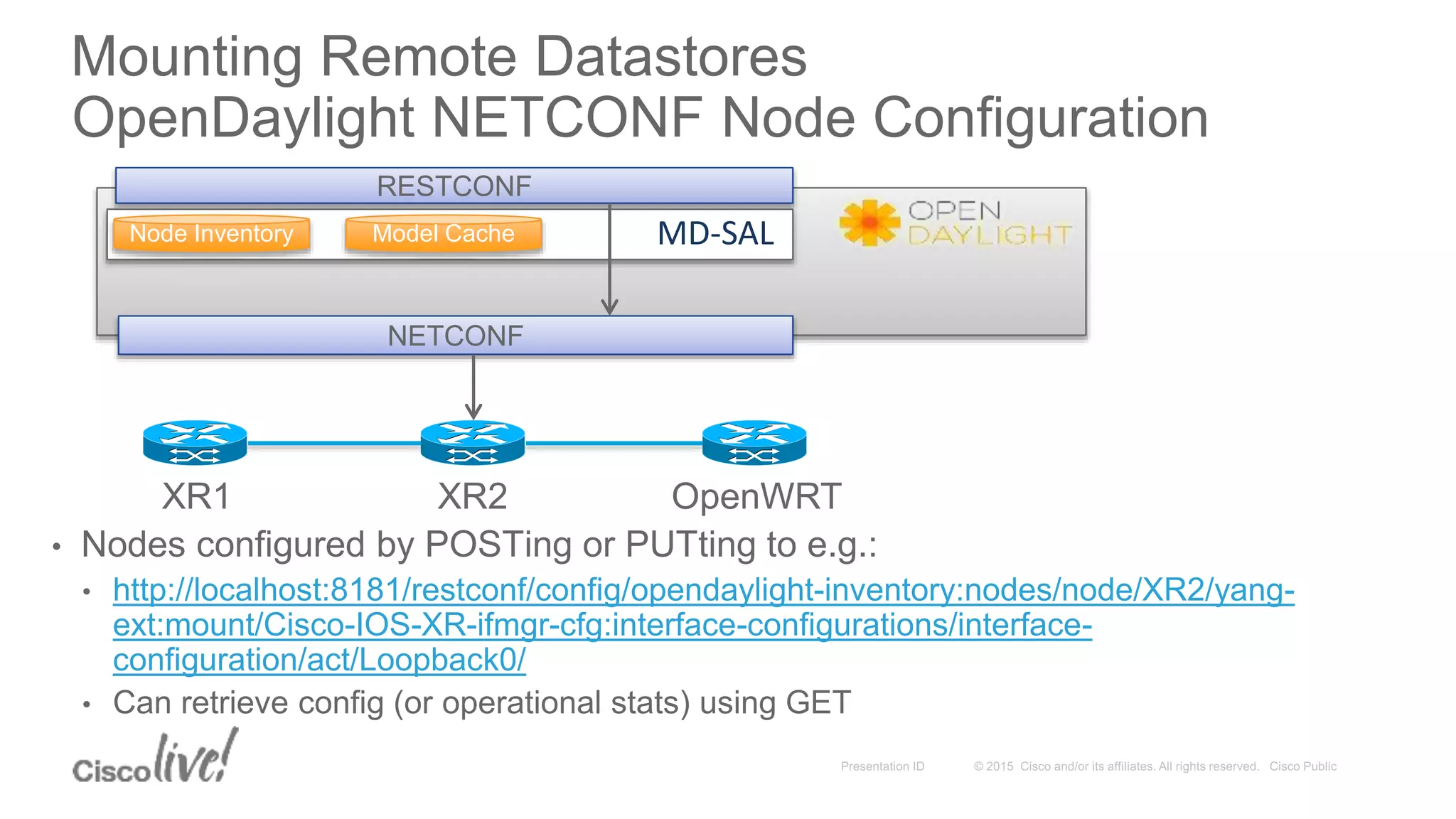
This document provides an overview of a workshop held by the IAB on network management. The goal of the workshop was to continue discussions between network operators and protocol developers and guide the IETF's focus on future work regarding network management.