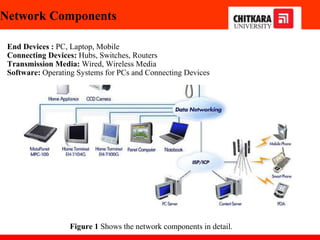
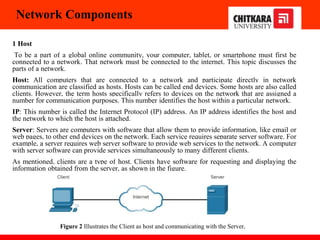
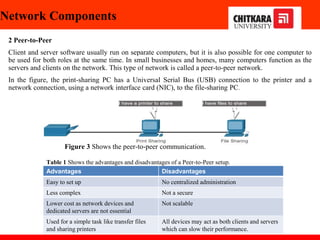
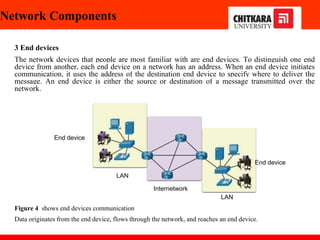
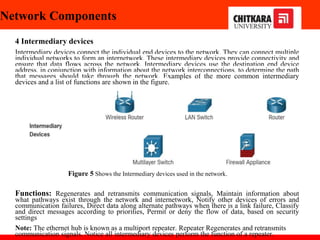
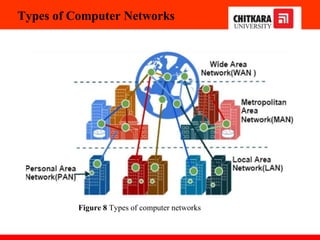
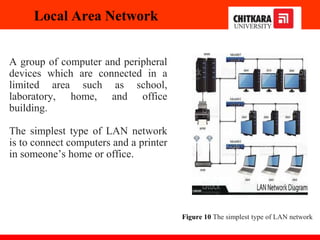
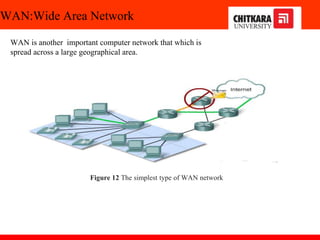
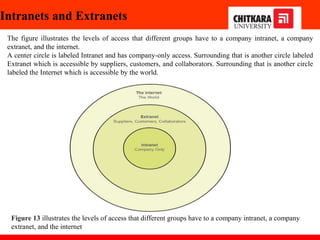
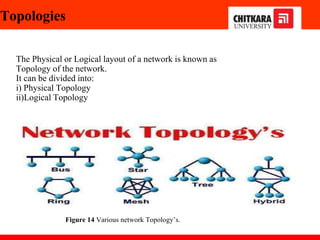
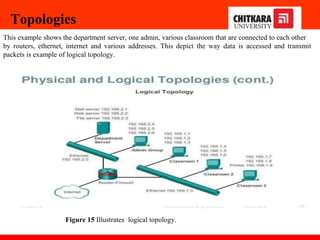
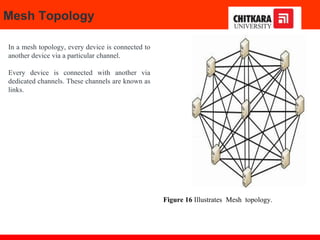
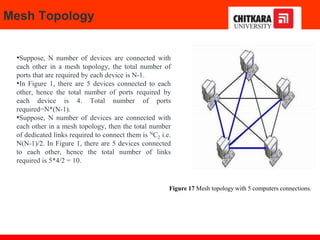
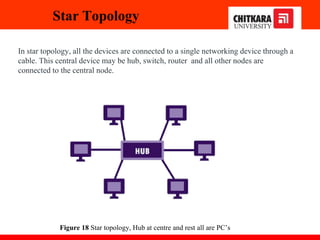
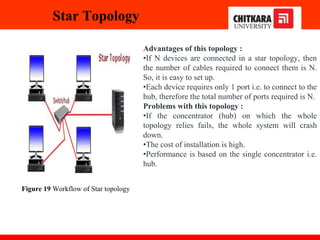
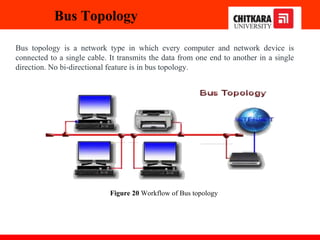
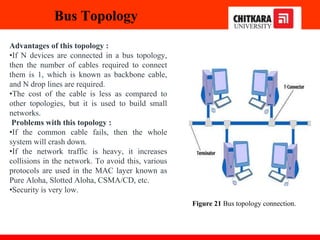
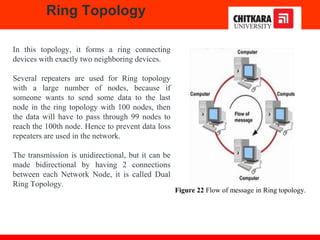
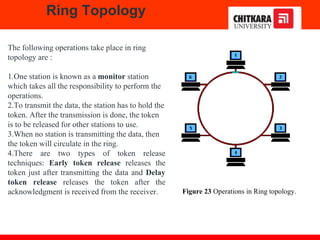
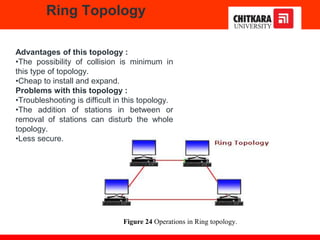
