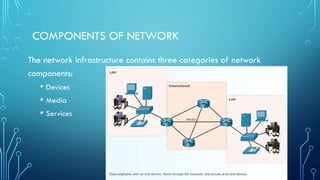
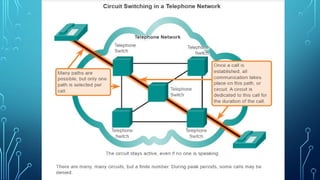
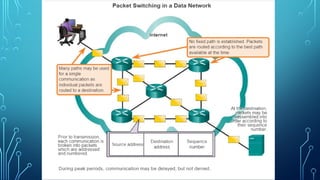
The document serves as a resource for understanding computer networks, authored by Andrew S. Tanenbaum and David J. Wetherall. It covers the basic components of network infrastructure, including end devices, intermediary devices, and media, as well as the importance of signal encoding and network topologies. Key terms such as network interface cards and physical ports are also defined to assist in grasping network connectivity and communication processes.