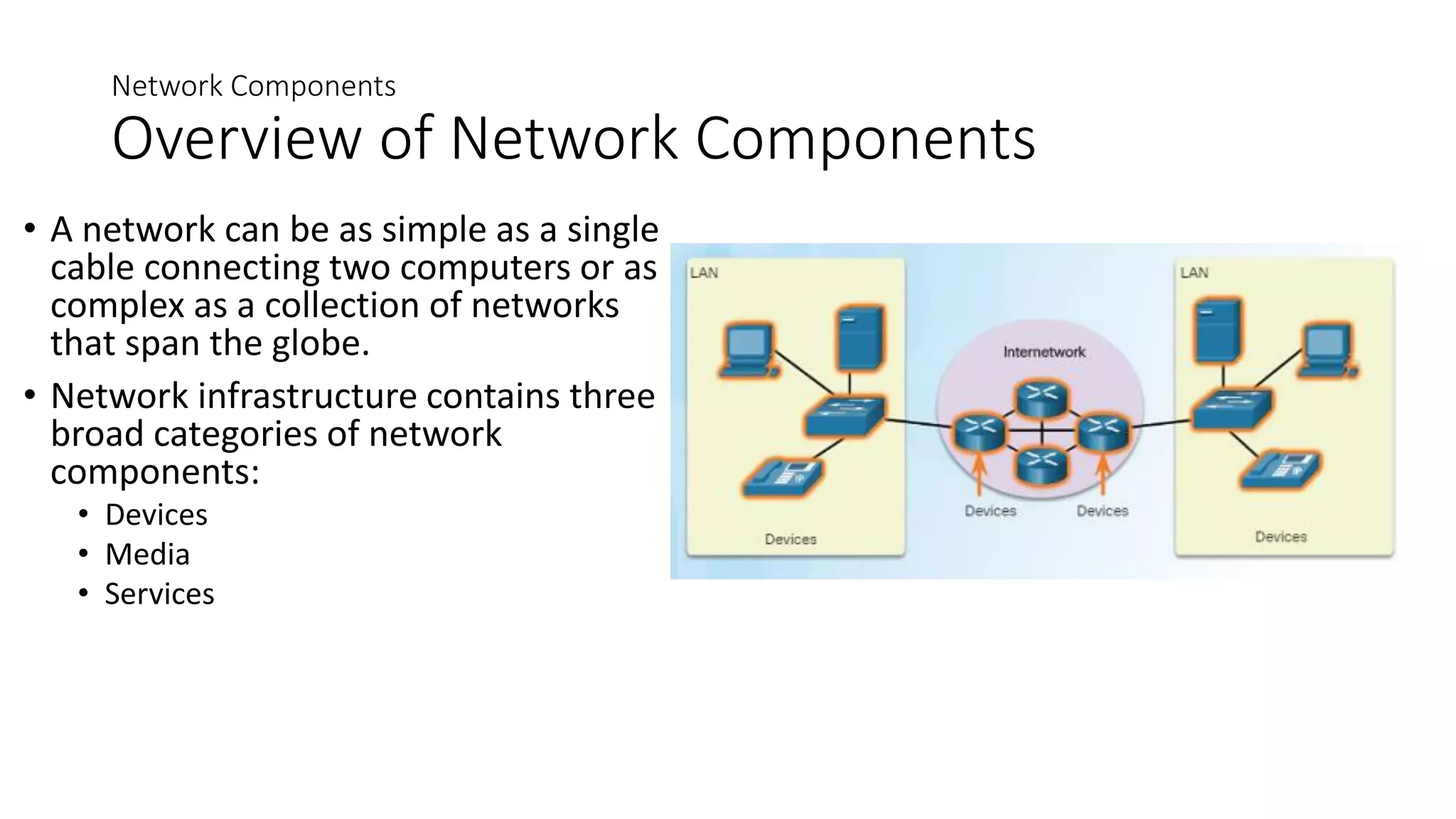
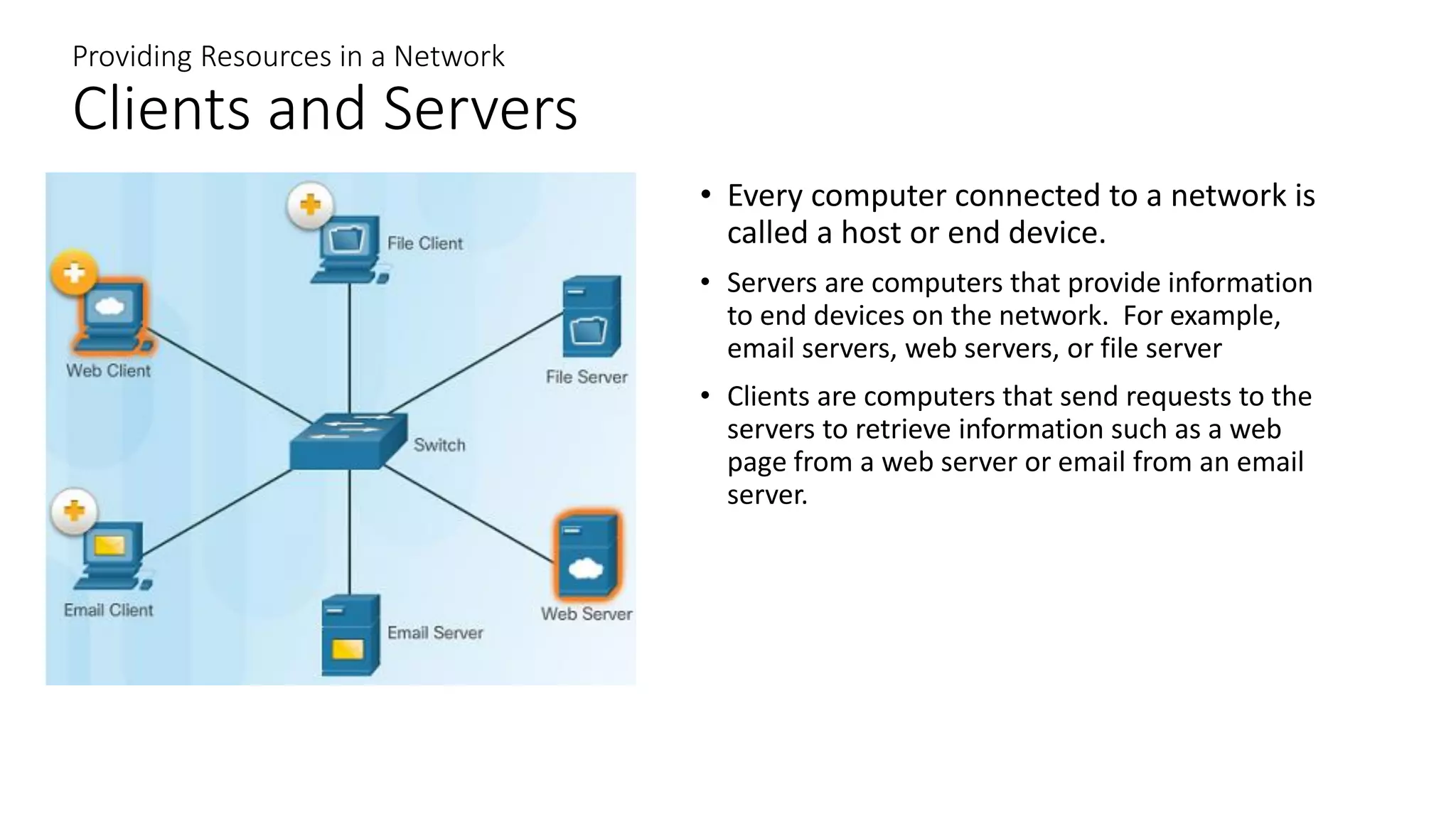
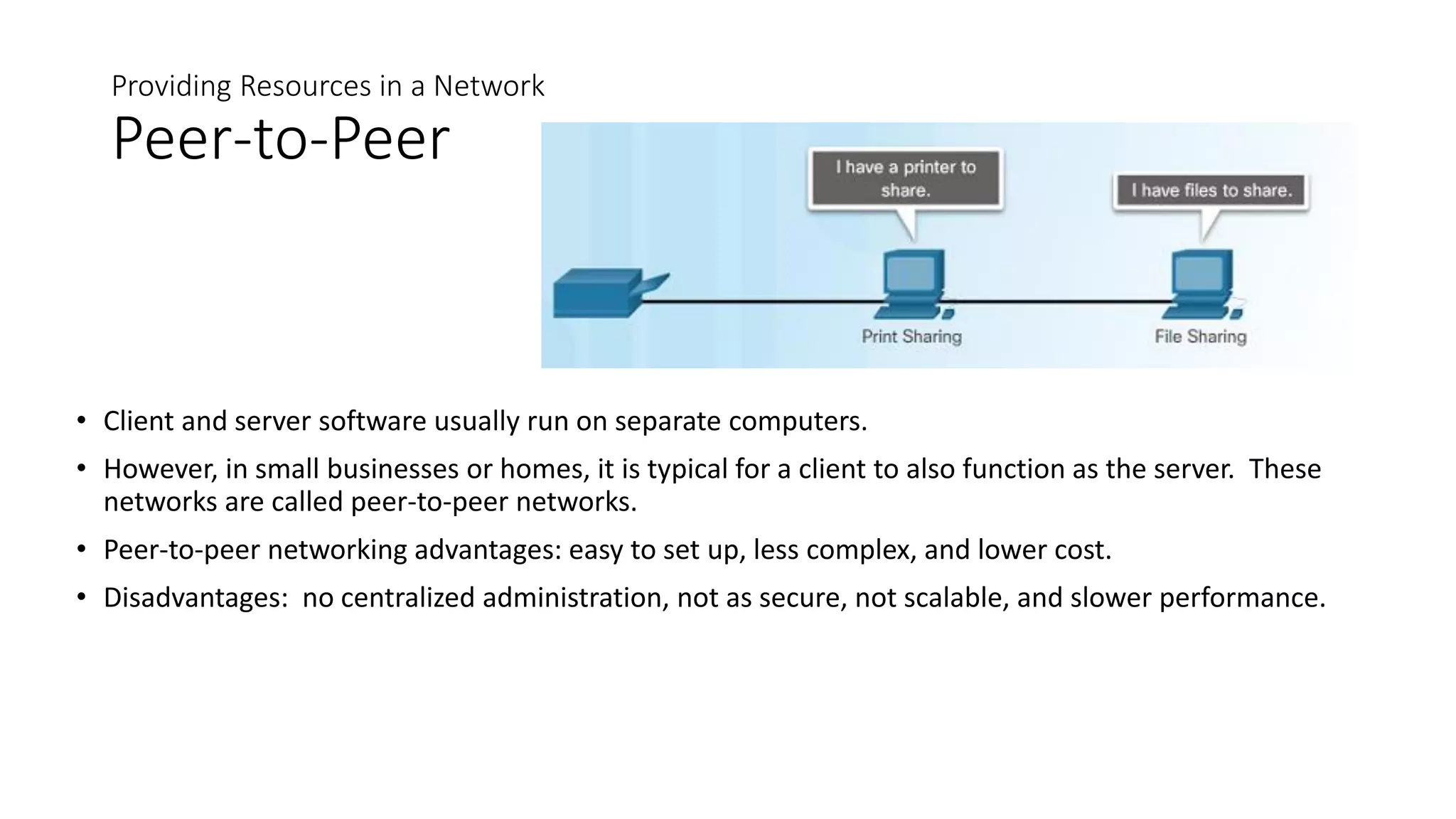