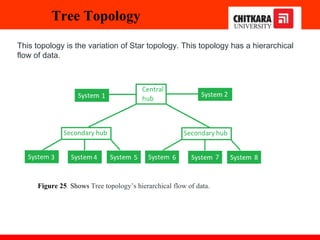
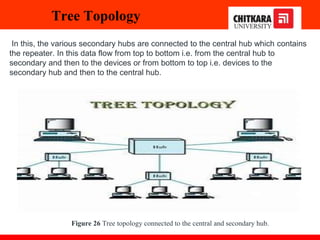
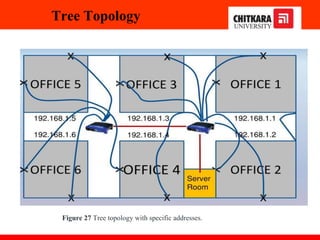
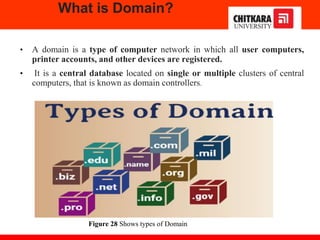
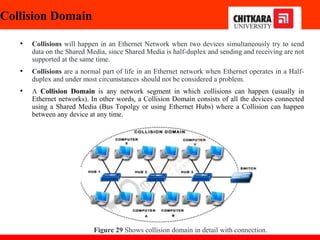
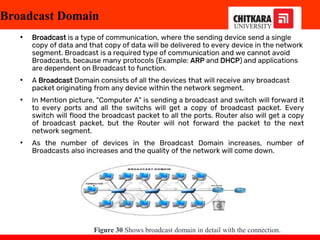
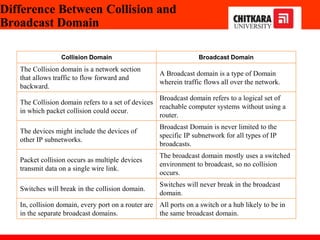
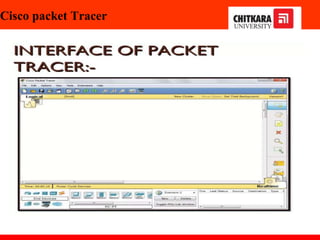
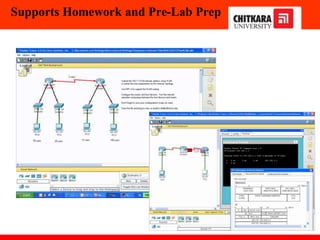
The document discusses the introduction and significance of computer networks in modern life, emphasizing their role in connectivity and productivity. It covers various components of networks, types of networks (e.g., LAN, WAN), network topologies, and important concepts like collision and broadcast domains. Additionally, it highlights recent trends in networking, such as BYOD and online collaboration tools.