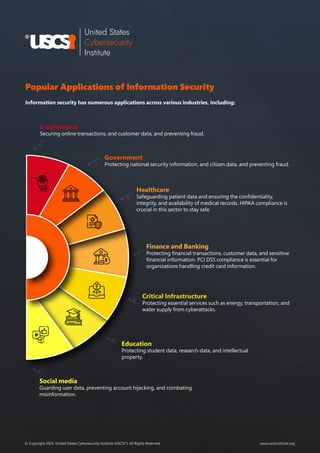
The document outlines the importance of information security, which encompasses practices, technologies, and processes designed to protect digital information from various threats, distinguishing it from cybersecurity. It highlights key goals such as risk management, compliance, business continuity, and data protection, while addressing common threats and best practices for implementation. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for continuous adaptation and monitoring in the face of evolving security challenges.