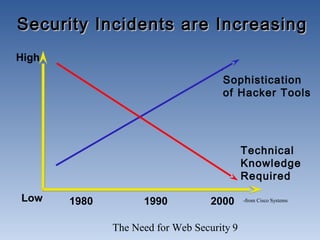
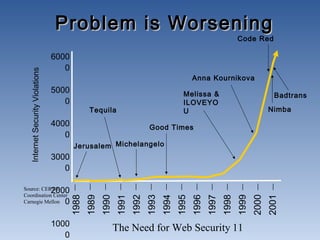
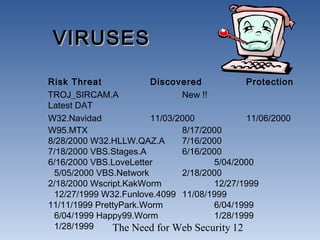
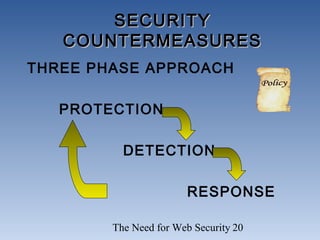
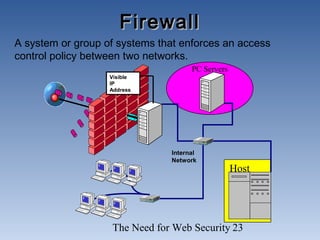
The document discusses the need for network security. It notes that more information is being created and shared digitally, creating vulnerabilities. The objectives are to understand security services like confidentiality and integrity, be aware of threats like viruses and hacking, and realize why comprehensive security programs are necessary. Such programs include elements like strong passwords, antivirus software, firewalls, backups, auditing, and user training. Cryptography and firewalls are discussed as important security countermeasures. The goal is to protect systems and data from increasing security risks on interconnected networks.