The document provides an introduction to the Network Security Lab Manual for the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at NorthCap University, Gurugram. It outlines 19 experiments covering topics such as network reconnaissance using tools like Wireshark, TCPDump, and Nmap, security issues related to protocols like IP, DNS, and ARP, session hijacking, VPN configuration, wireless hacking, and intrusion detection using Snort. The experiments aim to provide hands-on experience of basic network security concepts and analyzing attack-defense scenarios. General instructions for lab safety and discipline are also included.










![Network Security Lab Manual (CSL383)
2020-21
xiii
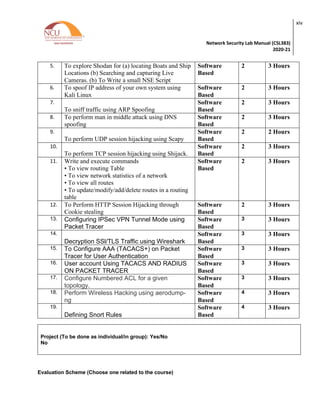
4. LIST OF EXPERIMENTS
Practical Content
Sr. No. Title of the Experiment Software/Hard
ware based
Unit
covered
Time
Required
1. Make a Detailed Report on Network Security
Threats covering Structured, Unstructured, Internal
and External Threats
Software
Based 1
3 Hours
2. Perform the following Scan using Wireshark and
analyze your results
(a)Analyze TCP session
(b) Perform and analyze these scans
(i) Start a Wireshark capture. Open a Windows->
command window and perform a Host Scan (using
ICMP packets) on a neighbours machine using
nmap –sP [neighbors ip address]. Stop the capture
and filter the traffic for ARP and ICMP packets.
(ii)Start a new Wireshark capture, and then
perform a host scan (ICMP scan) on a system out
with the subnet, such as nmap –sP
scanme.nmap.org.(Stop the capture and filter the
traffic for ARP and ICMP packets and Compare
with previous results.
(iii) Start a new Wireshark capture, and then
perform a complete Port Scan (in this case a TCP
SYN scan) and an Operating System Fingerprint
on a neighbours machine using nmap –O
[neighbours ip address] . The –O option should
provide the OS running on the scanned machine.
Stop the capture and filter for source address ==
your machines address if necessary.
Software
Based
2 3 Hours
3. To Analysis Network using Wireshark for
(a)Traffic Monitoring (TCP slow down and HTTP
slow down)
(b) Packet Sniffing
Software
Based
2 3 Hours
4. Explore , execute and analysis traffic using TCP
Dump and Net discover tools
Software
Based
2 3 Hours](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networksecuritylab-240403042431-5761bdca/85/Network-Security-LabNetwork-Security-Lab-13-320.jpg)

![Network Security Lab Manual (CSL383)
2020-21
xvii
INDEX
S.No Experiment Page
No.
Date of
Experi
ment
Date of
Submissio
n
Marks Signat
ure
1
Make a Detailed Report on Network
Security Threats covering Structured,
Unstructured, Internal and External
Threats
2 Perform the following Scan using
Wireshark and analyze your results
(a)Analyze TCP session
(b) Perform and analyze these scans
(i) Start a Wireshark capture. Open a
Windows-> command window and
perform a Host Scan (using ICMP
packets) on a neighbours machine
using nmap –sP [neighbors ip address].
Stop the capture and filter the traffic for
ARP and ICMP packets.
(ii)Start a new Wireshark capture, and
then perform a host scan (ICMP scan)
on a system out with the subnet, such
as nmap –sP scanme.nmap.org.(Stop
the capture and filter the traffic for ARP
and ICMP packets and Compare with
previous results.
(iii) Start a new Wireshark capture, and
then perform a complete Port Scan (in
this case a TCP SYN scan) and an
Operating System Fingerprint on a
neighbours machine using nmap –O
[neighbours ip address] . The –O option
should provide the OS running on the
scanned machine. Stop the capture
and filter for source address == your
machines address if necessary.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networksecuritylab-240403042431-5761bdca/85/Network-Security-LabNetwork-Security-Lab-17-320.jpg)




![Network Security Lab Manual (CSL383)
2020-21
xxii
EXPERIMENT NO. 2
Student Name and Roll Number:
Semester /Section:
Link to Code:
Date:
Faculty Signature:
Marks:
Objective:
To familiarize students with the working of Wireshark and how to analyse traffic moving in
and out of the network.
Outcome:
Students will able to analyse TCP sessions and various scans using NMAP and Wireshark.
Students will able to understand the working of NMAP.
Problem Statement:
Perform the following Scan using Wireshark and analyze your results
(a)Analyze TCP session
(b)Perform and analyze these scans
(i) Start a Wireshark capture. Open a Windows-> command window and perform a Host Scan
(using ICMP packets) on a neighbours machine using nmap –sP [neighbors ip address]. Stop the
capture and filter the traffic for ARP and ICMP packets.
(ii)Start a new Wireshark capture, and then perform a host scan (ICMP scan) on a system out with
the subnet, such as nmap –sP scanme.nmap.org.(Stop the capture and filter the traffic for ARP and
ICMP packets and Compare with previous results.
iii) Start a new Wireshark capture, and then perform a complete Port Scan (in this case a TCP SYN
scan) and an Operating System Fingerprint on a neighbours machine using nmap –O [neighbours ip
address] . The –O option should provide the OS running on the scanned machine. Stop the capture
and filter for source address == your machines address if necessary.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networksecuritylab-240403042431-5761bdca/85/Network-Security-LabNetwork-Security-Lab-22-320.jpg)