This document discusses the differences between various networking concepts including:
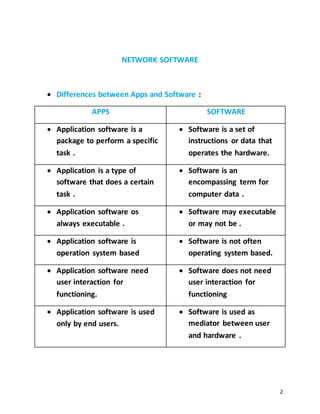
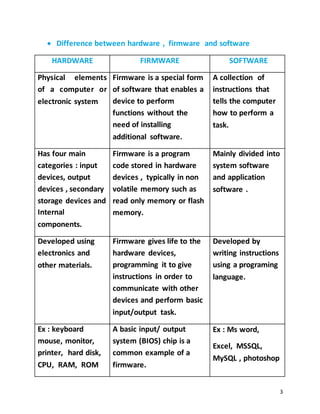
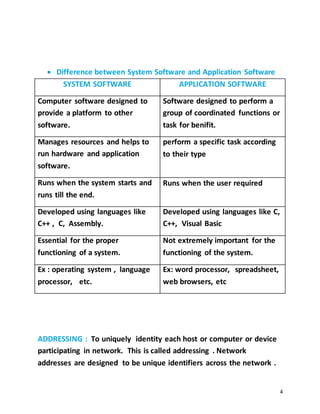
- Apps and software, hardware, firmware and software, and system software vs application software.
- Network addressing including physical MAC addressing and logical IP addressing. IPv4 and IPv6 addressing schemes are described along with classes of IPv4 addresses.
- Private and public IP addresses are defined, with private addresses used internally and public addresses used externally on the internet.
- The term host is defined as a computer or device that communicates with other hosts on a network, and typically refers to clients and servers rather than networking devices like switches and routers.