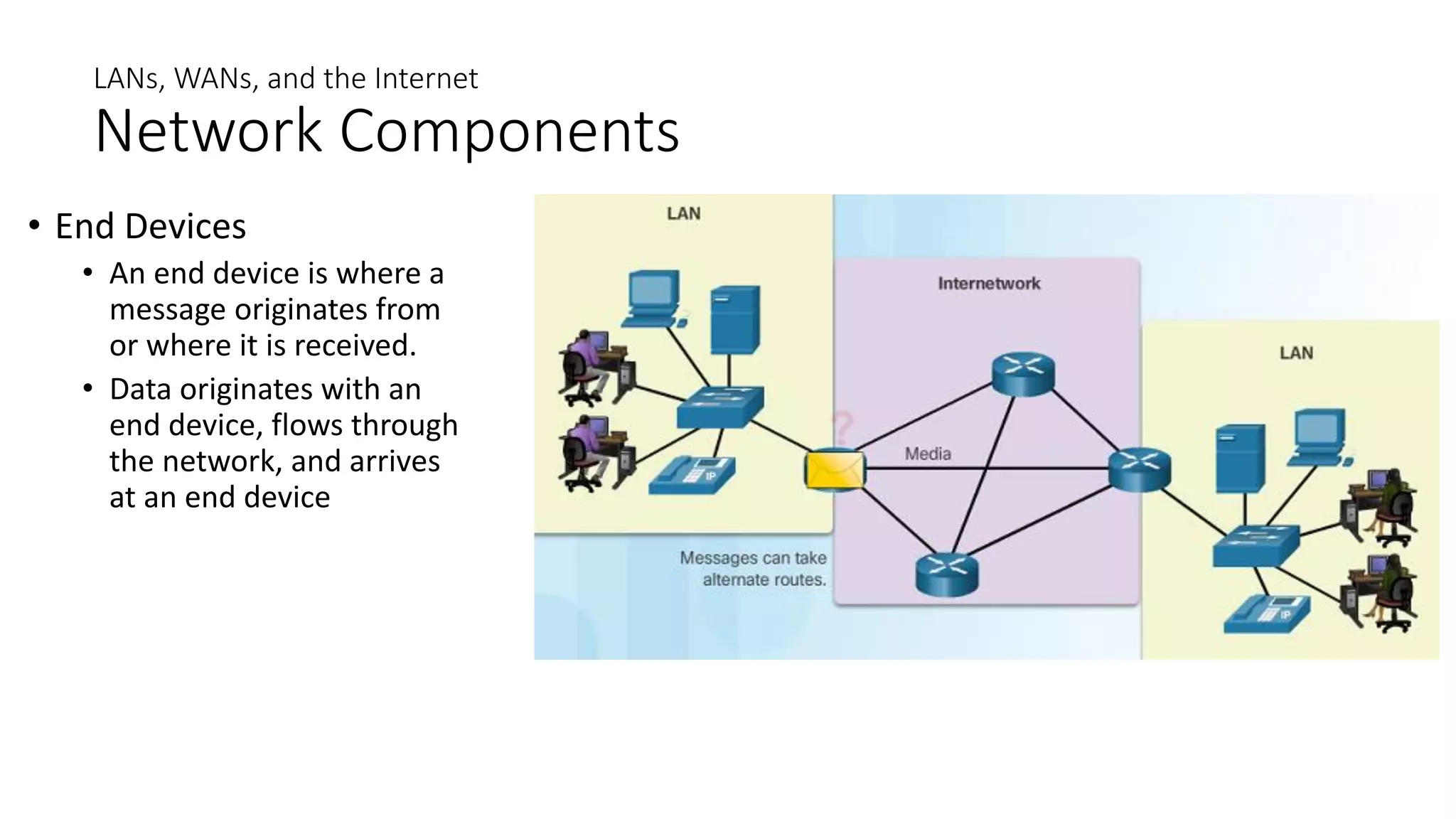
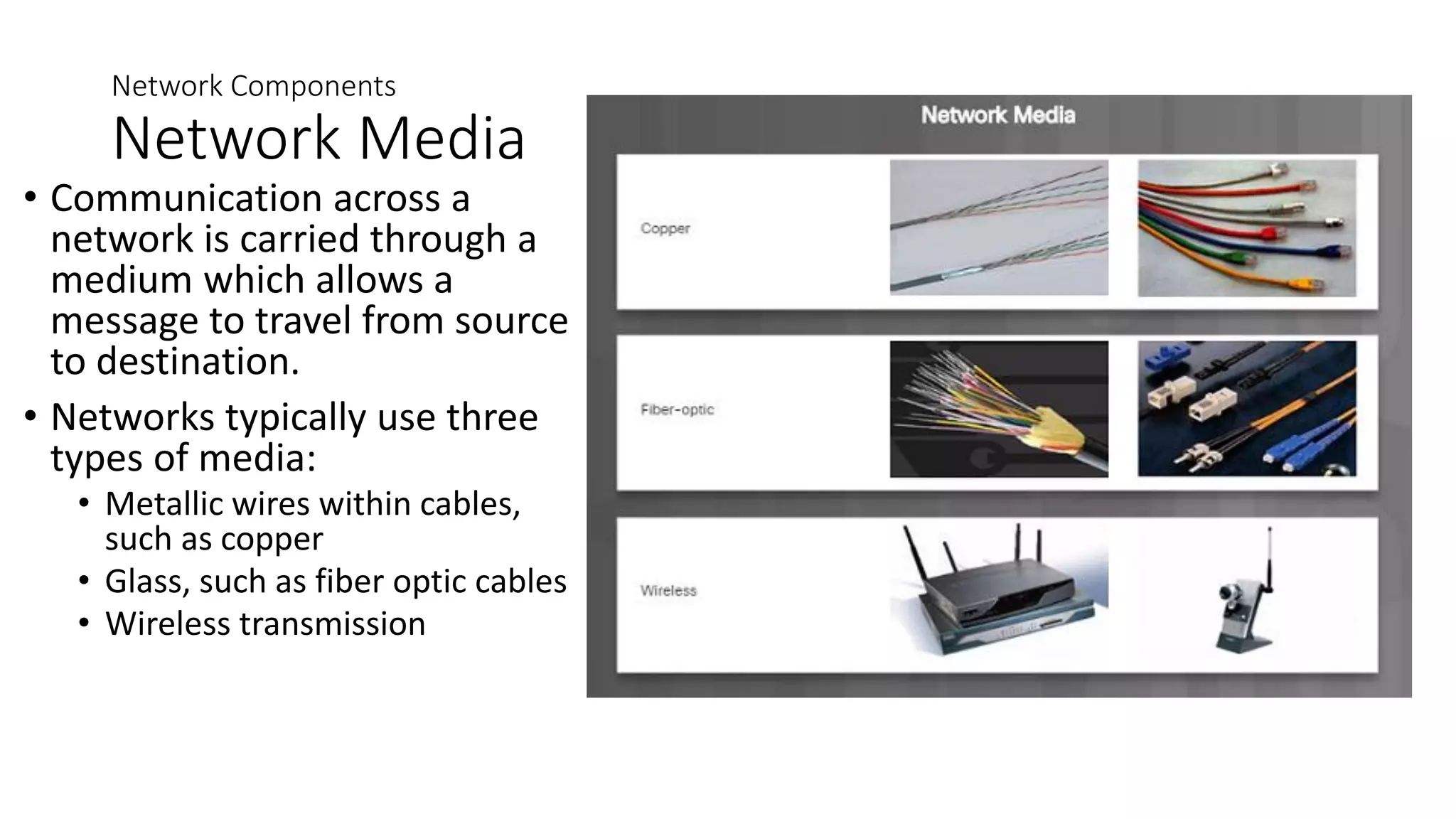
