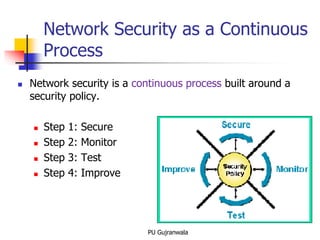
The document discusses key concepts in network and information security. It defines information security as measures taken to protect information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, inspection, recording or destruction. It identifies the critical characteristics of information security as confidentiality, integrity and availability. It also discusses network security as a continuous process of securing the network, monitoring for threats, testing security measures, and making improvements. Key related terms like assets, threats, vulnerabilities, risks, and countermeasures are also explained.