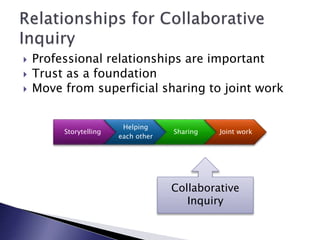
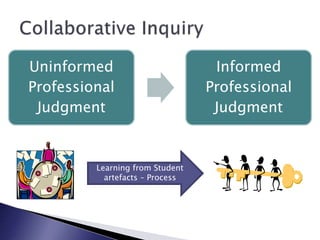
The document discusses the importance of mobilizing professional knowledge and the role of collaborative inquiry in improving educational practices and student achievement. It outlines strategies for creating network learning communities, emphasizing leadership, trust, and deep collaboration to foster a supportive school culture. Challenges include difficulty in cultivating necessary social processes and the need for focused efforts and leadership support for sustained success.