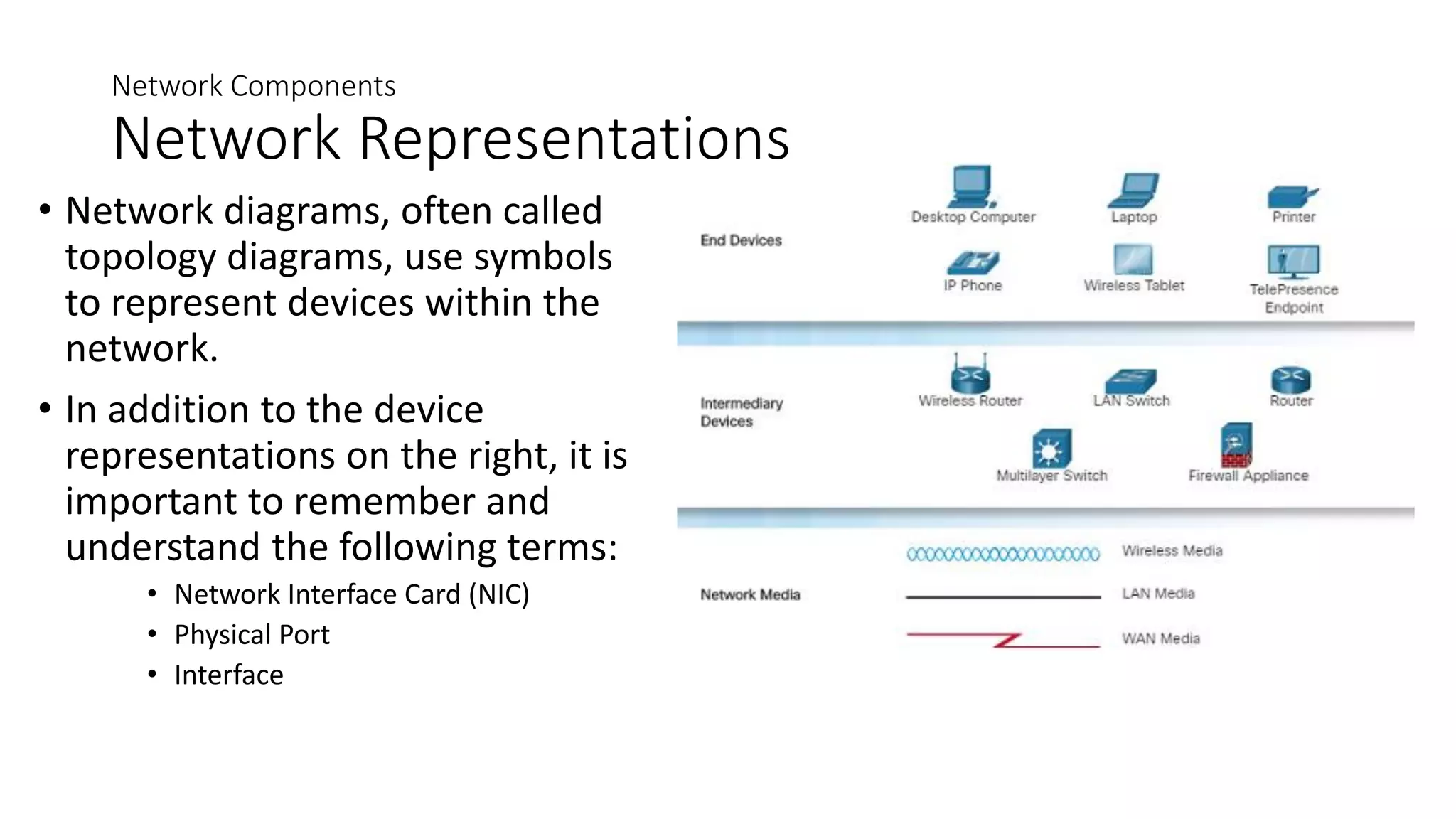
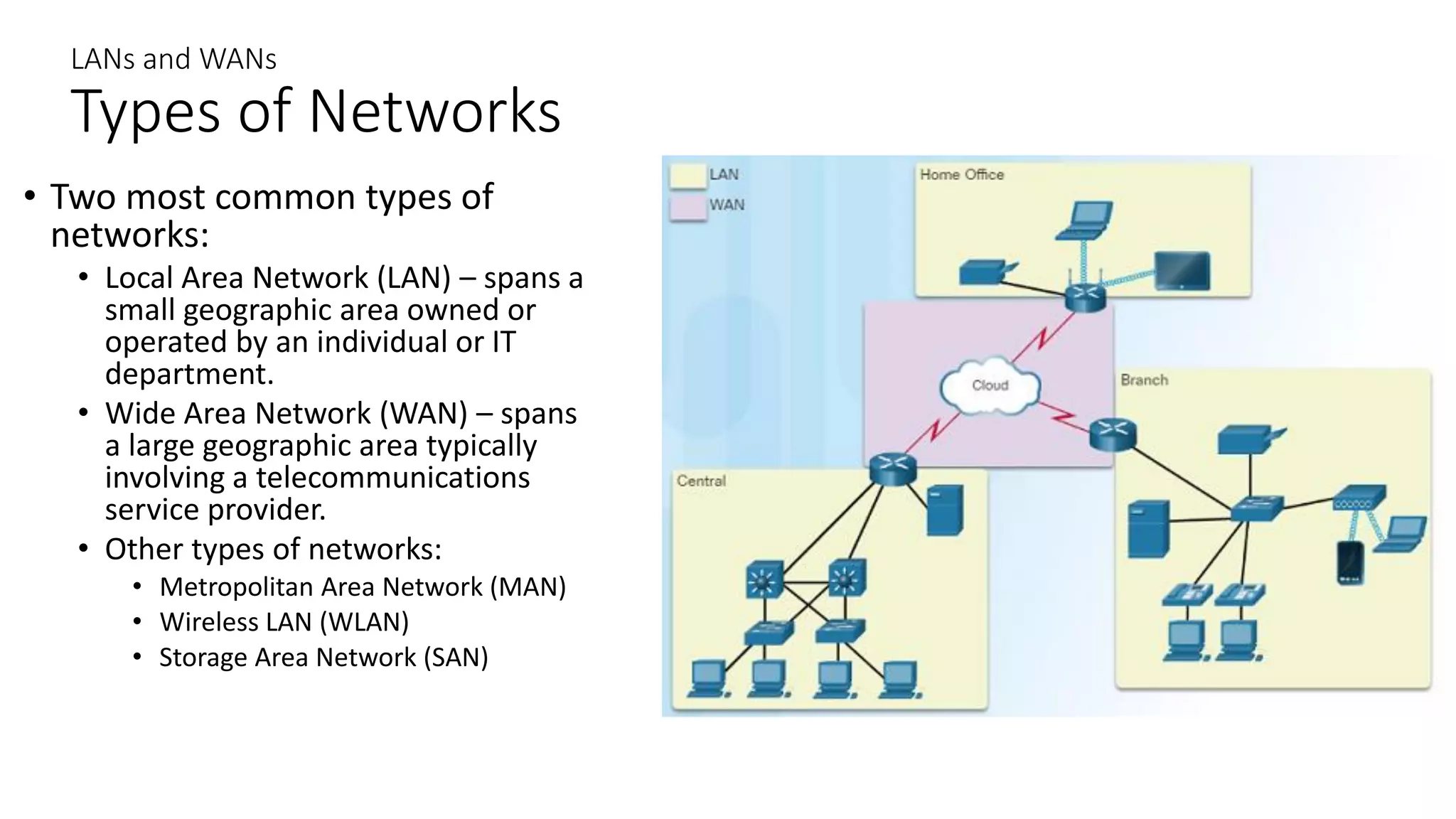
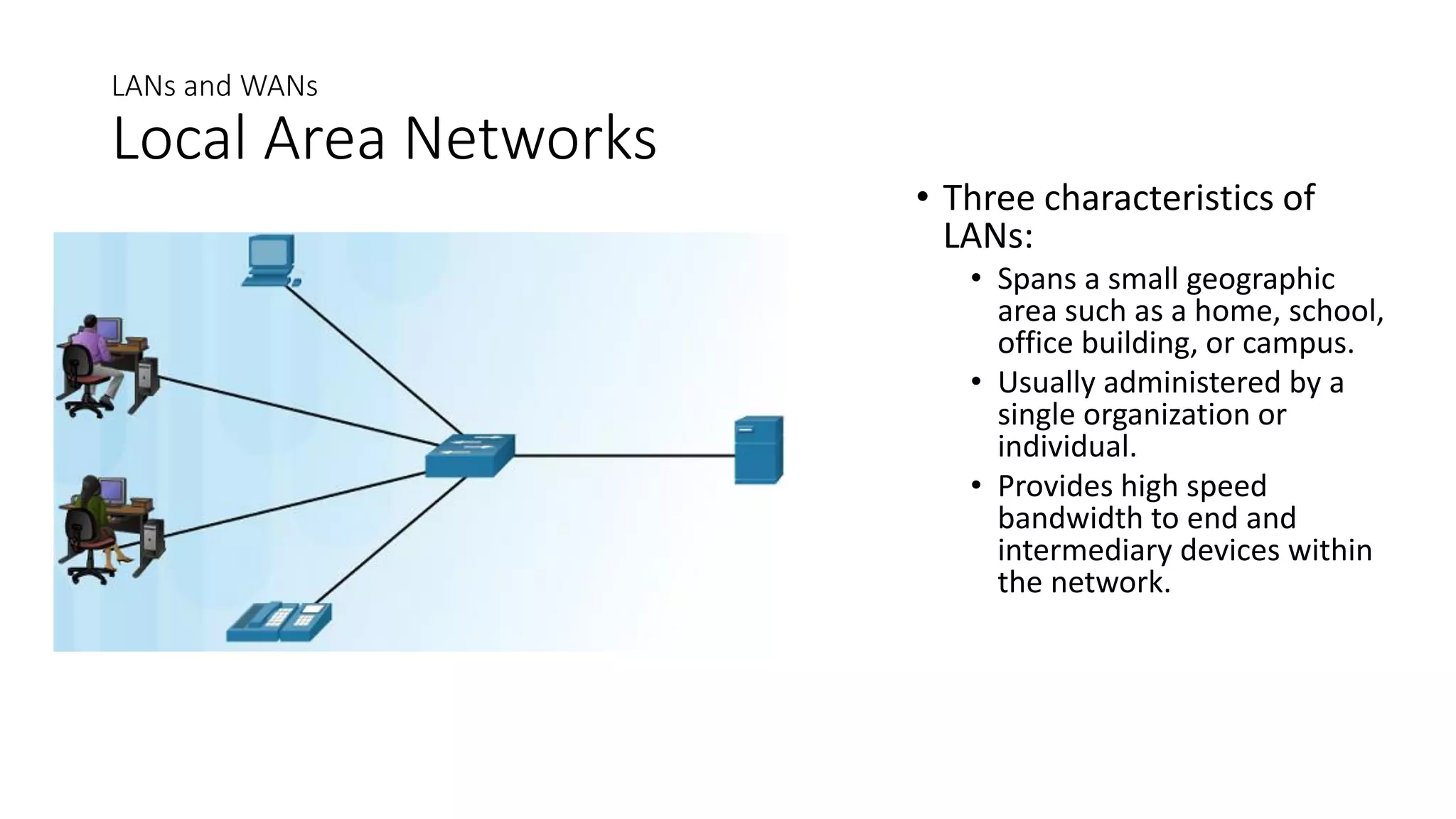
