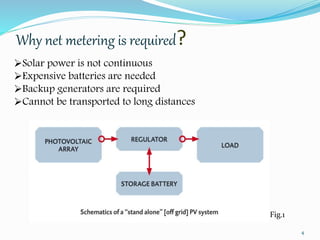
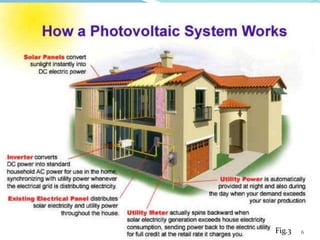
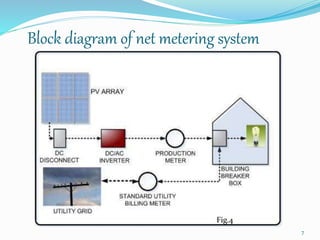
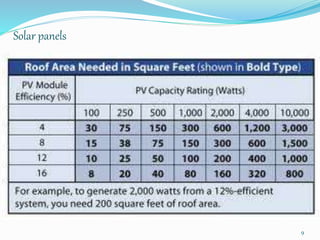
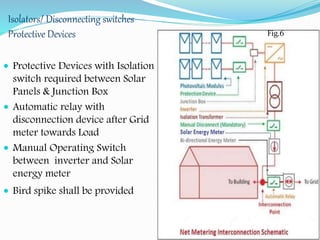
This document discusses net metering, which is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for excess electricity generated and added to the grid. It allows two-way power transfers so that solar customers can draw power from the grid when their panels are not generating enough. The document outlines the components of a net metering system like solar panels, inverters, meters and switches. It explains the benefits of net metering like financial credits and reduced equipment needs. It also provides details on net metering policies in India and states like Andhra Pradesh. The conclusion states that net metering provides opportunities for reliable solar power by allowing excess power to be supplied to the grid and drawing power when solar is insufficient.