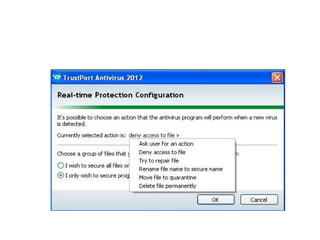
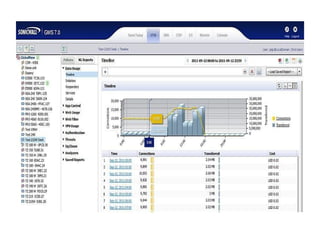
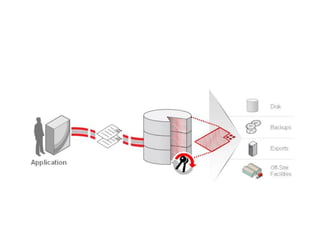
Network security plays a crucial role in protecting organizations' data. General solutions at the application level include auditing systems to ensure components are securely configured, performing security testing, and installing patches. Real-time protection uses behavioral analysis to detect and block unknown attacks. Multi-tier protection applies recovery objectives to backup critical systems across multiple servers. Centralized reporting and distributed management help monitor application security across business units. Selective encryption protects sensitive data as a last line of defense.