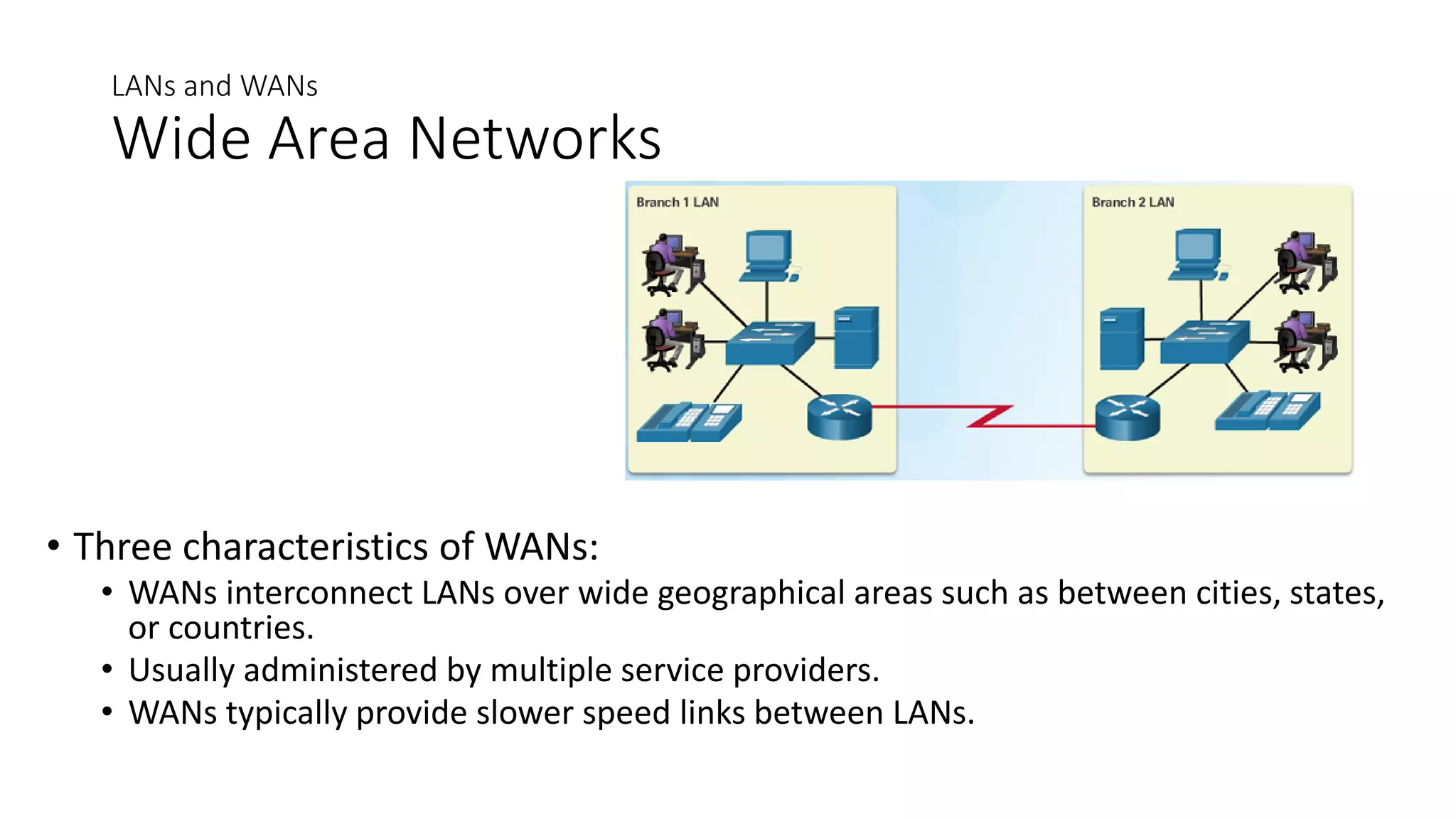
Networks can range from simple connections between two computers to complex global systems. They consist of devices, media, and services. Servers provide resources to clients, while peer-to-peer networks allow sharing without dedicated servers. Networks use end devices, intermediary devices like switches and routers, and physical media like cables. Local area networks span small areas like homes or offices while wide area networks connect multiple LANs over large distances.